
What is the difference between a compression and a rarefaction in a sound wave? Illustrate your answer with a sketch.
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: Sound waves are mechanical waves i.e. the waves that require presence of any medium for propagation. These waves oscillate in SHM (Simple Harmonic Motion). The medium of such waves are elastic in nature i.e. they regain the shape on removal of force or after propagation of sound the medium particles regain their positions.
Complete step by step solution:
Waves are the means of transfer of energy in vacuum, through substances etc. waves contain energy that is transferred from a position to another by help of medium or without medium. These are of two types.
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
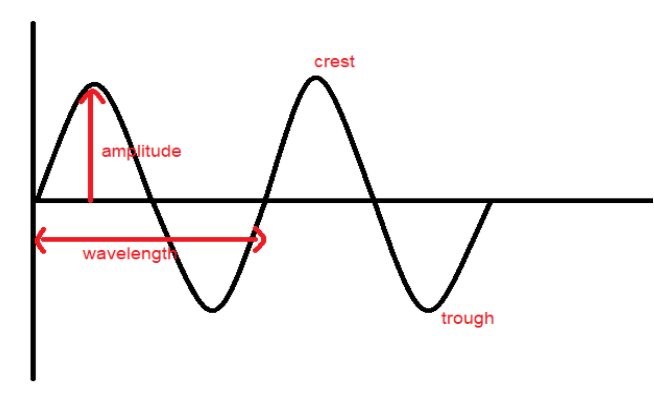
Transverse waves transfer particles perpendicular to direction of propagation of wave and energy. In transverse waves a particle oscillates or performs periodic motion in direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is heading or propagating.
The topmost part of waves forming hilly tops is known as crest in transverse waves while deepest point like an ocean's depth is known as trough in transverse waves.
E.g. light wave
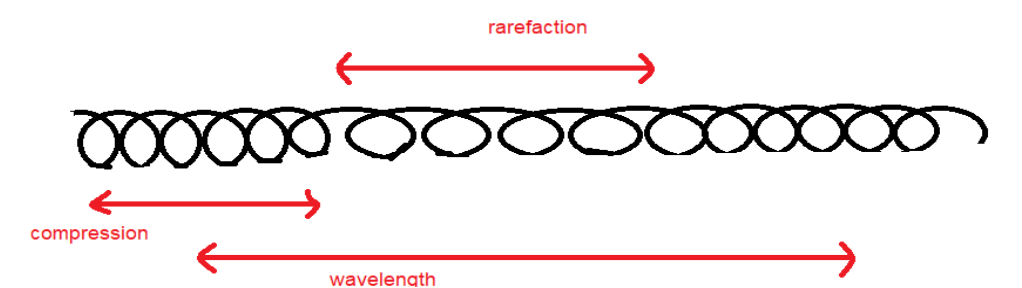
Longitudinal waves or compression, in contrast to longitudinal waves, transfer particles in direction parallel to direction of propagation of wave and energy. Particles show a zig-zag motion. These waves move like a striped part with some places having dark strips (called compression) while others having light strips (called rarefaction). Formation of these strips is explained, as these waves require medium to flow, that when a wave initiates at some end of a particle it will push the end leading to decrease in the gap of molecules forming compressions. As it passes the energy to the next set of molecules, it pressurizes the next set forming compression in the next set of molecules and leaving behind excess space for previously compressed molecules such that they expand and form rarefactions. So we can say that
Compression is the region of high pressure during propagation of a wave, appearing like a dark strip in a wave diagram.
Rarefaction is the region of expansion of particles due to compression in adjoining molecules during wave propagation, appearing in the light zone in the wave diagram.
E.g. Sound wave
Note:
The direction of motion of a particle with respect to direction of propagation of wave determines the type of wave we are dealing with. Crest, trough and compression, rarefaction respectively are the variables of each other in different motion. Although propagation is different, studying them reveal similar turns differentiated based on the motion performed.
Complete step by step solution:
Waves are the means of transfer of energy in vacuum, through substances etc. waves contain energy that is transferred from a position to another by help of medium or without medium. These are of two types.
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
Transverse waves transfer particles perpendicular to direction of propagation of wave and energy. In transverse waves a particle oscillates or performs periodic motion in direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is heading or propagating.
The topmost part of waves forming hilly tops is known as crest in transverse waves while deepest point like an ocean's depth is known as trough in transverse waves.
E.g. light wave

Longitudinal waves or compression, in contrast to longitudinal waves, transfer particles in direction parallel to direction of propagation of wave and energy. Particles show a zig-zag motion. These waves move like a striped part with some places having dark strips (called compression) while others having light strips (called rarefaction). Formation of these strips is explained, as these waves require medium to flow, that when a wave initiates at some end of a particle it will push the end leading to decrease in the gap of molecules forming compressions. As it passes the energy to the next set of molecules, it pressurizes the next set forming compression in the next set of molecules and leaving behind excess space for previously compressed molecules such that they expand and form rarefactions. So we can say that
Compression is the region of high pressure during propagation of a wave, appearing like a dark strip in a wave diagram.
Rarefaction is the region of expansion of particles due to compression in adjoining molecules during wave propagation, appearing in the light zone in the wave diagram.
E.g. Sound wave

Note:
The direction of motion of a particle with respect to direction of propagation of wave determines the type of wave we are dealing with. Crest, trough and compression, rarefaction respectively are the variables of each other in different motion. Although propagation is different, studying them reveal similar turns differentiated based on the motion performed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




