
Describe the light-dependent steps of photosynthesis. How are they linked to the dark reaction?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: It utilizes light energy to make two particles required for the following phase of photosynthesis: the energy storage molecule ATP and the diminished electron transporter NADPH. The light reaction occurs in the thylakoid membrane of organelles called chloroplasts in plants.
Complete step by step answer:
- Within the intermembrane space of the thylakoids, the light- dependent reactions can take place
- Chlorophyll in the Photosystems I and II retain a light, which triggers the arrival of high energy electrons (photoactivation).
- Excited electrons from Photosystem II are moved between transporter particles in an electron transport chain.
- For creating a proton gradient, the electron transport chain translocates $H^+$ ions from the stroma to within the thylakoid.
- Through ATP synthase, the protons are returned to the stroma, which uses their passage (with the help of chemiosmosis) for synthesizing ATP.
- Excited electrons from the Photosystem I am used to reducing $NADP^+$ (forming NADPH).
- The electrons lost from Photosystem I are replaced by the de- empowered electrons from Photosystem II.
- With the help of the photolysis of water, the electrons lost from Photosystem II are replaced.
- The results of the light- reliant responses (ATP and NADPH) are utilized in the light- independent reaction.
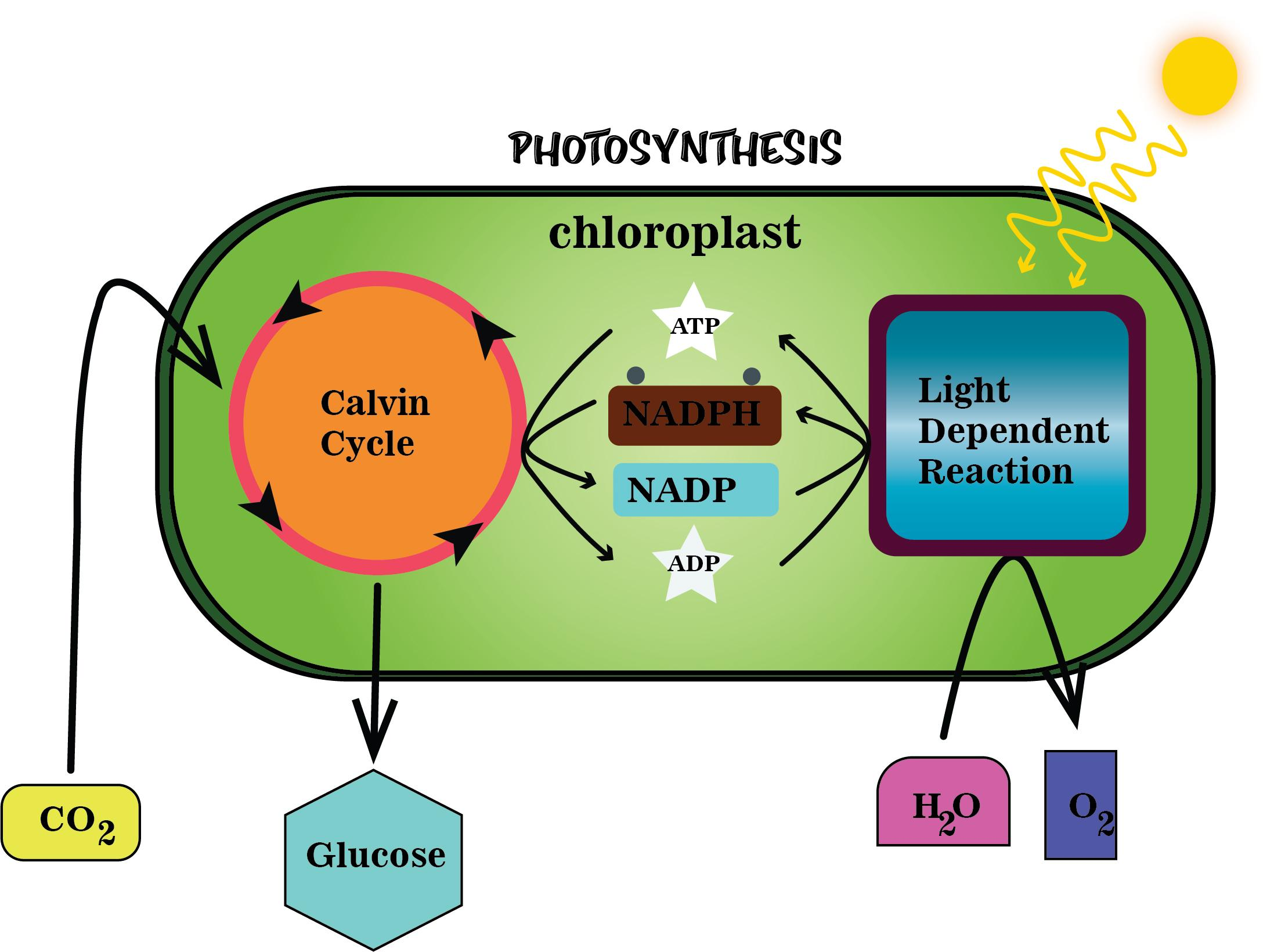
Dark reaction is the responses that are not straightforwardly reliant on light. In any case, they are connected to the light- dependent steps of photosynthesis since they utilize assimilatory forces i.e., ATP and NADPH in fixation and decrease of carbon dioxide. The Calvin cycle is likewise called the dark reaction or light- independent reaction since the part needn't bother with energy from the sun to occur. The Calvin cycle happens inside the stroma of the chloroplast. This is the place plants make sugar molecules that they can use to make other fundamental segments and that all different organisms can use for energy. The cycle utilizes ATP and NADPH incorporated in the light- dependent reaction to drive its responses forward. So despite the fact that the cycle itself doesn't utilize light energy, it relies upon the light reaction to provide it with the ATP and NADPH.
In the Z scheme, the energy changes (oxidation/reduction) that occur during photosynthesis. It includes 3 parts:
- The first vertical bar: Photosystem II electrons are energized by light
- The diagonal bar: As the Electrons pass through the Electron transport chain, they lose energy.
- The second vertical bar: Photosystem I electrons are energized by light.
