
What is the difference between isobutyl and sec-butyl?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: There are a number of organic groups which act as substituent in writing IUPAC name of the compound.The purpose of the IUPAC system of nomenclature is to establish an international standard of naming compounds to facilitate communication. The goal of the system is to give each structure a unique and unambiguous name, and to correlate each name with a unique and unambiguous structure.
Complete answer:
Isobutyl and sec-butyl are alkyl radicals which are produced from their parent compound butane.
Butane is represented by the general formula RH where R is called an alkyl group or radical and they are represented as \[{C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}\].
The alkyl group contains only one hydrogen atom less than the alkane. Hence, alkyl radical of butane has molecular formula $\left( {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2} - } \right)$
As we know the basic structure of butane is –
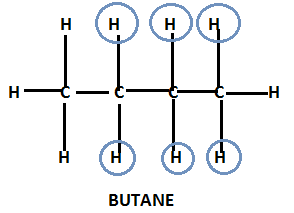
In the molecular structure of butane, we see that there are four secondary hydrogen atoms which are equivalent in nature. Replacing any one of these equivalent hydrogen by the methyl group from the parent structure of butane will lead to formation of a structure which is commonly known as isobutyl.
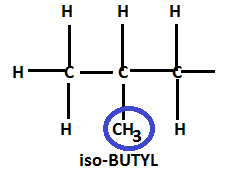
Hence, the total number of carbons in isobutyl remains the same, only the position of the methyl group is changed.
Similarly, removal of one of the secondary hydrogens from the parent structure will lead to the formation of a structure commonly known as sec-butyl.
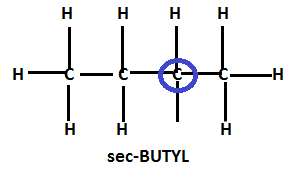
Hence, the total number of carbons in sec-butyl remains the same, the position of all the carbon remains the same, only the number of hydrogens is reduced by one.
Hence, the basic difference between isobutyl and sec-butyl is the arrangement of carbon atoms to the parent molecule.
Note:
Both compounds namely isobutyl and sec-butyl can react with the same reagent to form different products. For example, on reacting with aqueous sodium hydroxide isobutyl form $2 - $ methyl propane $ - 1 - $ ol, while sec-butyl form butan $ - 2 - $ ol in the presence of the same reagent.
Complete answer:
Isobutyl and sec-butyl are alkyl radicals which are produced from their parent compound butane.
Butane is represented by the general formula RH where R is called an alkyl group or radical and they are represented as \[{C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}\].
The alkyl group contains only one hydrogen atom less than the alkane. Hence, alkyl radical of butane has molecular formula $\left( {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2} - } \right)$
As we know the basic structure of butane is –

In the molecular structure of butane, we see that there are four secondary hydrogen atoms which are equivalent in nature. Replacing any one of these equivalent hydrogen by the methyl group from the parent structure of butane will lead to formation of a structure which is commonly known as isobutyl.

Hence, the total number of carbons in isobutyl remains the same, only the position of the methyl group is changed.
Similarly, removal of one of the secondary hydrogens from the parent structure will lead to the formation of a structure commonly known as sec-butyl.

Hence, the total number of carbons in sec-butyl remains the same, the position of all the carbon remains the same, only the number of hydrogens is reduced by one.
Hence, the basic difference between isobutyl and sec-butyl is the arrangement of carbon atoms to the parent molecule.
Note:
Both compounds namely isobutyl and sec-butyl can react with the same reagent to form different products. For example, on reacting with aqueous sodium hydroxide isobutyl form $2 - $ methyl propane $ - 1 - $ ol, while sec-butyl form butan $ - 2 - $ ol in the presence of the same reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




