
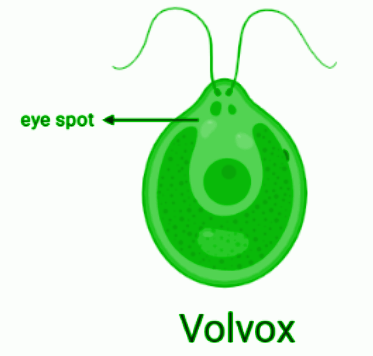
Diagram of Volvox
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Volvox is a green alga that belongs to the family Volvocaceae. In addition to it, Volvox is spherical in shape. Volvox can reproduce both sexually and asexually. They live in colonies.
Complete step by step answer: Volvox is a free-floating common freshwater chlorophyta green algae. These algae prefer to live in colonies which are surrounded by the gelatinous wall. These colonies appear to be ovoid or spherical in shape. The mature colony of Volvox consists of two different types of cells. They are germ cells and flagellated somatic cells. The two flagella present in the adult Volvox help them to swim through freshwater. With the help of cytoplasmic strands, each cell of the colony is attached to the other cell in the colony. The anterior and posterior pole is seen in the cell. Photosensitive eyespots present at the anterior pole help the colony to move towards the light. The mode of reproduction of volvox is asexual and the parent colony produces its daughter colonies within their own colony. The daughter colonies move out of the parent colony after it gets matured. Due to the presence of chlorophyll, each cell of Volvox is able to produce its own food by the process of photosynthesis. The mucilage produced by the volvox colony makes the colony well defined. The surface of the water looks green because of the presence of Volvox.
Note: The first Volvox was reported by Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox colony mostly appears in the rainy season. Volvox can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Environmental conditions and the production of sex-inducing pheromone triggers the switch from asexual to sexual reproduction.
Complete step by step answer: Volvox is a free-floating common freshwater chlorophyta green algae. These algae prefer to live in colonies which are surrounded by the gelatinous wall. These colonies appear to be ovoid or spherical in shape. The mature colony of Volvox consists of two different types of cells. They are germ cells and flagellated somatic cells. The two flagella present in the adult Volvox help them to swim through freshwater. With the help of cytoplasmic strands, each cell of the colony is attached to the other cell in the colony. The anterior and posterior pole is seen in the cell. Photosensitive eyespots present at the anterior pole help the colony to move towards the light. The mode of reproduction of volvox is asexual and the parent colony produces its daughter colonies within their own colony. The daughter colonies move out of the parent colony after it gets matured. Due to the presence of chlorophyll, each cell of Volvox is able to produce its own food by the process of photosynthesis. The mucilage produced by the volvox colony makes the colony well defined. The surface of the water looks green because of the presence of Volvox.

Note: The first Volvox was reported by Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox colony mostly appears in the rainy season. Volvox can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Environmental conditions and the production of sex-inducing pheromone triggers the switch from asexual to sexual reproduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




