
How did August Kekule’s discovery about carbon, change the science of chemistry?
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: The beginning of chemistry is connected with the carbon and thus becoming complex and complex but the first forming atom is carbon. Scientist August Kekule’s discovery is the number of bonds that carbon formed with other atoms. As we know carbon forms bonds by sharing electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know chemistry by carbon, so the first thing that would come if someone asked us about chemistry is carbon compounds. “August Kekule'' is the man who is credited for the initiation of our beloved subject chemistry. He discovered the tetravalent nature of carbon i.e. carbon can make bonds with only four atoms which surround it. He was the first one to draw chemical structure where atoms were connected by lines to represent the bonds.
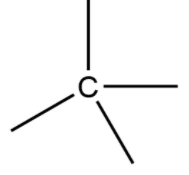
By that time to now, we are seeing compounds which are having carbon as the main atom. If we see the methane it is formed when carbon is connected by covalent bonds (bonds which are formed by sharing of electrons) with four hydrogens. Also there are many classes of hydrocarbons and in every class carbon is forming a compound by satisfying its valence with four bonds. There are alkanes ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ , alkenes ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ and alkynes ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$ which are having single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds respectively. After the discovery of tetravalency of carbon “August Kekule” discovered the structure of benzene.
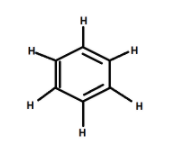
Benzene has a chemical formula as ${C_6}{H_6}$ and found to be very stable, called aromatic in nature. After that for finding stability in many compounds aromaticity is getting seen by the availability of benzene rings in compounds. Benzene is liquid at room temperature having 6 carbon atoms connected as a ring having alternate double and single bond satisfying three valences of carbon while the last is satisfied when carbon gets connected with hydrogen.
Note: Sometimes there are some structures which are very complex and forming with stereochemistry. Always consider first priority as to see that carbon is possessing four valances. In double and triple bonds carbon make two bonds and three bonds with other carbon atoms and satisfy remaining valances by connecting with other groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know chemistry by carbon, so the first thing that would come if someone asked us about chemistry is carbon compounds. “August Kekule'' is the man who is credited for the initiation of our beloved subject chemistry. He discovered the tetravalent nature of carbon i.e. carbon can make bonds with only four atoms which surround it. He was the first one to draw chemical structure where atoms were connected by lines to represent the bonds.

By that time to now, we are seeing compounds which are having carbon as the main atom. If we see the methane it is formed when carbon is connected by covalent bonds (bonds which are formed by sharing of electrons) with four hydrogens. Also there are many classes of hydrocarbons and in every class carbon is forming a compound by satisfying its valence with four bonds. There are alkanes ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ , alkenes ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ and alkynes ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$ which are having single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds respectively. After the discovery of tetravalency of carbon “August Kekule” discovered the structure of benzene.

Benzene has a chemical formula as ${C_6}{H_6}$ and found to be very stable, called aromatic in nature. After that for finding stability in many compounds aromaticity is getting seen by the availability of benzene rings in compounds. Benzene is liquid at room temperature having 6 carbon atoms connected as a ring having alternate double and single bond satisfying three valences of carbon while the last is satisfied when carbon gets connected with hydrogen.
Note: Sometimes there are some structures which are very complex and forming with stereochemistry. Always consider first priority as to see that carbon is possessing four valances. In double and triple bonds carbon make two bonds and three bonds with other carbon atoms and satisfy remaining valances by connecting with other groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




