
What is the difference between vapour and gas?
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Here, we have to differentiate between the vapour, and a gas. We can consider the example of vapour, and gas; i.e. water vapour, and hydrogen, oxygen existing in gaseous form respectively. On the basis of examples, we would be able to differentiate between the given terms.
Complete step by step answer:
> Now, we know that the matter has three states, i.e. liquid, solid, and gas.
> We can say that all the three states are interchangeable with each other through a different process. It can be better understood through the cycle mentioned, i.e.
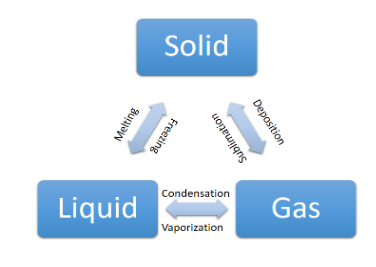
> With the help of this chart, it is easy for us to differentiate between the vapour, and a gas.
> We can say that the increase, and decrease in the temperature, and pressure will cause the change in state of matter.
> If we talk about the vapours first, then from the chart, we can say that vapour is formed when the transition takes place from liquid state to gaseous state.
> In other terms, we can say that vapour is the transition state; and it is formed by the boiling of liquid.
> Now, if we talk about the gas, then the above mentioned chart indicates that it is formed on the heating of liquid; when the liquid reaches above the critical temperature, and below the critical pressure.
> We can also say that when the water is boiling, first vapours will form, and on the complete phase change formation of gas will take place.
> Thus, vapour exists in between the liquid, and the gas phase.
- Let us differentiate vapour, and gas in the tabular form for better understanding.
- In the last we can conclude that the vapour is a transition state between the liquid, and gas; whereas gas is a state of matter.
Note:
1- There could be confusion regarding the critical temperature, and the critical pressure. Now, we know that the vapour state is formed in between the conversion. So, critical temperature is the temperature at which we cannot liquefy the substance. Thus, gas is liquefied above the critical temperature.
2- At the critical pressure liquid, and water vapour coexists, so for the gaseous state it is below the critical pressure for the conversion.
Complete step by step answer:
> Now, we know that the matter has three states, i.e. liquid, solid, and gas.
> We can say that all the three states are interchangeable with each other through a different process. It can be better understood through the cycle mentioned, i.e.

> With the help of this chart, it is easy for us to differentiate between the vapour, and a gas.
> We can say that the increase, and decrease in the temperature, and pressure will cause the change in state of matter.
> If we talk about the vapours first, then from the chart, we can say that vapour is formed when the transition takes place from liquid state to gaseous state.
> In other terms, we can say that vapour is the transition state; and it is formed by the boiling of liquid.
> Now, if we talk about the gas, then the above mentioned chart indicates that it is formed on the heating of liquid; when the liquid reaches above the critical temperature, and below the critical pressure.
> We can also say that when the water is boiling, first vapours will form, and on the complete phase change formation of gas will take place.
> Thus, vapour exists in between the liquid, and the gas phase.
- Let us differentiate vapour, and gas in the tabular form for better understanding.
| Gas | Vapour |
| It exists in the single state | It exists as a combination of two states i.e. liquid, and gas. |
| It is a state of matter. | It is a transition state, not the state of matter. |
| These are formed during the boiling of liquid. | This is formed above the critical temperature of liquid, and below the critical pressure. |
- In the last we can conclude that the vapour is a transition state between the liquid, and gas; whereas gas is a state of matter.
Note:
1- There could be confusion regarding the critical temperature, and the critical pressure. Now, we know that the vapour state is formed in between the conversion. So, critical temperature is the temperature at which we cannot liquefy the substance. Thus, gas is liquefied above the critical temperature.
2- At the critical pressure liquid, and water vapour coexists, so for the gaseous state it is below the critical pressure for the conversion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




