
Differentiate between transition and transversion.
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: It is a type of base substitution in which a particular nitrogenous base is changed to the other base of the same class. It is another type of base substitution in which a particular base from class converts into a base in the other class.
Complete answer:
Additional information: The transitions emerge essentially more frequently in coding regions because they are more certain than transversions to change the fundamental amino acids that the mutated base codes for, particularly if they seem in the third nucleotide of a codon.
After that, when comparing two genomes, we can use the ratio of transitions to transversions as a test for the presence of coding regions.
Note: Transition and transversion are two types of base substitutions that lead to point mutations. Both are responsible for changing the nitrogenous base of nucleic acid chains. And, both can happen spontaneously or in response to mutagens. A transition is a kind of base substitution that is caused by the conversion of a base to the other base of the same class.
Complete answer:
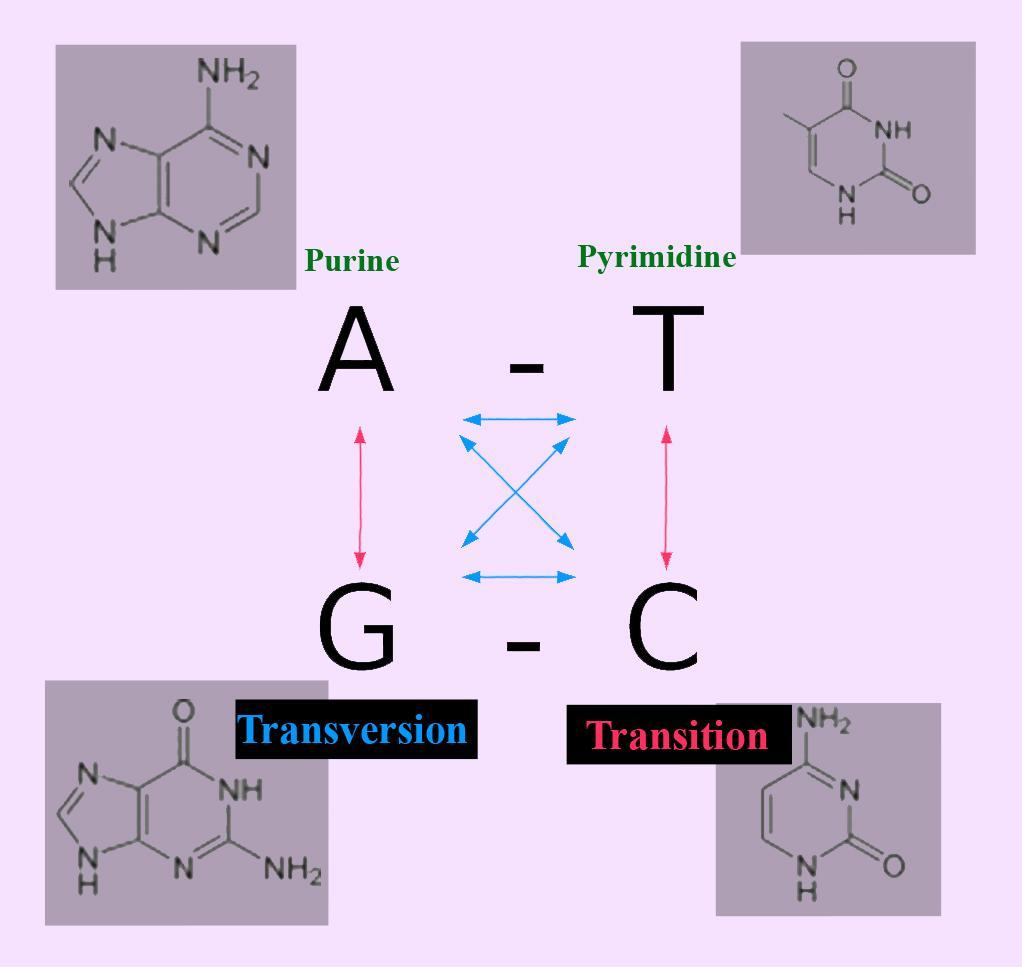
| Transition | Transversion |
| It is the substitution of a purine from another purine base or pyrimidine from another pyrimidine ($C\longleftrightarrow T$ or $A\longleftrightarrow G$). | A transversion is the substitution of a purine from a pyrimidine or pyrimidine from a purine. |
| Basically, this is the most common type of point mutation. | This is less common than transition. |
| There is one possible transition. | There are two possible transversions. |
| Transition is less likely to cause amino acid sequences. So this remains as a silent mutation | A transversion is more likely to cause amino acid sequence changes. So it pronouncedly affects the subsequent protein. |
| It can be observed, when interchanges of bases within single ring structures or within double-ring structures. | Interchange can happen in a single ring structure with a double ring structure or a double ring structure with a single ring structure. |
Additional information: The transitions emerge essentially more frequently in coding regions because they are more certain than transversions to change the fundamental amino acids that the mutated base codes for, particularly if they seem in the third nucleotide of a codon.

After that, when comparing two genomes, we can use the ratio of transitions to transversions as a test for the presence of coding regions.
Note: Transition and transversion are two types of base substitutions that lead to point mutations. Both are responsible for changing the nitrogenous base of nucleic acid chains. And, both can happen spontaneously or in response to mutagens. A transition is a kind of base substitution that is caused by the conversion of a base to the other base of the same class.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




