
Describe the structure of the common form of ice.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Ice is less dense than liquid water and so it floats. Ice is a solid form of water. This has a rigid lattice structure, in a tetrahedral crystalline form.
Complete answer:
Ice is a crystalline form of water.
Ice at normal conditions takes hexagonal form if crystallized at atmospheric pressure, but condenses to cubic form if the temperature is very low.
Each oxygen atom is tetrahedrally surrounded by four H-atoms. The three-dimensional structure of ice represented as:
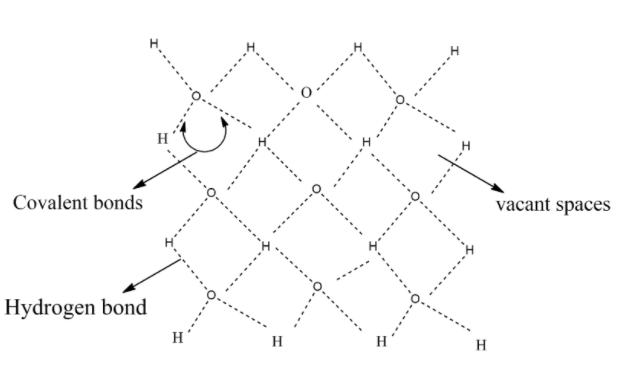
Out of 4 hydrogen atoms surrounded with oxygen atom, 2 hydrogen atoms represented in the above diagram are covalent bonds and the remaining 2 hydrogen atoms are Hydrogen bonds.
The structure also contains wide holes that can hold molecules of appropriate sizes interstitially.
Each O atom is surrounded by 4 other oxygen atoms at a distance of 276 pm.
The vacant spaces in the three-dimensional structure are known as interstitial sites.
Interstitial sites with compatible size atoms can exist in these spaces.
The common structure of ice is a tetrahedral arrangement.
The rigid hydrogen bonds in ice form an open network that causes the solid form of water to be less dense than the liquid form.
Note: Ice reaches its highest density at about ${{4}^{0}}C$. Between ${{4}^{0}}C$ and ${{0}^{o}}C$ , the density gradually decreases as the hydrogen bonds begin to form a network characterized by a general hexagonal structure with open spaces in the middle of the hexagons.
Complete answer:
Ice is a crystalline form of water.
Ice at normal conditions takes hexagonal form if crystallized at atmospheric pressure, but condenses to cubic form if the temperature is very low.
Each oxygen atom is tetrahedrally surrounded by four H-atoms. The three-dimensional structure of ice represented as:

Out of 4 hydrogen atoms surrounded with oxygen atom, 2 hydrogen atoms represented in the above diagram are covalent bonds and the remaining 2 hydrogen atoms are Hydrogen bonds.
The structure also contains wide holes that can hold molecules of appropriate sizes interstitially.
Each O atom is surrounded by 4 other oxygen atoms at a distance of 276 pm.
The vacant spaces in the three-dimensional structure are known as interstitial sites.
Interstitial sites with compatible size atoms can exist in these spaces.
The common structure of ice is a tetrahedral arrangement.
The rigid hydrogen bonds in ice form an open network that causes the solid form of water to be less dense than the liquid form.
Note: Ice reaches its highest density at about ${{4}^{0}}C$. Between ${{4}^{0}}C$ and ${{0}^{o}}C$ , the density gradually decreases as the hydrogen bonds begin to form a network characterized by a general hexagonal structure with open spaces in the middle of the hexagons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




