
Describe the structure of a dicot seed with a neat diagram.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: A seed is the characteristic feature of angiosperms. These are formed after the reproduction process in plants. The seed has an outer covering called the seed coat. The division angiosperm is included in kingdom Plantae.
Complete answer:
A dicot seed is present in the embryo of the angiosperms or flowering plants and it is also called dicotyledon seed. It is made of two cotyledons in the dicot seed. A seed contains an embryo and the embryo is further made up of parts-
• A radical
• Embryo axis
• Cotyledons
The seeds having two cotyledons are called Dicot seeds.
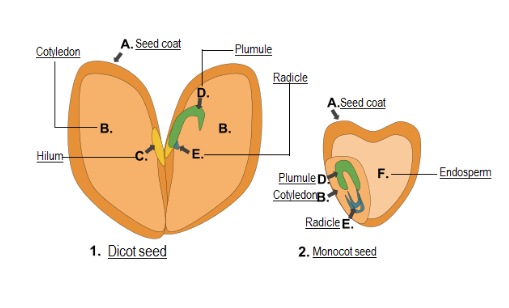
• Two cotyledons and embryo axis are present.
• The function of cotyledons is to store the food so it is swollen in appearance.
• Embryo axis has two poles- The shoot tip forming portion is called plumule(upper end) and the root tip portion is called Radicle(lower end).
• The seed coat is the outer layer and protects the inner embryo. It is further of two types- The outer layer is testa and the inner layer is tegmen.
• The attachment of seed to fruit is through Hilum.
• Examples of seeds include- Pear, Apple, Cashew, etc.
Note:
Some seeds are special and they possess a triploid endosperm.
The monocot seed has only one cotyledon but the dicot seed is having two cotyledons.
Dicot and monocot seeds are only present in flowering plants(angiosperms).
The wild banana contains seed and hence placed under monocot but the edible banana available in markets is hybrid and hence seedless.
Complete answer:
A dicot seed is present in the embryo of the angiosperms or flowering plants and it is also called dicotyledon seed. It is made of two cotyledons in the dicot seed. A seed contains an embryo and the embryo is further made up of parts-
• A radical
• Embryo axis
• Cotyledons
The seeds having two cotyledons are called Dicot seeds.

• Two cotyledons and embryo axis are present.
• The function of cotyledons is to store the food so it is swollen in appearance.
• Embryo axis has two poles- The shoot tip forming portion is called plumule(upper end) and the root tip portion is called Radicle(lower end).
• The seed coat is the outer layer and protects the inner embryo. It is further of two types- The outer layer is testa and the inner layer is tegmen.
• The attachment of seed to fruit is through Hilum.
• Examples of seeds include- Pear, Apple, Cashew, etc.
Note:
Some seeds are special and they possess a triploid endosperm.
The monocot seed has only one cotyledon but the dicot seed is having two cotyledons.
Dicot and monocot seeds are only present in flowering plants(angiosperms).
The wild banana contains seed and hence placed under monocot but the edible banana available in markets is hybrid and hence seedless.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




