
Describe the internal structure of the human heart.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Heart is the four chambered organs present in the chest region and it is surrounded by the membrane called pericardial membrane. The main function of the heart is to pump the blood and transport it to all parts of the body.
Complete answer:
The mass of the heart is two third at the center. The layer of the pericardial membrane covering the heart is divided into three types as epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. Epicardium is the outer layer; myocardium is the middle layer and the endocardium is the inner layer covering the heart.
Chambers of the heart:
The heart is of four chambers as right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle. The atria are thin walled chambers that transport blood to all the parts of the body where the veins are of thick-walled membrane and receive blood from all the parts of the body. This thickness of the heart varies due to the width of the myocardium present. Right chambers receive deoxygenated blood and left chambers receive oxygenated blood. These chambers have valves between them to maintain the flow of blood in one direction. The valves between the right auricle and ventricle are called tricuspid valves. And between the left auricle and ventricle is a bicuspid valve. Valves between the pulmonary trunk and right ventricle are semilunar valves and between the left ventricle and aorta is a semilunar valve.
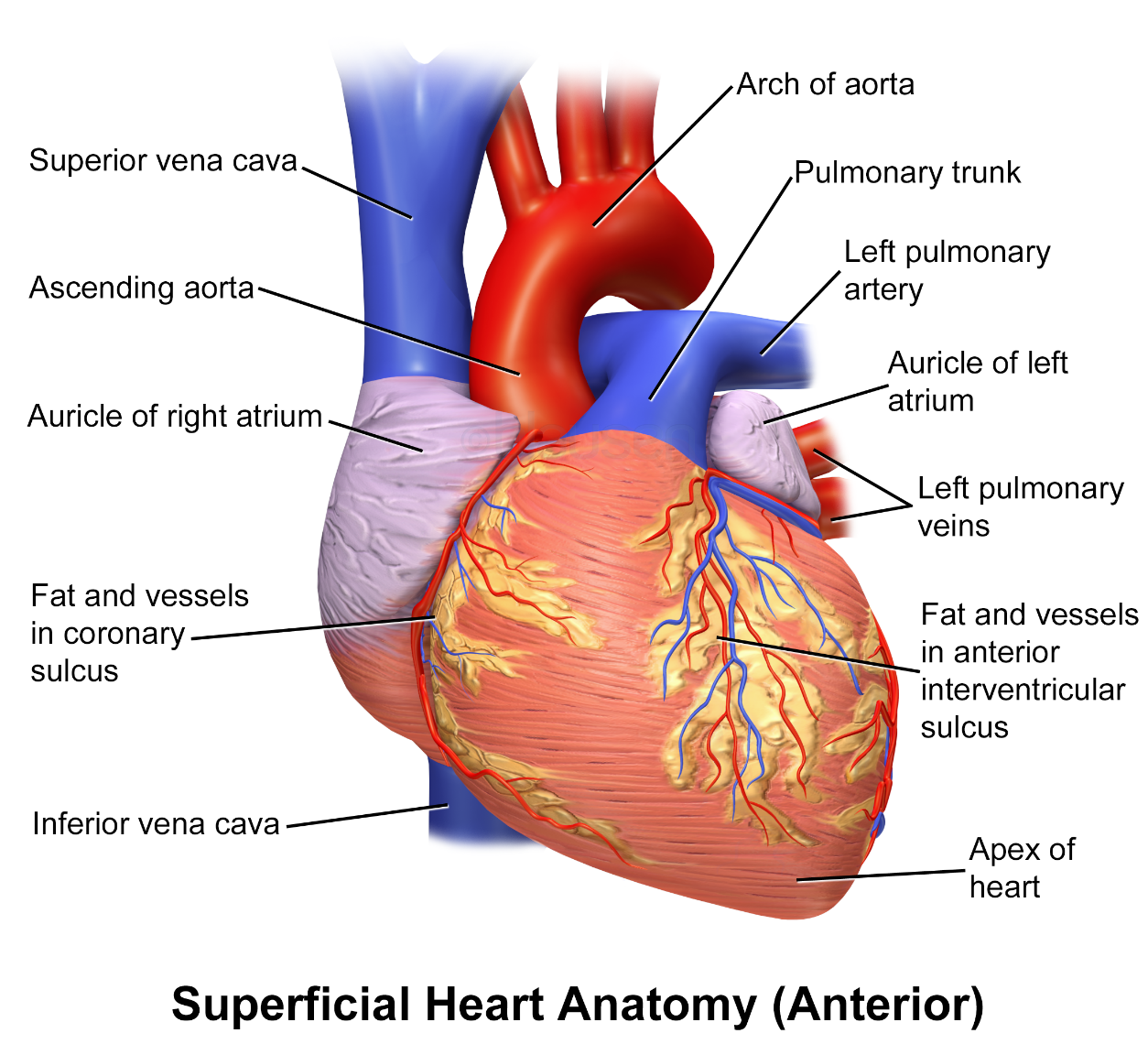
Note: The function of the heart is to pump the oxygenated blood to the other parts of the body and receive deoxygenated blood from all the parts of the body and carry it to the lungs for oxygenation. It makes the blood flow and supplies the nutrients and hormones to all the cells.
Complete answer:
The mass of the heart is two third at the center. The layer of the pericardial membrane covering the heart is divided into three types as epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. Epicardium is the outer layer; myocardium is the middle layer and the endocardium is the inner layer covering the heart.
Chambers of the heart:
The heart is of four chambers as right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle. The atria are thin walled chambers that transport blood to all the parts of the body where the veins are of thick-walled membrane and receive blood from all the parts of the body. This thickness of the heart varies due to the width of the myocardium present. Right chambers receive deoxygenated blood and left chambers receive oxygenated blood. These chambers have valves between them to maintain the flow of blood in one direction. The valves between the right auricle and ventricle are called tricuspid valves. And between the left auricle and ventricle is a bicuspid valve. Valves between the pulmonary trunk and right ventricle are semilunar valves and between the left ventricle and aorta is a semilunar valve.

Note: The function of the heart is to pump the oxygenated blood to the other parts of the body and receive deoxygenated blood from all the parts of the body and carry it to the lungs for oxygenation. It makes the blood flow and supplies the nutrients and hormones to all the cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




