
How do you differentiate \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\]?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint:Derivatives are defined as the varying rate of a function with respect to an independent variable. We cannot differentiate this directly. First we need to find the value of \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\]. After that we differentiate the obtained answer with respect to ‘x’. we know that \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\], \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\] and using Pythagoras identity we can find the value of \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\].
Complete step by step solution:
Given, \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\]
Let’s put \[\theta = \arctan (x)\]
Then we have \[\sec \left( \theta \right)\]
Now we took \[\theta = \arctan (x)\],
Then we have \[\tan \theta = x\]
This can be rewrite as
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{x}{1}\]
We know that \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\].
Let’s write a right angle triangle and we need to find hypotenuse side
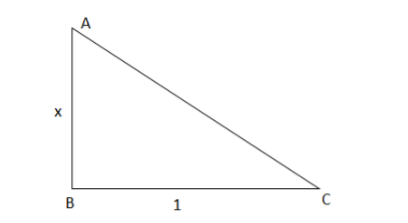
We need hypotenuse, that is AC.
By Pythagoras identity we have
\[\begin{gathered}
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {x^2} + 1 \\
AC = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Thus we have a hypotenuse side.
We know that \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\]
\[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{1}\]
That is we have,
\[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right) = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
Now differentiating with respect to ‘x’
\[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
\[ = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
We know that \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sqrt x ) = \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt x }}\dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}}\] and here we assume \[{x^2} + 1\] as one term ‘x’. Then we have
\[ = \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2} + 1} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{{2x}}{{2\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\]
\[ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\]
Thus the differentiation of \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\].
Note: We know the differentiation of \[{x^n}\] with respect to ‘x’ is \[\dfrac{{d({x^n})}}{{dx}} = n.{x^{n - 1}}\]. We also have different rules in the differentiation. Those are
\[ \bullet \]Linear combination rule: The linearity law is very important to emphasize its nature with alternate notation. Symbolically it is specified as \[h'(x) = af'(x) + bg'(x)\]
\[ \bullet \]Product rule: When a derivative of a product of two function is to be found, then we use product rule that is \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = u \times \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} + v \times
\dfrac{{du}}{{dx}}\].
\[ \bullet \]Chain rule: To find the derivative of composition function or function of a function, we use chain rule. That is \[fog'({x_0}) = [(f'og)({x_0})]g'({x_0})\].
We use these rules depending on the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\]
Let’s put \[\theta = \arctan (x)\]
Then we have \[\sec \left( \theta \right)\]
Now we took \[\theta = \arctan (x)\],
Then we have \[\tan \theta = x\]
This can be rewrite as
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{x}{1}\]
We know that \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\].
Let’s write a right angle triangle and we need to find hypotenuse side

We need hypotenuse, that is AC.
By Pythagoras identity we have
\[\begin{gathered}
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {x^2} + 1 \\
AC = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Thus we have a hypotenuse side.
We know that \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent side}}}}\]
\[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{1}\]
That is we have,
\[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right) = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
Now differentiating with respect to ‘x’
\[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
\[ = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} \]
We know that \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sqrt x ) = \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt x }}\dfrac{{dx}}{{dx}}\] and here we assume \[{x^2} + 1\] as one term ‘x’. Then we have
\[ = \dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2} + 1} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{{2x}}{{2\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\]
\[ = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\]
Thus the differentiation of \[\sec \left( {\arctan (x)} \right)\] is \[\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}\].
Note: We know the differentiation of \[{x^n}\] with respect to ‘x’ is \[\dfrac{{d({x^n})}}{{dx}} = n.{x^{n - 1}}\]. We also have different rules in the differentiation. Those are
\[ \bullet \]Linear combination rule: The linearity law is very important to emphasize its nature with alternate notation. Symbolically it is specified as \[h'(x) = af'(x) + bg'(x)\]
\[ \bullet \]Product rule: When a derivative of a product of two function is to be found, then we use product rule that is \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = u \times \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} + v \times
\dfrac{{du}}{{dx}}\].
\[ \bullet \]Chain rule: To find the derivative of composition function or function of a function, we use chain rule. That is \[fog'({x_0}) = [(f'og)({x_0})]g'({x_0})\].
We use these rules depending on the given problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




