
Desmosomes are concerned with
(a) Cell division
(b) Cellular excretion
(c) Cytolysis
(d) Cell adherence
Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint: A desmosome is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion, also referred to as a macula adherens. They are localized spot-like adhesions randomly clustered on the lateral sides of plasma membranes, a form of junctional complex. Desmosomes are one of the stronger forms of cell-to-cell adhesion. These are found in tissues, such as cardiac muscle tissue, bladder tissue, gastrointestinal mucosa, and epithelia. They experience strong mechanical stress.
Complete answer:
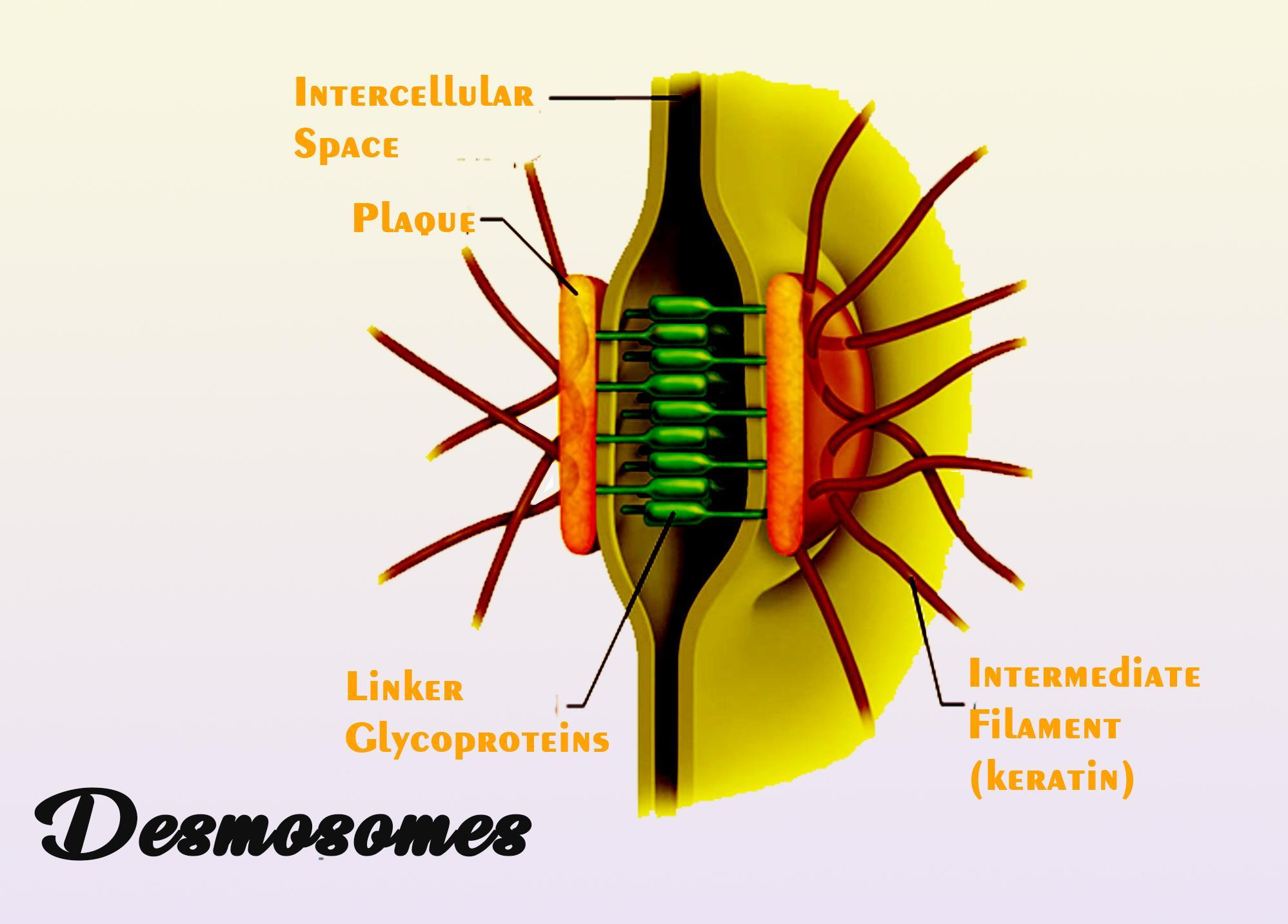
Desmosomes are a plasma membrane specialization. They are just like welded areas having intercellular thickening materials within adjacent cells. They exist in the tissue of the epithelium subjected to disturbance and act together to seal cells or provide cell-to-cell adherence. Desmosomes are a network of cadherin proteins, linker proteins, and keratin intermediate filaments consisting of desmosome-intermediate filament complexes (DIFC) . It is possible to break the DIFCs into three regions: the extracellular core region, or desmoglea, the dense outer plaque, or ODP, and the dense inner plaque, or IDP.
Additional information: The mechanism by which a parent cell splits into the daughter cells is cell division. As part of a broader cell cycle, cell division typically occurs. There are two different forms of cell division in eukaryotes: vegetative division is in which each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis) and reproductive cells, in which the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is halved to create haploid gametes (meiosis).
The excretion of cells is the mechanism by which the cells remove substances that are no longer useful through their membranes. The waste substances that are normally manufactured by cells are carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. However, depending on the form of the organism, in the case of plants, for instance, additional substances such as tannins exist.
When a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to diffuse into the cell, cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs. Through diffusion through the cell membrane or by selective membrane channels called aquaporins, water may reach the cell, which greatly facilitates water flow.
So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Cell adherence’.
Note: The interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), the transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface, resulting in cell adhesion. Cell adhesion binds cells in various ways, and cells may be involved in signal transduction to detect and respond to changes in the environment.
Complete answer:
Desmosomes are a plasma membrane specialization. They are just like welded areas having intercellular thickening materials within adjacent cells. They exist in the tissue of the epithelium subjected to disturbance and act together to seal cells or provide cell-to-cell adherence. Desmosomes are a network of cadherin proteins, linker proteins, and keratin intermediate filaments consisting of desmosome-intermediate filament complexes (DIFC) . It is possible to break the DIFCs into three regions: the extracellular core region, or desmoglea, the dense outer plaque, or ODP, and the dense inner plaque, or IDP.
Additional information: The mechanism by which a parent cell splits into the daughter cells is cell division. As part of a broader cell cycle, cell division typically occurs. There are two different forms of cell division in eukaryotes: vegetative division is in which each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis) and reproductive cells, in which the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is halved to create haploid gametes (meiosis).

The excretion of cells is the mechanism by which the cells remove substances that are no longer useful through their membranes. The waste substances that are normally manufactured by cells are carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. However, depending on the form of the organism, in the case of plants, for instance, additional substances such as tannins exist.
When a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to diffuse into the cell, cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs. Through diffusion through the cell membrane or by selective membrane channels called aquaporins, water may reach the cell, which greatly facilitates water flow.
So, the correct answer is ‘(d) Cell adherence’.
Note: The interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), the transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface, resulting in cell adhesion. Cell adhesion binds cells in various ways, and cells may be involved in signal transduction to detect and respond to changes in the environment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




