
Who discovered the golgi apparatus? Describe its structure and function.
Answer
487.8k+ views
Hint: The golgi apparatus is an important cell organelle of the cell, the Golgi is quite close to the nucleus. It's known as a perinuclear body, and it's located near the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins exiting the endoplasmic reticulum are transported to the Golgi for further processing. The cytoplasm contains all of the cell's organelles. It contains many chemicals, nucleic acids, and other things required by the organism.
Complete answer:
In 1898, an Italian surgeon named Camillo Golgi invented the Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi Apparatus's structure: In eukaryotic cells, the Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex, is widely seen. The Golgi complex is distinguished by its distinctive maze-like structure.
The Golgi Apparatus's Functions: The Golgi apparatus' principal job is to:
- Protein and lipids are synthesised by the Golgi apparatus, which is located near the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Moves food ingredients around the cell.
- It's known as the cell's storage.
Camillo Golgi originally reported the existence of the cell organelle currently known as the Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex, or simply "the Golgi" in 1898, when he observed a "internal reticular apparatus" permeated by a form of his chromogenic colouring in nerve cells. It was quickly discovered that the newly discovered cytoplasmic structure was seen in a wide range of cell types.
The actuality of the organelle, on the other hand, was questioned for decades until it was finally confirmed by electron microscopy. In the second part of the twentieth century, the Golgi apparatus was destined to become a focal point of cytology and cell biology study.
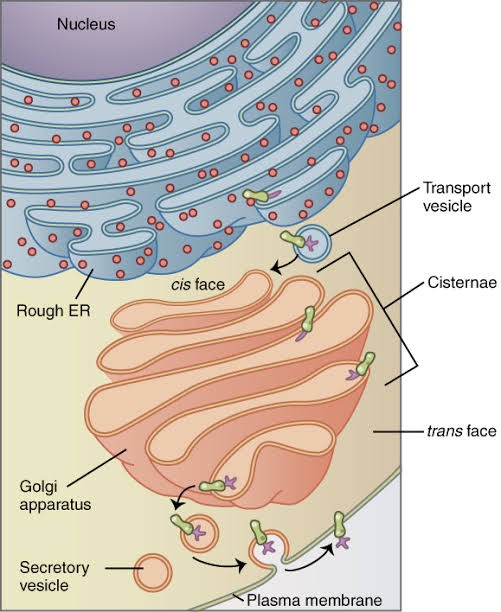
The Golgi apparatus is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed discs known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, often called "dictyosomes") that originate from vesicular clusters that bud off the endoplasmic reticulum in most eukaryotes.
A mammalian cell normally has 40 to 100 cisternae stacks. In most stacks, four to eight cisternae are present; however, some protists have as many as sixty cisternae. The cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans Golgi network (TGN) are two primary networks made up of cisterns divided into cis, medial, and trans compartments (TGN).
Note:-
The Golgi apparatus is a processing site for proteins, lipids, and other big molecules that are exported from the cell to their final destinations. Each cisterna is made up of a flattened disc containing enzymes that aid or change the protein payload passing through it. Its function is storage, modification and packaging of products.
Complete answer:
In 1898, an Italian surgeon named Camillo Golgi invented the Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi Apparatus's structure: In eukaryotic cells, the Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex, is widely seen. The Golgi complex is distinguished by its distinctive maze-like structure.
The Golgi Apparatus's Functions: The Golgi apparatus' principal job is to:
- Protein and lipids are synthesised by the Golgi apparatus, which is located near the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Moves food ingredients around the cell.
- It's known as the cell's storage.

Camillo Golgi originally reported the existence of the cell organelle currently known as the Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex, or simply "the Golgi" in 1898, when he observed a "internal reticular apparatus" permeated by a form of his chromogenic colouring in nerve cells. It was quickly discovered that the newly discovered cytoplasmic structure was seen in a wide range of cell types.
The actuality of the organelle, on the other hand, was questioned for decades until it was finally confirmed by electron microscopy. In the second part of the twentieth century, the Golgi apparatus was destined to become a focal point of cytology and cell biology study.
The Golgi apparatus is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed discs known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, often called "dictyosomes") that originate from vesicular clusters that bud off the endoplasmic reticulum in most eukaryotes.
A mammalian cell normally has 40 to 100 cisternae stacks. In most stacks, four to eight cisternae are present; however, some protists have as many as sixty cisternae. The cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans Golgi network (TGN) are two primary networks made up of cisterns divided into cis, medial, and trans compartments (TGN).
Note:-
The Golgi apparatus is a processing site for proteins, lipids, and other big molecules that are exported from the cell to their final destinations. Each cisterna is made up of a flattened disc containing enzymes that aid or change the protein payload passing through it. Its function is storage, modification and packaging of products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




