
Who discovered the root pressure?
A. Stephen hales
B. Priestley
C. Dixon
D. Renner
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: When a plant is carefully cut close to the base of the stem, the sap oozes from the stump. The fluid comes out forcibly, that pressure is known as root pressure.
Complete answer: Root pressure is a vital significance in plants, for it forces up water against the gravity to the tip of even the tallest plant.
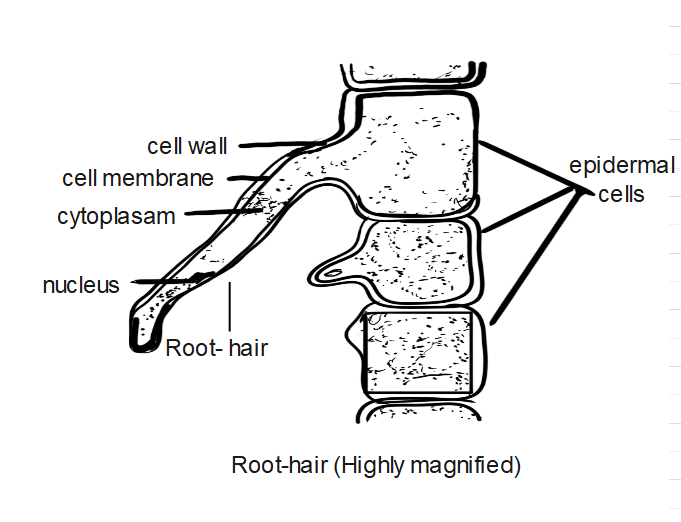
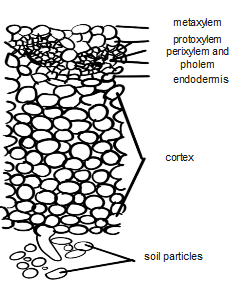
Let us observe a root and a part enlarged to show the root hairs. Now let us know what the pressure means and how it is developed. The water and mineral salts absorbed from the soil by the root hairs, gradually accumulate in the cortex. As a result, the cortical cells become fully turgid. Under this condition, their elastic walls being much stretched exert pressure on the fluid contents and force out a small quantity towards the xylem vessel. Now the cortical cells become flaccid, they again absorb water and become turgid and the same process continues. Thus, an intermittent pumping action goes on in the cortex of the root and this gives rise to a considerable pressure. As a result of this pressure, the water is forced into the xylem vessels through the passage cells of the endodermis and the unthicken areas and pits that the vessels are provided with. Besides, the lignified walls of vessels are also permeable to water. Root pressure is thus explained as the pressure exerted on the liquid contents of the cortical cells of the root under fully turgid conditions forcing the amount of them to the xylem vessels and thru them upwards into the stem up to the height. The gradient of water concentration that presents across the cortex produces a pushing force called root pressure. This root pressure theory was given by Priestley.
Hence, from the above discussion we can conclude that the option-B is the right answer.
Note: There are four different theories for the ascent of sap are cohesion tension theory, root pressure theory, theory of capillarity 4. vital force theory. In root pressure theory, osmotic, electro-osmotic and non-osmotic are three points about the mechanism of root pressure development.
Complete answer: Root pressure is a vital significance in plants, for it forces up water against the gravity to the tip of even the tallest plant.


Let us observe a root and a part enlarged to show the root hairs. Now let us know what the pressure means and how it is developed. The water and mineral salts absorbed from the soil by the root hairs, gradually accumulate in the cortex. As a result, the cortical cells become fully turgid. Under this condition, their elastic walls being much stretched exert pressure on the fluid contents and force out a small quantity towards the xylem vessel. Now the cortical cells become flaccid, they again absorb water and become turgid and the same process continues. Thus, an intermittent pumping action goes on in the cortex of the root and this gives rise to a considerable pressure. As a result of this pressure, the water is forced into the xylem vessels through the passage cells of the endodermis and the unthicken areas and pits that the vessels are provided with. Besides, the lignified walls of vessels are also permeable to water. Root pressure is thus explained as the pressure exerted on the liquid contents of the cortical cells of the root under fully turgid conditions forcing the amount of them to the xylem vessels and thru them upwards into the stem up to the height. The gradient of water concentration that presents across the cortex produces a pushing force called root pressure. This root pressure theory was given by Priestley.
Hence, from the above discussion we can conclude that the option-B is the right answer.
Note: There are four different theories for the ascent of sap are cohesion tension theory, root pressure theory, theory of capillarity 4. vital force theory. In root pressure theory, osmotic, electro-osmotic and non-osmotic are three points about the mechanism of root pressure development.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




