
Differentiate between peripheral and integral proteins?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The proteins are macromolecules formed from amino acids. They are large size molecules, polymers of units called amino acids. There are twenty different amino acids present in proteins and thousands of amino acids are attached to long chains to form a protein.
Complete answer:Peripheral proteins:- These proteins are membrane proteins that attach to the biological membrane to which they are associated. These proteins are attached to integral membrane proteins. In contrast to integral proteins, peripheral proteins collected from the water-soluble component, of all the proteins extracted during protein purification. Proteins with GPI anchors are an exception to this rule. The attachment of proteins to biological membranes regulates cell signaling. For example, the close association between enzymes and membranes may bring them into proximity with their lipid substrate. Membrane binding promotes rearrangement, dissociation, and conformational changes within many protein domains result in activation of their biological activity. Additionally, the positioning of proteins is localized to the inner or outer surfaces of their membrane. This facilitates the assembly of multi-protein complexes which increases the probability of appropriate protein-protein interaction.
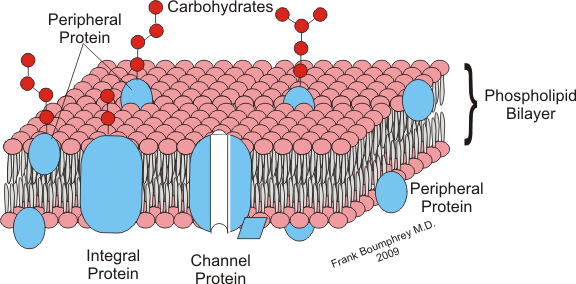
Integral proteins:- An integral membrane protein is a membrane protein that is attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins are transmembrane proteins. It comprises a fraction of the proteins encoded in a genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins are separated from the membranes by using detergents.
Note: The peripheral protein is located in the inner and outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer whereas integral protein is embedded in the whole bilayer. The structure shows a sandwich model of the cell membrane.
Complete answer:Peripheral proteins:- These proteins are membrane proteins that attach to the biological membrane to which they are associated. These proteins are attached to integral membrane proteins. In contrast to integral proteins, peripheral proteins collected from the water-soluble component, of all the proteins extracted during protein purification. Proteins with GPI anchors are an exception to this rule. The attachment of proteins to biological membranes regulates cell signaling. For example, the close association between enzymes and membranes may bring them into proximity with their lipid substrate. Membrane binding promotes rearrangement, dissociation, and conformational changes within many protein domains result in activation of their biological activity. Additionally, the positioning of proteins is localized to the inner or outer surfaces of their membrane. This facilitates the assembly of multi-protein complexes which increases the probability of appropriate protein-protein interaction.

Integral proteins:- An integral membrane protein is a membrane protein that is attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins are transmembrane proteins. It comprises a fraction of the proteins encoded in a genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins are separated from the membranes by using detergents.
Note: The peripheral protein is located in the inner and outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer whereas integral protein is embedded in the whole bilayer. The structure shows a sandwich model of the cell membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




