
Dipole moment $N{{F}_{3}}$is smaller than:
(A) $N{{H}_{3}}$
(B) $C{{O}_{2}}$
(C) $B{{F}_{3}}$
(D) $CC{{l}_{4}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The measure of charge distribution within a molecule is known as the Dipole moment of the molecule. The dipole moment is seen in any system where there is a separation of charges.
Complete step by step solution:
-The measure of the polarity of a chemical bond between two atoms in a molecule is known as bond dipole moment.
-Bond dipole moment occurs due to the difference in the electronegativities of the chemically bonded atoms within the molecule. The higher the electronegativity difference between the two atoms, the more will be the ionic character to the bond and vice versa.
-Dipole moment has both magnitudes as well as direction, hence it is a vector quantity.
-The dipole moment is the mathematical product of the total amount of positive charge or negative charge and the distance between the centre of the charge distribution. The dipole moment is represented by a symbol $'\mu '$.
\[\mu =q\times r\]
where $\mu $is the dipole moment
q is the separated charge
r is the distance between them
-We will start predicting the answer to this question by comparing the electronegativity differences between the atoms of the compounds given in the question $N{{F}_{3}}$.
(i) The electronegativity difference between N-H in $N{{H}_{3}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Nitrogen (3.0) – Hydrogen (2.2) = 0.8
(ii) The electronegativity difference between C-O in $C{{O}_{2}}$ and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Oxygen (3.4) - Carbon (2.5) = 0.9
(iii)The electronegativity difference between B-F in $B{{F}_{3}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$ is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Fluorine (3.9) - Boron (2.4) = 1.86
(iv) The electronegativity difference between C-Cl in $CC{{l}_{4}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Chlorine (3.1) - Carbon (2.5) = 0.6
From the above values, we can easily eliminate the options (C) and (D) as they have a larger difference in their electronegativity values.
-Now considering atomic sizes for option A and B,
Fluorine and Hydrogen have comparable atomic sizes (Fluorine 42 pm and Hydrogen at 53 pm), whereas Oxygen and Fluorine have a larger difference (Fluorine 42 pm and Oxygen 60pm). Moreover, the bond distance for N-H and the N-F is 100 pm and 137pm respectively.
-Considering the above parameters, we expect the dipole moment $N{{F}_{3}}$ to be similar or slightly higher than $N{{H}_{3}}$, but we observed the dipole moment value for $N{{H}_{3}}$is 1.46 Debye and for $N{{F}_{3}}$as 0.24. This difference is so because we haven’t taken into consideration the molecular shape.
-Dipole moment is a vector quantity, is directional. Ideally, the net dipole moment is the sum of all the individual bond moments, but for complex molecules like $N{{H}_{3}}$and $N{{F}_{3}}$, the net dipole moment cannot be directly calculated by the vector addition of the bond moments. Apart from the molecular shape, the contribution of the lone pair to the net dipole moment must also be considered.
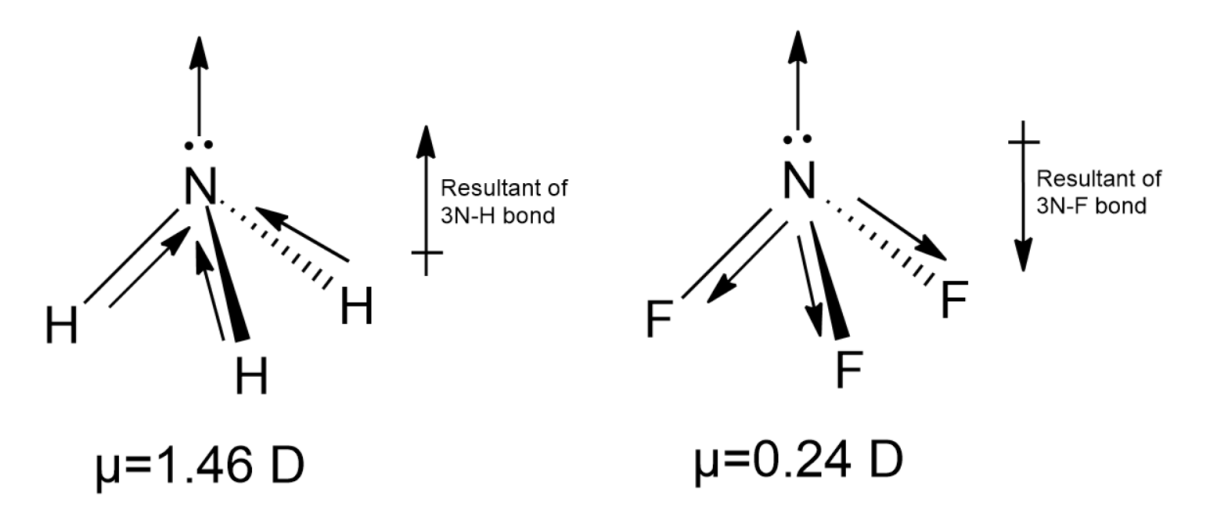
So, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Nitrogen fluoride is colourless, inorganic, and nonflammable gas. It is an extremely strong greenhouse gas. Nitrogen fluoride is used in the plasma etching of silicon wafers and also used in hydrogen fluoride and deuterium fluoride lasers. It is a greenhouse gas with a glocal warming potential greater than carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step solution:
