
Describe the role of rods and cones in visual perception.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Rod and cone cells are types of photoreceptor cells found in the inner layer of the retina. These cells contain light-sensitive proteins known as photopigments. Thus these pigments are responsible for the detection of color and its intensity.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The inner layer is the retina and it contains three layers of neural cells – from inside to outside – ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptor cells. We find two types of photoreceptor cells known as rods and cones.
The daylight or the photopic vision and color vision are provided by the functioning of cones and the twilight or the scotopic vision is provided by the function of the rods. The rods have a purplish- red protein called the rhodopsin or visual purple. It is formed by a derivative of Vitamin- A and hence this vitamin is essential for the proper functioning of eyes.
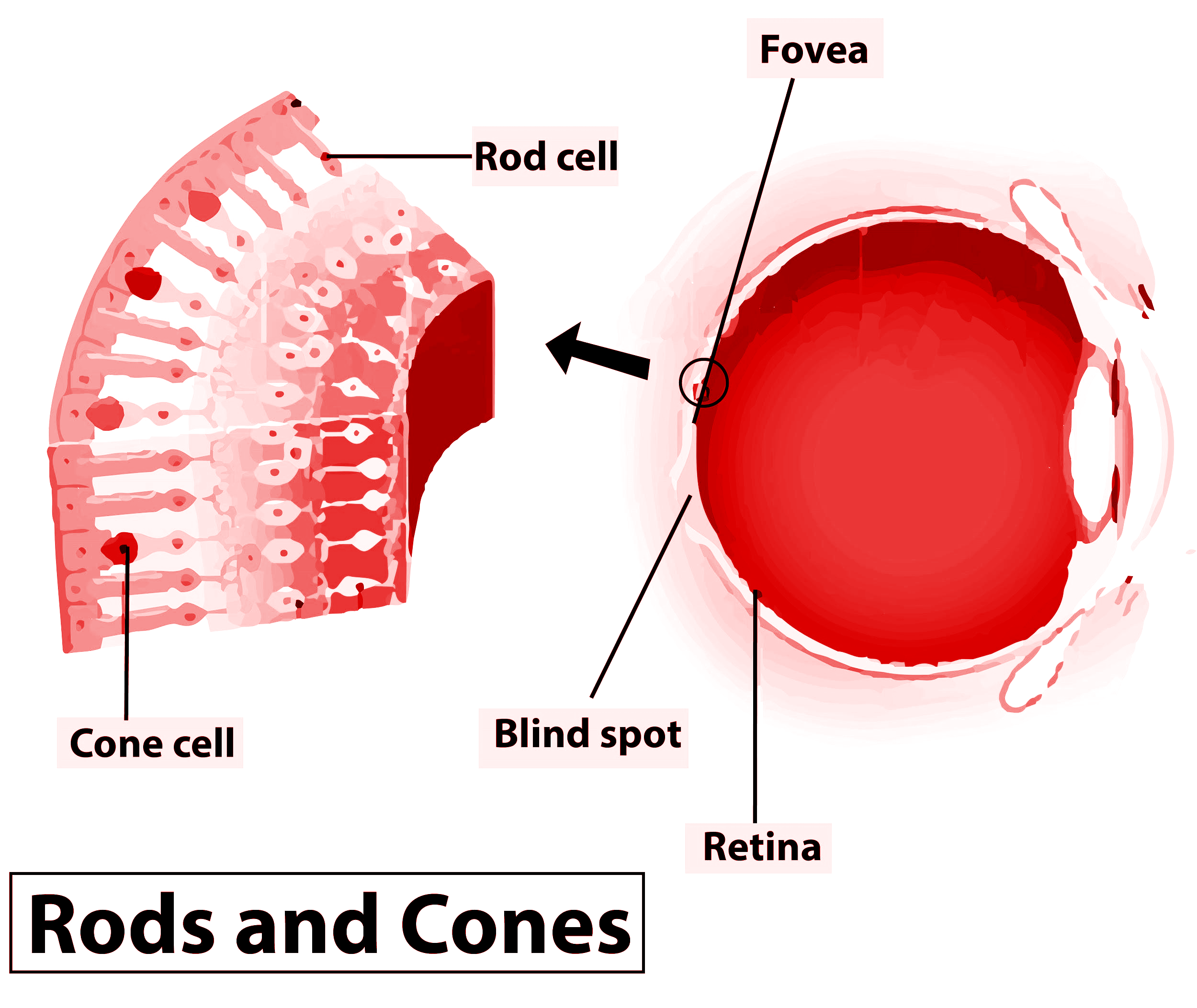
In the human eye, we find three types of cones that possess their own characteristic photopigments that respond to colors of red, green, and blue lights. The sensations of different colors are induced by various combinations of these cones and their photopigments. When these cones are being stimulated equally, a sensation of white light is produced as white light has all colors in it.
Note:
- The optic nerves leave and also allow blood vessels to enter inside the eye at a specific point which is medial to and slightly above the posterior pole of the eyeball. Photoreceptor cells are not seen in this region and no image is formed, hence it is called the blind spot.
- At the posterior pole of the eye just next to the blind spot, there is a yellow- pigmented spot called macula lutea which has a central pit called the fovea.
- The fovea is a thinned-out portion of the retina where cones cells are present but not rod cells. It is the point where the visual acuity (resolution) is the greatest as cones sense are responsible for color detection.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The inner layer is the retina and it contains three layers of neural cells – from inside to outside – ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptor cells. We find two types of photoreceptor cells known as rods and cones.
The daylight or the photopic vision and color vision are provided by the functioning of cones and the twilight or the scotopic vision is provided by the function of the rods. The rods have a purplish- red protein called the rhodopsin or visual purple. It is formed by a derivative of Vitamin- A and hence this vitamin is essential for the proper functioning of eyes.

In the human eye, we find three types of cones that possess their own characteristic photopigments that respond to colors of red, green, and blue lights. The sensations of different colors are induced by various combinations of these cones and their photopigments. When these cones are being stimulated equally, a sensation of white light is produced as white light has all colors in it.
Note:
- The optic nerves leave and also allow blood vessels to enter inside the eye at a specific point which is medial to and slightly above the posterior pole of the eyeball. Photoreceptor cells are not seen in this region and no image is formed, hence it is called the blind spot.
- At the posterior pole of the eye just next to the blind spot, there is a yellow- pigmented spot called macula lutea which has a central pit called the fovea.
- The fovea is a thinned-out portion of the retina where cones cells are present but not rod cells. It is the point where the visual acuity (resolution) is the greatest as cones sense are responsible for color detection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




