
Differentiate between skeletal muscles, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle (at least two points in each).
Answer
523k+ views
Hint: Differentiate between the structure (striated or unstriated muscles; types of cells that make the tissue), function (voluntary or involuntary movement; self-stimulating or not; help in fluid and blood flow), and locations (present in which organs, attached to which structures) of these muscles.
Complete answer:
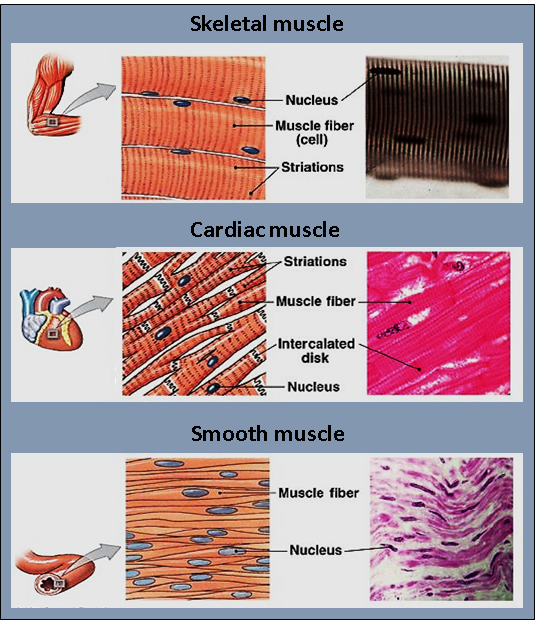
Muscle tissues are one of the four fundamental tissues (epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous) found in the body. They are the soft tissues that help in the movement and in maintaining the posture of the body. Muscle tissues can be differentiated into three forms: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles based on the structure and functions of these muscles.
Additional Information:
-42% of an average adult male body mass is made up of skeletal muscles and in females, they make up 36% of body mass of an average adult female.
-Muscles not only help in movement and maintaining the posture of the body, but they also help in regulating different organs (like the heart), create heat to warm up the body, and helps in the movement of substances around the body (like the movement of blood from heart and food in the digestive system)
-The striated appearance of skeletal muscles is due to the formation of actin and myosin muscle fibers. Skeletal muscles are well supplied with blood vessels and nerves.
-Cardiac muscles are arranged in bundles of muscle fibers sheets and show involuntary movement as they are regulated by the autonomic part of the nervous system.
-Cardiac muscles are though mainly controlled by the central nervous system (CNS), they can also contract without signals from CNS due to pacemaker cells.
Note: Muscle fatigue is the decrease in the ability of the muscles to perform over time due to a decrease in the force behind the muscles. That overall affects the body by making it weaker. Skeletal muscles fatigue more easily than cardiac or smooth muscles because skeletal muscles are not essential in homeostasis and survival. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle that may cause a threat to life.
Complete answer:
Muscle tissues are one of the four fundamental tissues (epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous) found in the body. They are the soft tissues that help in the movement and in maintaining the posture of the body. Muscle tissues can be differentiated into three forms: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles based on the structure and functions of these muscles.
- •
| Features | Skeletal muscles | Smooth muscles | Cardiac muscles |
| Movement | Voluntary | Involuntary | Involuntary |
| Location | Attached to skin and bones | The lining of walls of internal organs | Present in heart |
| Cells | Long, multinucleated, cylindrical cells | Uni-nucleated, single tapering cells | Straight uni-nucleated cells with branching chains. |
| Muscle type | Myofibrils are arranged orderly to form striated muscle | Varying lengths of myofibrils forms un-striated muscle | The ordered arrangement of myofibrils forms striated muscle. |
| Controlled by | Nervous system | Nervous and endocrine system and other chemicals and stretching | The central nervous system, endocrine system, and different chemicals |
| Stimulation | Non-self-stimulating, stimulated by motor neurons of the nervous system | Self-stimulating | Self-stimulating |
| Energy requirement | High | Low | Intermediate |
| Contraction speed | Fast, non-rhythmic contraction | Slow and rhythmic in some organs | Intermediate speed and rhythmic contraction |
| Fatigue creation | Fatigues easily | Does not fatigue | Does not fatigue |
| Strength | Increases with stretching | Stress-relaxation response | Increases with stretching |
| Function | Movement and locomotion | Maintain the flow of food and fluids through the internal organs | Helps in pumping blood flow into and out of the heart. |

Additional Information:
-42% of an average adult male body mass is made up of skeletal muscles and in females, they make up 36% of body mass of an average adult female.
-Muscles not only help in movement and maintaining the posture of the body, but they also help in regulating different organs (like the heart), create heat to warm up the body, and helps in the movement of substances around the body (like the movement of blood from heart and food in the digestive system)
-The striated appearance of skeletal muscles is due to the formation of actin and myosin muscle fibers. Skeletal muscles are well supplied with blood vessels and nerves.
-Cardiac muscles are arranged in bundles of muscle fibers sheets and show involuntary movement as they are regulated by the autonomic part of the nervous system.
-Cardiac muscles are though mainly controlled by the central nervous system (CNS), they can also contract without signals from CNS due to pacemaker cells.
Note: Muscle fatigue is the decrease in the ability of the muscles to perform over time due to a decrease in the force behind the muscles. That overall affects the body by making it weaker. Skeletal muscles fatigue more easily than cardiac or smooth muscles because skeletal muscles are not essential in homeostasis and survival. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle that may cause a threat to life.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




