
What is the difference between amino groups and amine?
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the nomenclature of the functional group attached to an organic molecule. A functional group can be defined as the moiety or substance that affects and changes the characteristics of the chemical reaction of a molecule.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what an amine is.
A compound that contains the basic nitrogen atom along with the lone pair is known as an amine.
Amines are usually a derivative of ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$).
Organic amines are formed when an alkyl or an aryl group replaces one or more hydrogen atoms from ammonia.
Monochloramine ($NCl{{H}_{2}}$) is an example of amine derived from inorganic derivatives of ammonia.
Now, a compound that contains the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ substituent group or moiety is known as the amino group. It is usually present in primary ($1{}^\circ $) amines.
So, the difference between amine and amino group is essentially a matter of nomenclature i.e., a compound containing basic nitrogen atom along with the lone pair is called an amine, and the functional group present in primary ($1{}^\circ $) amines is the amino group.
For example, $C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}$ is an amine named methylamine and contains the amino functional group.
Note:
It should be noted that there are three types of amines depending upon the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.
- Primary amine ($1{}^\circ $): 1 hydrogen atom is replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.
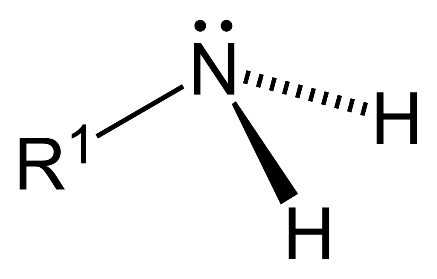
- Secondary amine ($2{}^\circ $): 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.
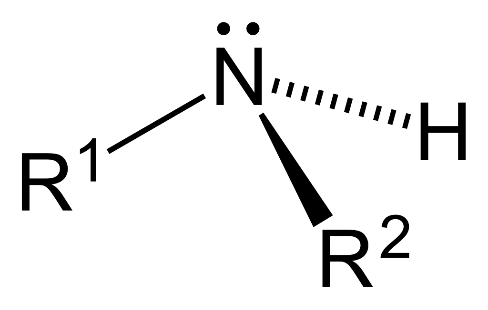
- Tertiary amine ($3{}^\circ $): 3 hydrogen atoms are replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.
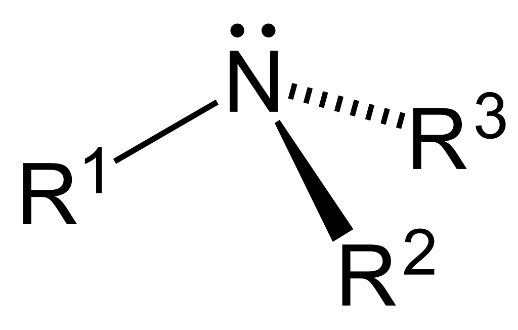
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what an amine is.
A compound that contains the basic nitrogen atom along with the lone pair is known as an amine.
Amines are usually a derivative of ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$).
Organic amines are formed when an alkyl or an aryl group replaces one or more hydrogen atoms from ammonia.
Monochloramine ($NCl{{H}_{2}}$) is an example of amine derived from inorganic derivatives of ammonia.
Now, a compound that contains the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ substituent group or moiety is known as the amino group. It is usually present in primary ($1{}^\circ $) amines.
So, the difference between amine and amino group is essentially a matter of nomenclature i.e., a compound containing basic nitrogen atom along with the lone pair is called an amine, and the functional group present in primary ($1{}^\circ $) amines is the amino group.
For example, $C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}$ is an amine named methylamine and contains the amino functional group.
Note:
It should be noted that there are three types of amines depending upon the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.
- Primary amine ($1{}^\circ $): 1 hydrogen atom is replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.

- Secondary amine ($2{}^\circ $): 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.

- Tertiary amine ($3{}^\circ $): 3 hydrogen atoms are replaced by substituent alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