-The measure of the polarity of a chemical bond between two atoms in a molecule is known as bond dipole moment.
-Bond dipole moment occurs due to the difference in the electronegativities of the chemically bonded atoms within the molecule. The higher the electronegativity difference between the two atoms, the more will be the ionic character to the bond and vice versa.
-Dipole moment has both magnitudes as well as direction, hence it is a vector quantity.
-The dipole moment is the mathematical product of the total amount of positive charge or negative charge and the distance between the centre of the charge distribution. The dipole moment is represented by a symbol $'\mu '$.
\[\mu =q\times r\]
where $\mu $is the dipole moment
q is the separated charge
r is the distance between them
-We will start predicting the answer to this question by comparing the electronegativity differences between the atoms of the compounds given in the question $N{{F}_{3}}$.
(i) The electronegativity difference between N-H in $N{{H}_{3}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Nitrogen (3.0) – Hydrogen (2.2) = 0.8
(ii) The electronegativity difference between C-O in $C{{O}_{2}}$ and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Oxygen (3.4) - Carbon (2.5) = 0.9
(iii)The electronegativity difference between B-F in $B{{F}_{3}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$ is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Fluorine (3.9) - Boron (2.4) = 1.86
(iv) The electronegativity difference between C-Cl in $CC{{l}_{4}}$and N-F in $N{{F}_{3}}$is calculated as-
Fluorine (3.9) - Nitrogen (3.0) = 0.9
Chlorine (3.1) - Carbon (2.5) = 0.6
From the above values, we can easily eliminate the options (C) and (D) as they have a larger difference in their electronegativity values.
-Now considering atomic sizes for option A and B,
Fluorine and Hydrogen have comparable atomic sizes (Fluorine 42 pm and Hydrogen at 53 pm), whereas Oxygen and Fluorine have a larger difference (Fluorine 42 pm and Oxygen 60pm). Moreover, the bond distance for N-H and the N-F is 100 pm and 137pm respectively.
-Considering the above parameters, we expect the dipole moment $N{{F}_{3}}$ to be similar or slightly higher than $N{{H}_{3}}$, but we observed the dipole moment value for $N{{H}_{3}}$is 1.46 Debye and for $N{{F}_{3}}$as 0.24. This difference is so because we haven’t taken into consideration the molecular shape.
-Dipole moment is a vector quantity, is directional. Ideally, the net dipole moment is the sum of all the individual bond moments, but for complex molecules like $N{{H}_{3}}$and $N{{F}_{3}}$, the net dipole moment cannot be directly calculated by the vector addition of the bond moments. Apart from the molecular shape, the contribution of the lone pair to the net dipole moment must also be considered.

So, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Nitrogen fluoride is colourless, inorganic, and nonflammable gas. It is an extremely strong greenhouse gas. Nitrogen fluoride is used in the plasma etching of silicon wafers and also used in hydrogen fluoride and deuterium fluoride lasers. It is a greenhouse gas with a glocal warming potential greater than carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




