
When the destructive distillation of coal is done, the non-volatile residue left in the retort is:
(A) Gas carbon
(B) Coke
(C) Coal tar
(D) Lampblack
Answer
492.6k+ views
Hint: When inorganic materials are exposed to destructive distillation, only a small number of products are produced. When organic materials are put through this process, however, a variety of products are created. In fact, the destructive distillation of some organic materials can result in the production of hundreds of products. However, the majority of these items are generally of no commercial value.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The pyrolysis of the organic (or inorganic) feedstock inside a distillation apparatus, followed by the collection of the volatile products generated during the pyrolysis, is the destructive distillation process. It should be emphasised, however, that the gathered products will only account for a small portion of the starting feedstock's mass. This is because the distillation equipment retains a large part of the initial feedstock in the form of ash, non-volatile tar, and char. When opposed to combustion, destructive distillation consumes a less amount of organic materials (post combustion, the mass of the products formed are equal to the mass of the initial feedstock and the required amount of oxidant). Destructive distillation may be thought of as a tweaked version of the conventional charcoal-burning method. It's worth mentioning that this procedure is important for industry in a number of places throughout the world, the most prominent of which being Scandinavia. It's also worth noting that contemporary destructive distillation techniques have been improved in a variety of ways to enhance the extraction of valuable compounds from feedstock.
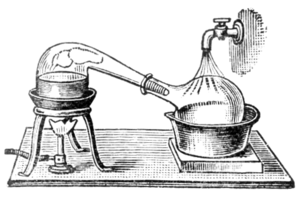
Heat decomposes organic material like wood, coal, and oil shale in the absence of air, resulting in valuable products including coke, coal gas, gas carbon, coal tar, ammonia liquor, and coal oil. Coke is the non-volatile residue remaining in the retort.
Option B is the correct response.
Note:
Destructive distillation and other kinds of pyrolysis have historically led to the discovery of numerous chemical compounds and the clarification of their structures before modern organic chemists had devised techniques to synthesise or study the parent molecules. Investigation of the results of destructive distillation, as well as those of other destructive procedures, played an important role in allowing chemists to derive the chemical composition of many natural materials, particularly in the early days. Deduction of the structures of pyranoses and furanoses is a well-known example.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The pyrolysis of the organic (or inorganic) feedstock inside a distillation apparatus, followed by the collection of the volatile products generated during the pyrolysis, is the destructive distillation process. It should be emphasised, however, that the gathered products will only account for a small portion of the starting feedstock's mass. This is because the distillation equipment retains a large part of the initial feedstock in the form of ash, non-volatile tar, and char. When opposed to combustion, destructive distillation consumes a less amount of organic materials (post combustion, the mass of the products formed are equal to the mass of the initial feedstock and the required amount of oxidant). Destructive distillation may be thought of as a tweaked version of the conventional charcoal-burning method. It's worth mentioning that this procedure is important for industry in a number of places throughout the world, the most prominent of which being Scandinavia. It's also worth noting that contemporary destructive distillation techniques have been improved in a variety of ways to enhance the extraction of valuable compounds from feedstock.

Heat decomposes organic material like wood, coal, and oil shale in the absence of air, resulting in valuable products including coke, coal gas, gas carbon, coal tar, ammonia liquor, and coal oil. Coke is the non-volatile residue remaining in the retort.
Option B is the correct response.
Note:
Destructive distillation and other kinds of pyrolysis have historically led to the discovery of numerous chemical compounds and the clarification of their structures before modern organic chemists had devised techniques to synthesise or study the parent molecules. Investigation of the results of destructive distillation, as well as those of other destructive procedures, played an important role in allowing chemists to derive the chemical composition of many natural materials, particularly in the early days. Deduction of the structures of pyranoses and furanoses is a well-known example.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




