
Describe the process of respiration in fish.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: Respiration in aquatic animals is different from terrestrial animals because of the low amount of oxygen present in water.
Complete answer:
Fishes are living in water and possess gills at either side of their head that are made up of feathery structures known as gill filaments. The gills of vertebrates typically grow in the walls of the pharynx, with a series of gill slits opening to the exterior. Fish consume oxygen-rich water through their mouths and pump it through their gills. As water passes from the gill filaments, blood inside the capillary network extracts the dissolved oxygen. The circulatory system then transports the oxygen to all body tissues and finally to the cells while picking up carbon dioxide which is removed from the body through the gills.
Functions of gills:
- Fish gills are organs that allow fish to breathe underwater by exchanging the oxygen and carbon dioxide using gills.
- As water contains a very low amount of dissolved oxygen, fish exchange gases by pulling oxygen-rich water through their mouths and forcing it over their gills.
- These gills are connected with blood vessels for the easy exchange of gases.
- Gills help the vertebrates to increase their surface area for oxygen exchange.
- Gills transfer the ions and water, as well as the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids, and ammonia.
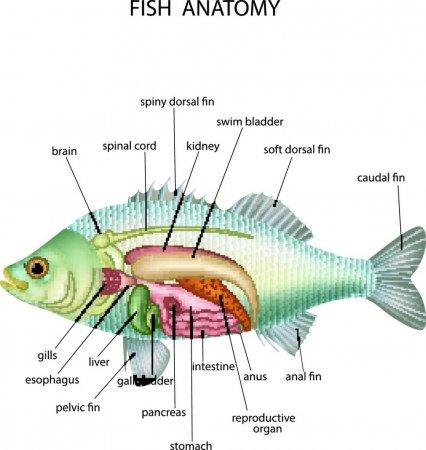
Figure: Internal structure of a fish
Note: Most fish are ectothermic or cold-blooded allowing their body temperatures to differ as ambient temperatures change however, some of the large fishes like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature.
Complete answer:
Fishes are living in water and possess gills at either side of their head that are made up of feathery structures known as gill filaments. The gills of vertebrates typically grow in the walls of the pharynx, with a series of gill slits opening to the exterior. Fish consume oxygen-rich water through their mouths and pump it through their gills. As water passes from the gill filaments, blood inside the capillary network extracts the dissolved oxygen. The circulatory system then transports the oxygen to all body tissues and finally to the cells while picking up carbon dioxide which is removed from the body through the gills.
Functions of gills:
- Fish gills are organs that allow fish to breathe underwater by exchanging the oxygen and carbon dioxide using gills.
- As water contains a very low amount of dissolved oxygen, fish exchange gases by pulling oxygen-rich water through their mouths and forcing it over their gills.
- These gills are connected with blood vessels for the easy exchange of gases.
- Gills help the vertebrates to increase their surface area for oxygen exchange.
- Gills transfer the ions and water, as well as the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids, and ammonia.

Figure: Internal structure of a fish
Note: Most fish are ectothermic or cold-blooded allowing their body temperatures to differ as ambient temperatures change however, some of the large fishes like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




