
How do you determine the linear function whose graph is a line that contains the points $\left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $\left( {2,10} \right)$ ?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: The equation of a line that passes through two points can be calculated by using the two-point form of the equation of a line. We will substitute the given two points into the two-point form of a line. Then after simplifying we can determine the required linear function.
Formula used:
The two-point form of a line passing through the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know we can determine the equation of a line that passes through two points by using the two-point form of a line.
Now, the two given points are
$A = \left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $B = \left( {2,10} \right)$ .
Now, we know that the first coordinate is the x-coordinate and the second coordinate is the y-coordinate.
Here,
For point $A$, ${x_1} = - 1$ and ${y_1} = - 8$
For point $B$, ${x_2} = 2$ and ${y_2} = 10$
Now, as we know that, the two-point form of a line is
$\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Now, we can determine the linear function by substituting the ${x_1} = - 1$ , ${x_2} = 2$ , ${y_1} = - 8$ and ${y_2} = 10$ in the two-point form of the equation of a line.
After substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{y - ( - 8)}}{{x - ( - 1)}} = \dfrac{{10 - ( - 8)}}{{2 - ( - 1)}}$
Now, after opening the brackets of numerators as well as denominators on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{10 + 8}}{{2 + 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{18}}{3}$
On Right-hand side, simplifying by dividing $18\;$ by $3$ , we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{6}{1}$
Now, by cross multiplying, we get
$1(y + 8) = 6(x + 1)$
$ \Rightarrow y + 8 = 6x + 6$
Now, by subtracting $8$ on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$$y + 8 - 8 = 6x + 6 - 8$
$ \Rightarrow y = 6x - 2$
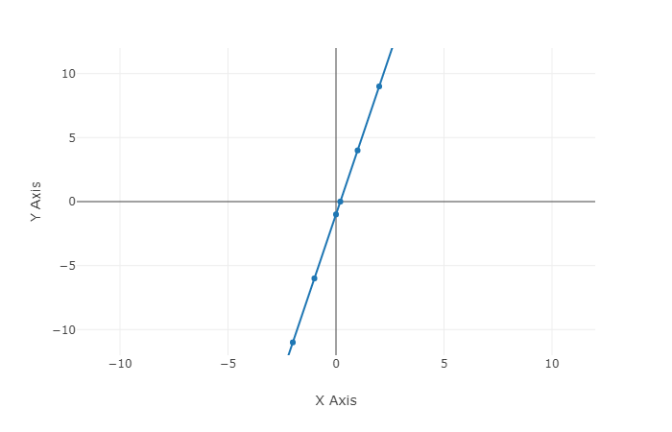
∴ $y = 6x - 2$ is the required linear function whose graph is a line that passes through the points $( - 1, - 8)$ and $(2,10)$.
Note:
There is an alternate way to prove the two points form of the equation of a straight line. Consider the point-slope form of the equation of a line,
we have, $y - {y_1} = m(x - {x_1})$ - - - - - - $(1.)$
Since the line is passing through the point $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ in $\left( {1.} \right)$ and the slope of the line is $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ . So, $(1.)$ becomes $y - {y_1} = \left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$.
Formula used:
The two-point form of a line passing through the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know we can determine the equation of a line that passes through two points by using the two-point form of a line.

Now, the two given points are
$A = \left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $B = \left( {2,10} \right)$ .
Now, we know that the first coordinate is the x-coordinate and the second coordinate is the y-coordinate.
Here,
For point $A$, ${x_1} = - 1$ and ${y_1} = - 8$
For point $B$, ${x_2} = 2$ and ${y_2} = 10$
Now, as we know that, the two-point form of a line is
$\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Now, we can determine the linear function by substituting the ${x_1} = - 1$ , ${x_2} = 2$ , ${y_1} = - 8$ and ${y_2} = 10$ in the two-point form of the equation of a line.
After substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{y - ( - 8)}}{{x - ( - 1)}} = \dfrac{{10 - ( - 8)}}{{2 - ( - 1)}}$
Now, after opening the brackets of numerators as well as denominators on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{10 + 8}}{{2 + 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{18}}{3}$
On Right-hand side, simplifying by dividing $18\;$ by $3$ , we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{6}{1}$
Now, by cross multiplying, we get
$1(y + 8) = 6(x + 1)$
$ \Rightarrow y + 8 = 6x + 6$
Now, by subtracting $8$ on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$$y + 8 - 8 = 6x + 6 - 8$
$ \Rightarrow y = 6x - 2$
∴ $y = 6x - 2$ is the required linear function whose graph is a line that passes through the points $( - 1, - 8)$ and $(2,10)$.
Note:
There is an alternate way to prove the two points form of the equation of a straight line. Consider the point-slope form of the equation of a line,
we have, $y - {y_1} = m(x - {x_1})$ - - - - - - $(1.)$
Since the line is passing through the point $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ in $\left( {1.} \right)$ and the slope of the line is $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ . So, $(1.)$ becomes $y - {y_1} = \left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




