
How do you determine if \[x\sin x\] is an even or odd function?
Answer
491.4k+ views
Hint: In mathematics, a function is defined as a binary relation between two sets that relates each element of the first set to exactly one set in the second set. Suppose that ‘A’ and ‘B’ are two sets. Then a function relating these two sets is written as \[f:A \to B\]. Read as \['f{\text{ maps }}A{\text{ to }}B'\].
Odd functions and even functions are functions which satisfy a particular symmetric relation.
Even function:
Let \[f\] be a real-valued function. Then, \[f\] is said to be an even function if \[f(x) = f( - x)\]
For example, take a function \[f(x) = \cos x\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = \cos ( - x)\]
And we know that, \[\cos ( - x) = \cos x\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = \cos ( - x) = \cos x\]
When we observe here, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are equal. So, \[f( - x) = f(x)\]
So, \[f\] is an even function.
Odd function:
Let \[f\] be a real-valued function. Then, \[f\] is said to be an odd function if \[f( - x) = - f(x)\]
For example, take a function \[f(x) = {x^3}\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = {\left( { - x} \right)^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = {\left( { - 1 \times x} \right)^3} = - {x^3}\]
When we observe this, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are additive inverse to each other. So, \[f( - x) = - f(x)\].
So, \[f\] is an odd function.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, the given question is \[x\sin x\]
So, take \[f(x) = x\sin x\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = ( - x)(\sin ( - x))\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = ( - x)( - \sin x)\]
So, we get the final result as,
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = x\sin x\]
When we observe here, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are equal. So, \[f( - x) = f(x)\]
Therefore, \[x\sin x\] is an even function.
We can see the graph of $x \sin x $ below
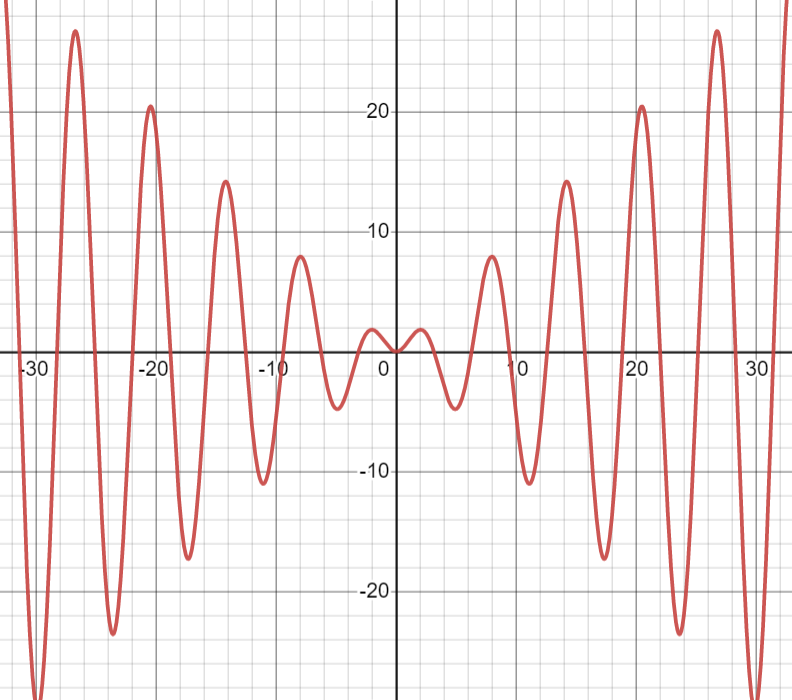
Note:
If you plot graphs for functions like \[y = f(x)\], then an even function is symmetrical about the Y-axis. And an odd function is not symmetrical about the Y-axis.
Another form of defining an even function is, if \[f(x) - f( - x) = 0\], then \[f(x)\] is an even function.
And similarly, if \[f( - x) + f(x) = 0\], then \[f(x)\] is an odd function.
Odd functions and even functions are functions which satisfy a particular symmetric relation.
Even function:
Let \[f\] be a real-valued function. Then, \[f\] is said to be an even function if \[f(x) = f( - x)\]
For example, take a function \[f(x) = \cos x\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = \cos ( - x)\]
And we know that, \[\cos ( - x) = \cos x\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = \cos ( - x) = \cos x\]
When we observe here, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are equal. So, \[f( - x) = f(x)\]
So, \[f\] is an even function.
Odd function:
Let \[f\] be a real-valued function. Then, \[f\] is said to be an odd function if \[f( - x) = - f(x)\]
For example, take a function \[f(x) = {x^3}\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = {\left( { - x} \right)^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = {\left( { - 1 \times x} \right)^3} = - {x^3}\]
When we observe this, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are additive inverse to each other. So, \[f( - x) = - f(x)\].
So, \[f\] is an odd function.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, the given question is \[x\sin x\]
So, take \[f(x) = x\sin x\]
So, substitute \[ - x\] in place of \[x\].
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = ( - x)(\sin ( - x))\]
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = ( - x)( - \sin x)\]
So, we get the final result as,
\[ \Rightarrow f( - x) = x\sin x\]
When we observe here, \[f(x)\] and \[f( - x)\] are equal. So, \[f( - x) = f(x)\]
Therefore, \[x\sin x\] is an even function.
We can see the graph of $x \sin x $ below

Note:
If you plot graphs for functions like \[y = f(x)\], then an even function is symmetrical about the Y-axis. And an odd function is not symmetrical about the Y-axis.
Another form of defining an even function is, if \[f(x) - f( - x) = 0\], then \[f(x)\] is an even function.
And similarly, if \[f( - x) + f(x) = 0\], then \[f(x)\] is an odd function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




