
Describe the structure of bean seed.
Answer
529.1k+ views
Hint: The shape of the bean seed is kidney-like with various structures surrounding it.
Complete answer:
Seed in plants is the result of fertilization which has several structures constituting it.
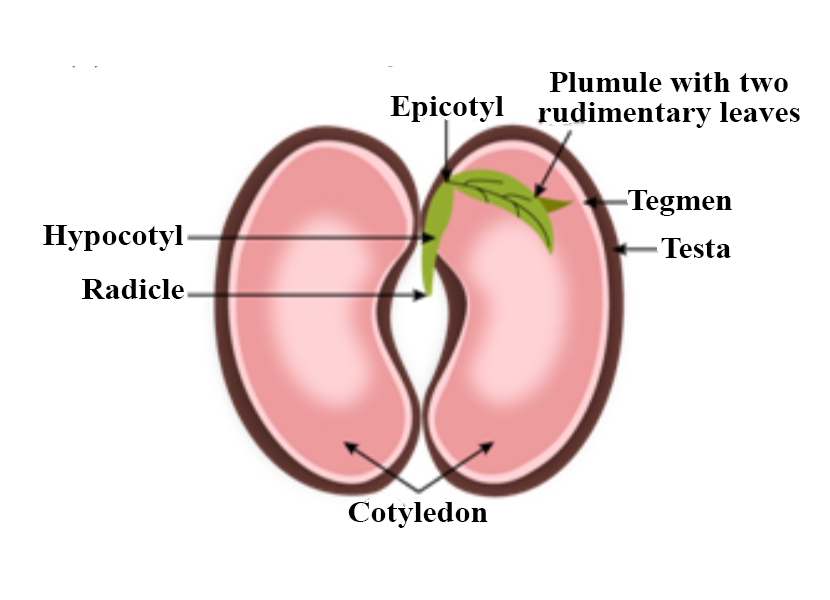
Structure of bean seed
Seed consists of various parts:
- Testa – it is the outermost protective covering of the seed which is hard but thin. It helps in protecting the embryonic plant.
- Micropyle – it is a tiny opening on the surface of the testa through which water enters and helps in the germination of the plant.
- Cotyledon – they are the storage tissue of the plant, generally contain high quantities of starch, and act as a source of food for the developing embryo. Cotyledons number depends upon the type of plant: monocotyledons have a single cotyledon while dicotyledons have two cotyledons. The position of the cotyledons depends upon the type of germination: epigeous (cotyledons remain below the ground) and hypogeous (cotyledons remain above the ground).
- Radicle – it is one half of an embryo which is situated below the cotyledons, inside the testa. It is the first root produced by the seed. When water is present, this radicle pushes down through the micropyle and into the soil.
- Plumule – it is the second half of the embryo which produces the first leaf of the plant. It appears as a bud when water is present and will develop into a shoot.
- Hilum – it is a scar left by the stalk which attached the ovule to the ovary wall before it became a seed.
- Endosperm – storage organ in many plants where starch is stored.
Note: The development of cotyledons are of two types:
Hypocotyl – part of the stem, between the cotyledons and the foot. It is found below the cotyledons and above the radicle.
Epicotyl – part of stem above the cotyledons and below the plumule.
Complete answer:
Seed in plants is the result of fertilization which has several structures constituting it.
Structure of bean seed
Seed consists of various parts:
- Testa – it is the outermost protective covering of the seed which is hard but thin. It helps in protecting the embryonic plant.
- Micropyle – it is a tiny opening on the surface of the testa through which water enters and helps in the germination of the plant.
- Cotyledon – they are the storage tissue of the plant, generally contain high quantities of starch, and act as a source of food for the developing embryo. Cotyledons number depends upon the type of plant: monocotyledons have a single cotyledon while dicotyledons have two cotyledons. The position of the cotyledons depends upon the type of germination: epigeous (cotyledons remain below the ground) and hypogeous (cotyledons remain above the ground).
- Radicle – it is one half of an embryo which is situated below the cotyledons, inside the testa. It is the first root produced by the seed. When water is present, this radicle pushes down through the micropyle and into the soil.
- Plumule – it is the second half of the embryo which produces the first leaf of the plant. It appears as a bud when water is present and will develop into a shoot.
- Hilum – it is a scar left by the stalk which attached the ovule to the ovary wall before it became a seed.
- Endosperm – storage organ in many plants where starch is stored.

Note: The development of cotyledons are of two types:
Hypocotyl – part of the stem, between the cotyledons and the foot. It is found below the cotyledons and above the radicle.
Epicotyl – part of stem above the cotyledons and below the plumule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




