
Describe types of epithelial tissues with help of labelled diagrams.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Epithelial tissues are present all over the body. These tissues cover all the body surfaces, body line cavities, and hollow organs. These are the major tissues in the glands. Epithelial tissues are mainly of 8 types. They protect the other tissues, regulation and exchange of chemicals, secretion of hormones, etc.
Complete answer:
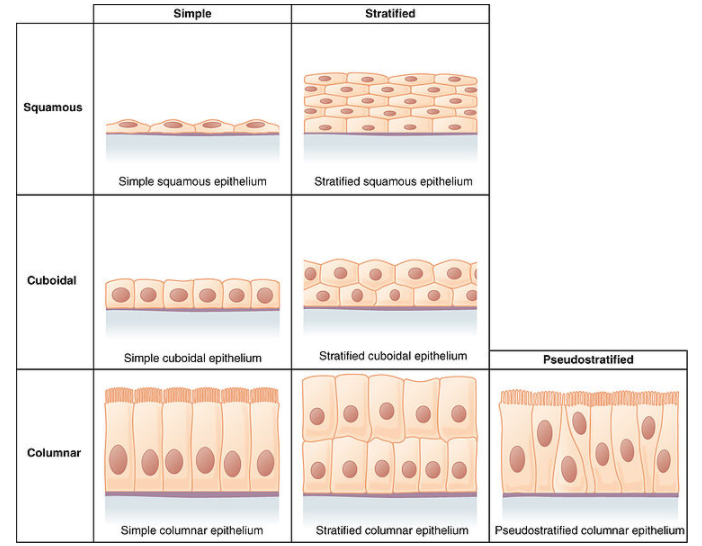
The epithelial tissues are mainly divided into eight types:
-Simple squamous epithelium: It is located in the air sacs of lungs and lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels. It allows the materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration. It also secretes lubricating substances.
-Simple cuboidal epithelium: These are located in the ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules. It secretes and absorbs the materials in and out through the tissues.
-Simple columnar epithelium: These are found in bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus. These are also found in the digestive tract. It absorbs and also secretes mucus and enzymes.
-Stratified squamous epithelium: It is found in the lines of esophagus, mouth, and vagina. It also protects against abrasion.
-Stratified cuboidal epithelial: It is located in the sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands. It secretes materials and also protects other tissues.
-Stratified columnar epithelium: These are located in the male urethra and the ducts of some glands. These are the protective tissues.
-Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: It is located in the ciliated tissues lines of the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract. It secretes mucus.
-Transitional epithelium: These are located in the lines of bladder, urethra, and the ureters. It allows the expansion of urinary organs.
Note: The respiratory epithelium is ciliated and contains polarized cells which form a tube with cilia projecting into the lumen. These cilia provide chemosensation, thermoception, and mechanosensation of the extracellular environment by playing a sensory role. Some of the tissues also contain receptors to sense the stimulus.
Complete answer:

The epithelial tissues are mainly divided into eight types:
-Simple squamous epithelium: It is located in the air sacs of lungs and lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels. It allows the materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration. It also secretes lubricating substances.
-Simple cuboidal epithelium: These are located in the ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules. It secretes and absorbs the materials in and out through the tissues.
-Simple columnar epithelium: These are found in bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus. These are also found in the digestive tract. It absorbs and also secretes mucus and enzymes.
-Stratified squamous epithelium: It is found in the lines of esophagus, mouth, and vagina. It also protects against abrasion.
-Stratified cuboidal epithelial: It is located in the sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands. It secretes materials and also protects other tissues.
-Stratified columnar epithelium: These are located in the male urethra and the ducts of some glands. These are the protective tissues.
-Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: It is located in the ciliated tissues lines of the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract. It secretes mucus.
-Transitional epithelium: These are located in the lines of bladder, urethra, and the ureters. It allows the expansion of urinary organs.
Note: The respiratory epithelium is ciliated and contains polarized cells which form a tube with cilia projecting into the lumen. These cilia provide chemosensation, thermoception, and mechanosensation of the extracellular environment by playing a sensory role. Some of the tissues also contain receptors to sense the stimulus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




