
Differentiate between denaturation and renaturation of proteins.
Answer
603.6k+ views
Hint: As the words suggest, denaturation means to change the nature of something, and here involves boiling proteins while renaturation means to bring back in its original form, and thus is the inverse process of denaturation.
Complete answer:
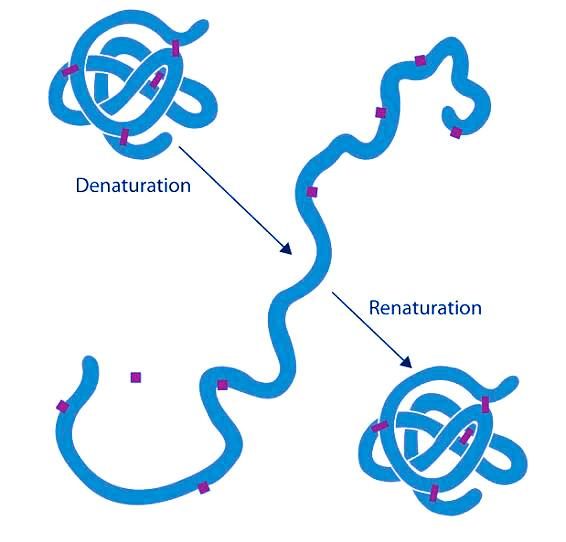
Note: SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), is a discontinuous electrophoretic system developed by Ulrich K. Laemmli which is commonly used as a method to separate proteins with molecular masses between 5 and 250 kDa. The combined use of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, also known as sodium lauryl sulfate) and polyacrylamide gel allows to eliminate the influence of structure and charge, and proteins are separated solely on the basis of differences in their molecular weight.
Complete answer:
| Denaturation of Proteins | Renaturation of Proteins |
| In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from its original state when exposed to a denaturing agent. In biology, examples of biomolecules that denature are proteins and nucleic acids (e.g. DNA). | Renaturation in molecular biology refers to the reconstruction of a protein or nucleic acid (such as DNA) to their original form especially after denaturation. This process is therefore the inverse of denaturation. |
| A denatured protein, for instance, means a protein whose three-dimensional (3D) structure is disrupted due to exposure to certain chemical or physical factors (called denaturants). | In denaturation, the proteins or nucleic acids lose their native biomolecular structure. For instance, a DNA molecule is denatured through heating. The heat-denatured DNA separates into two strands. However, it can revert to its original form by cooling slowly the two strands and then reform into its original double-stranded helix. |
| When a protein is exposed to a denaturant, its structure is altered resulting in the loss of its innate biological activity and function. | One way through which a denatured protein is restored to its original form is by removing the SDS and denaturing agents following denaturation during PAGE or IEF protein identification. |

Note: SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), is a discontinuous electrophoretic system developed by Ulrich K. Laemmli which is commonly used as a method to separate proteins with molecular masses between 5 and 250 kDa. The combined use of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, also known as sodium lauryl sulfate) and polyacrylamide gel allows to eliminate the influence of structure and charge, and proteins are separated solely on the basis of differences in their molecular weight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