Note: During the light-dependent reactions, an electron that's excited in Photosystem II is passed down an electron transport chain to Photosystem I (losing energy along the way). The electron is excited again and passes down the second leg of the electron transport chain to a final electron acceptor in the photosystem II.
Complete step by step answer:
- Within the intermembrane space of the thylakoids, the light- dependent reactions can take place
- Chlorophyll in the Photosystems I and II retain a light, which triggers the arrival of high energy electrons (photoactivation).
- Excited electrons from Photosystem II are moved between transporter particles in an electron transport chain.
- For creating a proton gradient, the electron transport chain translocates $H^+$ ions from the stroma to within the thylakoid.
- Through ATP synthase, the protons are returned to the stroma, which uses their passage (with the help of chemiosmosis) for synthesizing ATP.
- Excited electrons from the Photosystem I am used to reducing $NADP^+$ (forming NADPH).
- The electrons lost from Photosystem I are replaced by the de- empowered electrons from Photosystem II.
- With the help of the photolysis of water, the electrons lost from Photosystem II are replaced.
- The results of the light- reliant responses (ATP and NADPH) are utilized in the light- independent reaction.

Dark reaction is the responses that are not straightforwardly reliant on light. In any case, they are connected to the light- dependent steps of photosynthesis since they utilize assimilatory forces i.e., ATP and NADPH in fixation and decrease of carbon dioxide. The Calvin cycle is likewise called the dark reaction or light- independent reaction since the part needn't bother with energy from the sun to occur. The Calvin cycle happens inside the stroma of the chloroplast. This is the place plants make sugar molecules that they can use to make other fundamental segments and that all different organisms can use for energy. The cycle utilizes ATP and NADPH incorporated in the light- dependent reaction to drive its responses forward. So despite the fact that the cycle itself doesn't utilize light energy, it relies upon the light reaction to provide it with the ATP and NADPH.
In the Z scheme, the energy changes (oxidation/reduction) that occur during photosynthesis. It includes 3 parts:
- The first vertical bar: Photosystem II electrons are energized by light
- The diagonal bar: As the Electrons pass through the Electron transport chain, they lose energy.
- The second vertical bar: Photosystem I electrons are energized by light.
Note: During the light-dependent reactions, an electron that's excited in Photosystem II is passed down an electron transport chain to Photosystem I (losing energy along the way). The electron is excited again and passes down the second leg of the electron transport chain to a final electron acceptor in the photosystem II.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




