
Describe the working of an AC generator with the help of a labelled circuit diagram. What changes must be made in the arrangement to convert it to a DC generator.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The AC generators are one of the most widely used technologies which exploit the electromagnetic induction. We will need to study the different parts and the mechanical design involved in making the Alternating current generator for commercial purposes.
Complete answer:
We know that the Alternating current generators use the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction for converting a form of mechanical energy into the required power in the form of electrical energy. According to Faraday's law, the rate of change in the magnetic flux of a coil will induce an electromotive force (emf) in the coil. Mathematically, it is given as –
\[\begin{align}
& \varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \phi =B.A \\
& \Rightarrow \phi =BA\cos \omega t \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d(BA\cos \omega t)}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =NBA\omega \sin \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
We understand that the emf induced is dependent on the angular velocity of the rotation of the coil with N turns and A, area of cross-section.
The AC generators utilise these aspects in the emf production. It consists of a fixed magnetic source, a coil of wire wound on a metal core, known as armature, slip rings and carbon brushes. The armature is kept in between the magnetic field as is rotated by some mechanical energy continuously. The rotation of the armature coil results in a change in the magnetic flux as the effective area being perpendicular to the magnetic field changes at every instant.
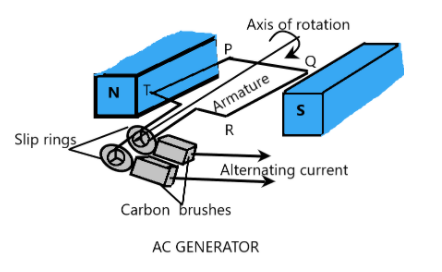
As a result, an emf is produced in the coil which is connected to external load by means of slip rings which makes possible the continuous rotation of the coil. We also observe that the direction of emf changes at every half rotation, this leads to the creation of alternating current in the external load.
We can use a commutator, which detaches the coil after half rotation to give a steady direction of current flow in the circuit. This produces the DC current in the circuit.
Note:
The AC generators are used in all the hydroelectric power plants around the world. The angular frequency of the AC generator varies from country to country. The standard frequency of AC current is 50Hz to 60Hz. In India, it is 50Hz, whereas in the USA it is 60Hz.
Complete answer:
We know that the Alternating current generators use the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction for converting a form of mechanical energy into the required power in the form of electrical energy. According to Faraday's law, the rate of change in the magnetic flux of a coil will induce an electromotive force (emf) in the coil. Mathematically, it is given as –
\[\begin{align}
& \varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \text{but,} \\
& \phi =B.A \\
& \Rightarrow \phi =BA\cos \omega t \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d(BA\cos \omega t)}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =NBA\omega \sin \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
We understand that the emf induced is dependent on the angular velocity of the rotation of the coil with N turns and A, area of cross-section.
The AC generators utilise these aspects in the emf production. It consists of a fixed magnetic source, a coil of wire wound on a metal core, known as armature, slip rings and carbon brushes. The armature is kept in between the magnetic field as is rotated by some mechanical energy continuously. The rotation of the armature coil results in a change in the magnetic flux as the effective area being perpendicular to the magnetic field changes at every instant.

As a result, an emf is produced in the coil which is connected to external load by means of slip rings which makes possible the continuous rotation of the coil. We also observe that the direction of emf changes at every half rotation, this leads to the creation of alternating current in the external load.
We can use a commutator, which detaches the coil after half rotation to give a steady direction of current flow in the circuit. This produces the DC current in the circuit.
Note:
The AC generators are used in all the hydroelectric power plants around the world. The angular frequency of the AC generator varies from country to country. The standard frequency of AC current is 50Hz to 60Hz. In India, it is 50Hz, whereas in the USA it is 60Hz.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




