
Differentiate between nucleoside and nucleotide.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Nucleosides are the building blocks for nucleotides and nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleosides and nucleotides are similar kinds of molecules.
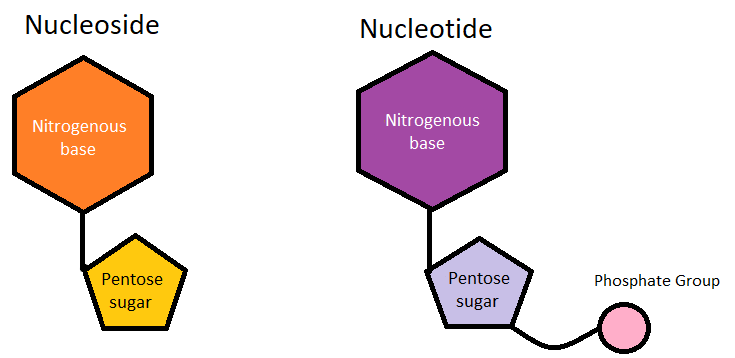
Complete answer: A nucleotide is a building block of nucleic acids present inside the nucleus of a cell. On the other hand, a nucleoside is a nucleobase that is attached to a sugar molecule and when a phosphate group is provided to it, it gives rise to a nucleotide that forms the nucleic acid. So, a nucleoside is the building block of a nucleotide. Nucleotide acts as a monomer for the production of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. But nucleoside is a single unit molecule that is attached to pentose sugar. The nucleotide molecule consists of one nucleoside and one phosphate group that is attached by a phosphodiester bond to form DNA and RNA polymers. But the nucleoside molecule is made of nucleobases attached to pentose sugar only making a beta-glycosidic bond. Nucleotides are mainly of two types. They are differentiated based on the type of nucleoside they are composed of. These are purines and pyrimidines. Purines consist of a nucleoside with an imidazole ring fused to its heterocyclic aromatic ring and pyrimidines are heterocyclic aromatic rings having nitrogen at 1 and 3 positions of the ring. For example, cytosine and thymine are pyrimidines and Adenine and guanine are purines. These nucleotides undergo polymerization and form the complex DNA molecule by complementary base pairing between one purine and one pyrimidine. Some examples of nucleotides are deoxyribonucleotides, ribonucleotides, ATP, CAM, etc. Examples of nucleosides are cytidine, guanosine, thymidine, inosine, etc. In cells, nucleotides are the functional units and not the nucleosides.
Note: Nucleotides polymerize to make DNA and RNA but they also make energy-storing molecules like ATP and GTP and cell signalling molecules like CAM. Also, nucleosides are essentially used as anticancer compounds and they also exhibit anti-viral properties.
Complete answer: A nucleotide is a building block of nucleic acids present inside the nucleus of a cell. On the other hand, a nucleoside is a nucleobase that is attached to a sugar molecule and when a phosphate group is provided to it, it gives rise to a nucleotide that forms the nucleic acid. So, a nucleoside is the building block of a nucleotide. Nucleotide acts as a monomer for the production of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. But nucleoside is a single unit molecule that is attached to pentose sugar. The nucleotide molecule consists of one nucleoside and one phosphate group that is attached by a phosphodiester bond to form DNA and RNA polymers. But the nucleoside molecule is made of nucleobases attached to pentose sugar only making a beta-glycosidic bond. Nucleotides are mainly of two types. They are differentiated based on the type of nucleoside they are composed of. These are purines and pyrimidines. Purines consist of a nucleoside with an imidazole ring fused to its heterocyclic aromatic ring and pyrimidines are heterocyclic aromatic rings having nitrogen at 1 and 3 positions of the ring. For example, cytosine and thymine are pyrimidines and Adenine and guanine are purines. These nucleotides undergo polymerization and form the complex DNA molecule by complementary base pairing between one purine and one pyrimidine. Some examples of nucleotides are deoxyribonucleotides, ribonucleotides, ATP, CAM, etc. Examples of nucleosides are cytidine, guanosine, thymidine, inosine, etc. In cells, nucleotides are the functional units and not the nucleosides.

Note: Nucleotides polymerize to make DNA and RNA but they also make energy-storing molecules like ATP and GTP and cell signalling molecules like CAM. Also, nucleosides are essentially used as anticancer compounds and they also exhibit anti-viral properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




