
Differentiate between racemose and cymose inflorescence.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The inflorescence refers to the arrangement of clusters of flowers in a plant. Flowers can be arranged in two major types; either they can be in clusters making racemes or they form a cyme.
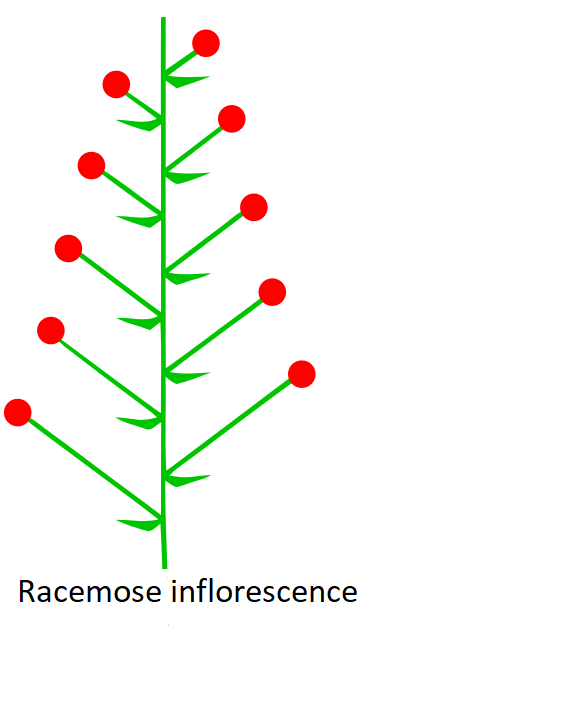
Complete answer: Inflorescence refers to a specific pattern in which the cluster of flowers is arranged at the reproductive portion of the plant. The main stem that holds the whole cluster of flowers is called the peduncle, whereas the major axis that holds secondary branches within the inflorescence is known as rachis. Furthermore, each flower in inflorescence has its individual stalk and is called a pedicel. The racemose inflorescence or indeterminate simple inflorescence is an arrangement in which the cluster of flowers resembles the cluster of grapes. It involves a cluster of flowers having separate flowers attached by short equal stalks on a central stem. The flowers present at the base of this stem are first to grow. It can be of various types like raceme, spike, corymb, umbel, spadix, flower head, and catkin.
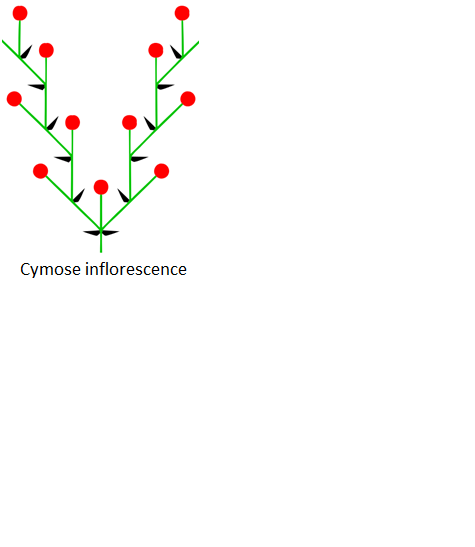
The determinate or the cymose inflorescence involves a flower cluster having a central stem. In this, a single terminal flower is the first to develop and the other flowers in the cluster development from the lateral stems. It is of various types including double cyme, Bostryx, Drepanium, Rhipidium, Dichasium, etc. The main axis or main stem in racemose inflorescence continues to grow. But in a cymose inflorescence, it terminates to grow. The growth of flowers, rachis, and pedicel is unlimited. But in a cymose inflorescence, the growth gets limited at a certain time. The flowers in racemose grow in an acropetal succession manner, which implies that the apex of the rachis will have younger flowers and the base will have older or first borne flowers. In cymose, the flowers are borne in a manner in which the flowers at the base are younger and at the top are the older flowers, and this is called basipetal succession. In the racemose inflorescence, the flowers tend to cluster towards the centre. Thus, the arrangement is centripetal. However, flowers in cymose inflorescence tend to grow away from the centre. This arrangement is called a centrifugal. Various examples of the racemose inflorescence are Iberis umbellata, Plantago media, Epilobium angustifolium, etc. Some examples of the cymose inflorescence are Gladiolus imbricatus, Canna sp., etc.
Note: The most common kind of definite compound inflorescence is the panicle. A panicle is a definite inflorescence that is increasingly more strongly and irregularly branched from the top to the bottom and where each branching has a terminal flower.
Complete answer: Inflorescence refers to a specific pattern in which the cluster of flowers is arranged at the reproductive portion of the plant. The main stem that holds the whole cluster of flowers is called the peduncle, whereas the major axis that holds secondary branches within the inflorescence is known as rachis. Furthermore, each flower in inflorescence has its individual stalk and is called a pedicel. The racemose inflorescence or indeterminate simple inflorescence is an arrangement in which the cluster of flowers resembles the cluster of grapes. It involves a cluster of flowers having separate flowers attached by short equal stalks on a central stem. The flowers present at the base of this stem are first to grow. It can be of various types like raceme, spike, corymb, umbel, spadix, flower head, and catkin.
The determinate or the cymose inflorescence involves a flower cluster having a central stem. In this, a single terminal flower is the first to develop and the other flowers in the cluster development from the lateral stems. It is of various types including double cyme, Bostryx, Drepanium, Rhipidium, Dichasium, etc. The main axis or main stem in racemose inflorescence continues to grow. But in a cymose inflorescence, it terminates to grow. The growth of flowers, rachis, and pedicel is unlimited. But in a cymose inflorescence, the growth gets limited at a certain time. The flowers in racemose grow in an acropetal succession manner, which implies that the apex of the rachis will have younger flowers and the base will have older or first borne flowers. In cymose, the flowers are borne in a manner in which the flowers at the base are younger and at the top are the older flowers, and this is called basipetal succession. In the racemose inflorescence, the flowers tend to cluster towards the centre. Thus, the arrangement is centripetal. However, flowers in cymose inflorescence tend to grow away from the centre. This arrangement is called a centrifugal. Various examples of the racemose inflorescence are Iberis umbellata, Plantago media, Epilobium angustifolium, etc. Some examples of the cymose inflorescence are Gladiolus imbricatus, Canna sp., etc.


Note: The most common kind of definite compound inflorescence is the panicle. A panicle is a definite inflorescence that is increasingly more strongly and irregularly branched from the top to the bottom and where each branching has a terminal flower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




