
Diethyl amine is treated with ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}$(Caro’s acid) to give,
1. Tetraethyl hydrazine
2. Diethyl ether
3. Diethyl hydroxyl amine
4. Ethyl alcohol and ethyl amine
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we need to recall that the reaction between secondary amines and Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid). Diethyl amine is a secondary amine as the amine group ($N{{H}_{2}}$) is linked to a secondary carbon atom.
Complete answer:
In the general reaction of amines, we saw that the reaction between secondary amines and Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid) leads to the formation of Dialkyl hydroxylamine as the final product. Caro’s acid is one of the strongest oxidising agents. It oxides the Dialkyl amine and itself reduces to sulphuric acid. It works as an –OH donor.
General reaction of Amine with Caro’s acid- (R is the alkyl group)
$R-NH-R\text{+ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}\text{ }\to \text{ R}-N(OH)-R+\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
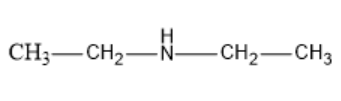
Let us first see the structure of diethylamine:
Structure of Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid):
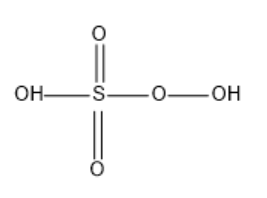
In Caro’s acid we can see that there are two free hydroxyl groups one attached to Sulphur and the other attached to oxygen.
Now, the chemical reaction between Diethylamine and Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid) at 373K results in the formation of Diethyl hydroxyl amine and Sulphuric acid.
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-NH-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}\text{ }\xrightarrow{373K}\text{ }{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-N(OH)-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
We can observe that the –H attached to nitrogen in diethyl amine is substituted by –OH in the product to form Diethyl hydroxyl amine.
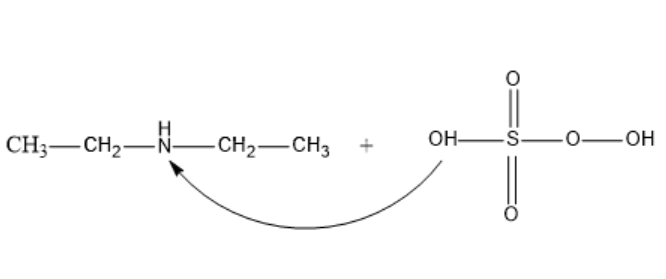
In the structural formula, let’s understand that the – OH group attacks the Diethylamine on the Nitrogen atom and displaces the –H.
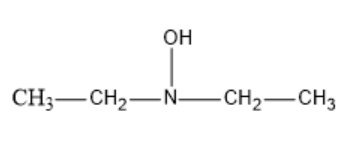
The resultant structure formed of Diethyl hydroxyl amine will be:
The structural chemical reaction is-
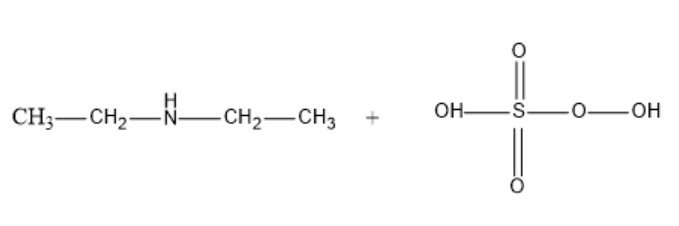
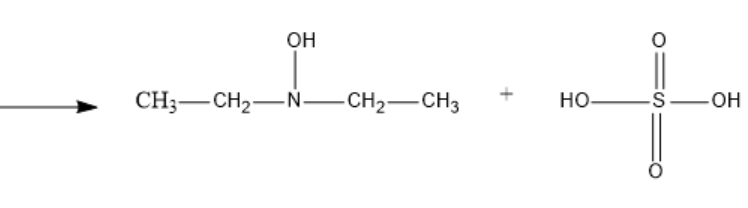
So, the correct answer is “Option 3”.
Note:
Caro’s acid is formed by the reaction between Hydrogen peroxide (${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$) and sulphuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$). So, it has peroxy in its IUPAC name. Caro’s acid is a clear, colourless solution and has an oily uniformity. It also has the ability to destroy alcohols, phenols, aldehydes and ketones.
Complete answer:
In the general reaction of amines, we saw that the reaction between secondary amines and Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid) leads to the formation of Dialkyl hydroxylamine as the final product. Caro’s acid is one of the strongest oxidising agents. It oxides the Dialkyl amine and itself reduces to sulphuric acid. It works as an –OH donor.
General reaction of Amine with Caro’s acid- (R is the alkyl group)
$R-NH-R\text{+ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}\text{ }\to \text{ R}-N(OH)-R+\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
Let us first see the structure of diethylamine:

Structure of Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid):

In Caro’s acid we can see that there are two free hydroxyl groups one attached to Sulphur and the other attached to oxygen.
Now, the chemical reaction between Diethylamine and Caro’s acid (peroxy mono sulphuric acid) at 373K results in the formation of Diethyl hydroxyl amine and Sulphuric acid.
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-NH-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}\text{ }\xrightarrow{373K}\text{ }{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-N(OH)-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
We can observe that the –H attached to nitrogen in diethyl amine is substituted by –OH in the product to form Diethyl hydroxyl amine.
In the structural formula, let’s understand that the – OH group attacks the Diethylamine on the Nitrogen atom and displaces the –H.

The resultant structure formed of Diethyl hydroxyl amine will be:

The structural chemical reaction is-


So, the correct answer is “Option 3”.
Note:
Caro’s acid is formed by the reaction between Hydrogen peroxide (${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$) and sulphuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$). So, it has peroxy in its IUPAC name. Caro’s acid is a clear, colourless solution and has an oily uniformity. It also has the ability to destroy alcohols, phenols, aldehydes and ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




