
Development of similar habits in pouched and placental mammals found in similar habitats is called
(a) Divergent evolution
(b) Convergent evolution
(c) Adaptive Radiation
(d) Macroevolution
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Development of similar habits in pouched and placental mammals found in similar habitats is a process of evolution in which two different species, not closely related independently evolve similar traits, as a result, to adapt to the similar habitat they together live in.
Complete answer:
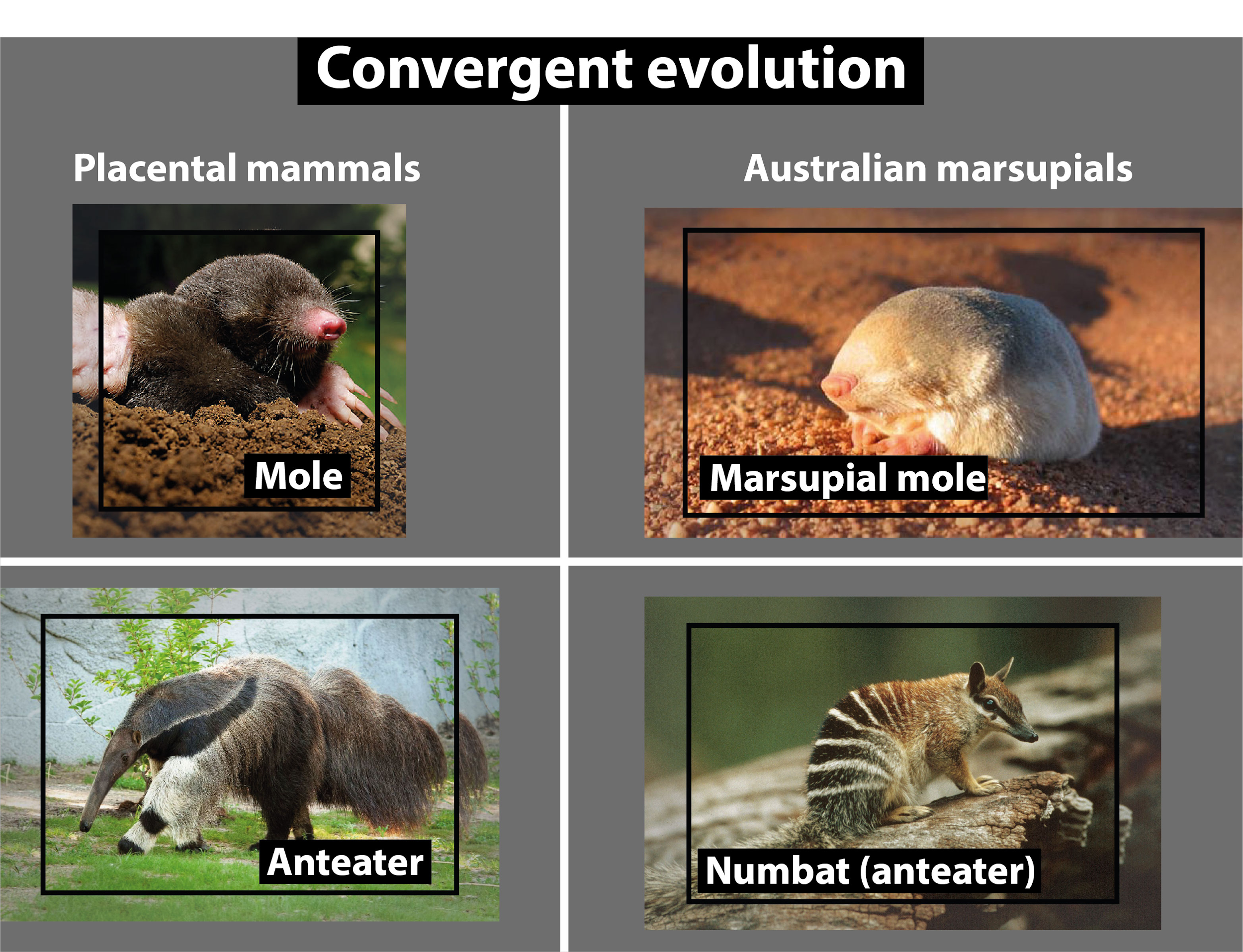
Convergent evolution is a process of evolution in which two entirely separated species, not even closely related to each other evolve independently when living in a similar ecological habitat to adapt to the surrounding similar environment.
It was seen that many placental mammals resembled the marsupial mammals not only in structure but also in leading similar ways of life. These similarities in these two different types of mammals are due to living in similar ecological niches. Hence, two different types of organisms converged towards similarity which depicts that convergent evolution has taken place.
Additional Information:
Evolution means an act of unfolding or unrolling or in simple words, it is an orderly change from one form to another.
The structures in different organisms that are not similar anatomically though they perform a similar function are called analogous organs. Morphologically they may or may not be similar which means that analogous structures may or may not look alike externally. The property of bearing analogous structure is known as an analogy.
Here the different structures evolve towards the same direction just to adapt to similar needs in similar habitats.
When the two species with common ancestry evolve completely different traits to adapt to the different surrounding environment and habitat, it is known as divergent evolution.
When the competition for food and living space increases, a single ancestral species evolves into different forms and occupies different habitats, this type of evolution is known as adaptive radiation.
Macroevolution is the evolution of a large group at or above the species level.
So, the correct answer is, “Convergent evolution.”
Note: -Convergent evolution gave rise to the analogous structures.
-The analogous structures do not exhibit a common origin. It doesn’t indicate common ancestry, unlike homologous structures that indicate common ancestry.
-When two species are similar in a particular character, it is a parallel evolution only if the ancestors are related closely otherwise it’s a convergent evolution if the ancestors are not related closely.
- Convergent evolution is just opposite to the divergent evolution.
Complete answer:
Convergent evolution is a process of evolution in which two entirely separated species, not even closely related to each other evolve independently when living in a similar ecological habitat to adapt to the surrounding similar environment.
It was seen that many placental mammals resembled the marsupial mammals not only in structure but also in leading similar ways of life. These similarities in these two different types of mammals are due to living in similar ecological niches. Hence, two different types of organisms converged towards similarity which depicts that convergent evolution has taken place.
Additional Information:
Evolution means an act of unfolding or unrolling or in simple words, it is an orderly change from one form to another.
The structures in different organisms that are not similar anatomically though they perform a similar function are called analogous organs. Morphologically they may or may not be similar which means that analogous structures may or may not look alike externally. The property of bearing analogous structure is known as an analogy.
Here the different structures evolve towards the same direction just to adapt to similar needs in similar habitats.
When the two species with common ancestry evolve completely different traits to adapt to the different surrounding environment and habitat, it is known as divergent evolution.
When the competition for food and living space increases, a single ancestral species evolves into different forms and occupies different habitats, this type of evolution is known as adaptive radiation.
Macroevolution is the evolution of a large group at or above the species level.
So, the correct answer is, “Convergent evolution.”
Note: -Convergent evolution gave rise to the analogous structures.
-The analogous structures do not exhibit a common origin. It doesn’t indicate common ancestry, unlike homologous structures that indicate common ancestry.
-When two species are similar in a particular character, it is a parallel evolution only if the ancestors are related closely otherwise it’s a convergent evolution if the ancestors are not related closely.
- Convergent evolution is just opposite to the divergent evolution.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




