
Discuss the continuity of the function $f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
{{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right),x\ne 0 \\
0,\text{ }x=0 \\
\end{matrix} \right.$ at x=0.
Answer
612k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that if a function f(x) is continuous at a point, then the left hand limit and the right hand limit at that point are equal and are equal to the value of the function at that point. Hence, we have $f\left( x \right)$ is continuous at x= a if $\underset{x\to {{a}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{x\to {{a}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=f\left( a \right)$. Hence find the left hand limit and the right hand limit at x= 0. Verify if the limits are equal or not. Check if the limits are equal and are they equal to the functional value and hence verify whether f(x) is continuous at x =0. Use the fact that $\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,x\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)=0$ and use \[\underset{x\to {{a}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( a-h \right)\] and $\underset{x\to {{a}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( a+h \right)$ and hence find LHL and RHL.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have $f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
{{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right),x\ne 0 \\
0,\text{ }x=0 \\
\end{matrix} \right.$
Now, we have
LHL $=\underset{x\to {{0}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( 0-h \right)$
Hence, we have
LHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( -h \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{\left( -h \right)}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{-1}{h} \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{h}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{-1}{h} \right)$
We know that $\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0$
Hence, we have LHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left( -h \right)\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0\times 0=0$
Now, RHL $=\underset{x\to {{0}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( 0+h \right)$
Hence, we have
RHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( h \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{h}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)$
We know that $\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0$
Hence, we have RHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\times \underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0\times 0=0$
Hence LHL = RHL = 0.
Also f(0) = 0.
Hence, we have
LHL = RHL = f(0).
Hence, the function is continuous at x=0.
Note: Graph of f(x):
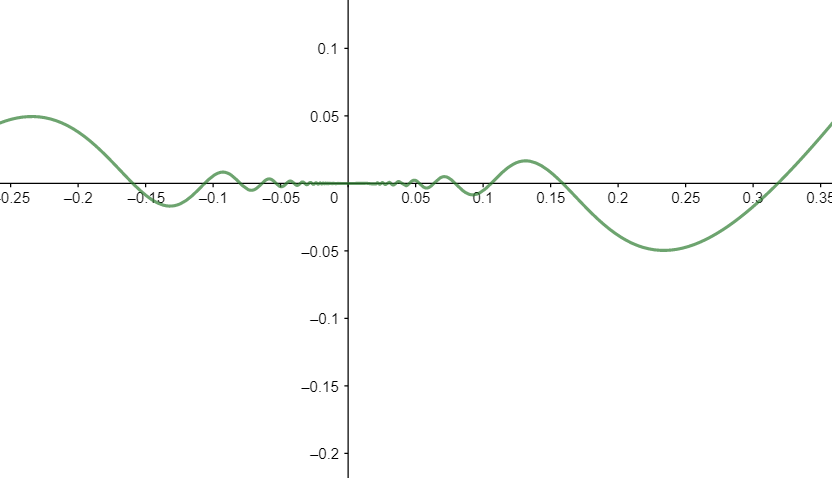
As can be seen from the graph of f(x), f(x) is continuous at x=0.
[2] Alternative solution:
We know that if f(x) is continuous at x =a, then $\forall \varepsilon >0$ there exists $\delta >0$ such that $\left| f\left( x \right)-f\left( a \right) \right|<\varepsilon $, whenever $\left| x-a \right|<\delta $.
We have $f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
{{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right),x\ne 0 \\
0,\text{ }x=0 \\
\end{matrix} \right.$
Claim: f(x) is continuous at x=0.
We have $\left| f\left( x \right)-f\left( a \right) \right|=\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-0 \right|=\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right) \right|$
Since $\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)\le 1$, we have $\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right) \right|\le \left| {{x}^{2}} \right|\le {{\left| x \right|}^{2}}$.
Hence $\forall \varepsilon >0\exists \delta =\sqrt{\varepsilon }>0$ such that whenever $\left| x-0 \right|<\delta \Rightarrow \left| {{x}^{2}} \right|<\varepsilon \Rightarrow \left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-0 \right|<\varepsilon $.
Hence f(x) is continuous at x= 0.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have $f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
{{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right),x\ne 0 \\
0,\text{ }x=0 \\
\end{matrix} \right.$
Now, we have
LHL $=\underset{x\to {{0}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( 0-h \right)$
Hence, we have
LHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( -h \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{\left( -h \right)}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{-1}{h} \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{h}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{-1}{h} \right)$
We know that $\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0$
Hence, we have LHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left( -h \right)\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0\times 0=0$
Now, RHL $=\underset{x\to {{0}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( 0+h \right)$
Hence, we have
RHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( h \right)=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{h}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)$
We know that $\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0$
Hence, we have RHL $=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\times \underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{h} \right)=0\times 0=0$
Hence LHL = RHL = 0.
Also f(0) = 0.
Hence, we have
LHL = RHL = f(0).
Hence, the function is continuous at x=0.
Note: Graph of f(x):

As can be seen from the graph of f(x), f(x) is continuous at x=0.
[2] Alternative solution:
We know that if f(x) is continuous at x =a, then $\forall \varepsilon >0$ there exists $\delta >0$ such that $\left| f\left( x \right)-f\left( a \right) \right|<\varepsilon $, whenever $\left| x-a \right|<\delta $.
We have $f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
{{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right),x\ne 0 \\
0,\text{ }x=0 \\
\end{matrix} \right.$
Claim: f(x) is continuous at x=0.
We have $\left| f\left( x \right)-f\left( a \right) \right|=\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-0 \right|=\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right) \right|$
Since $\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)\le 1$, we have $\left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right) \right|\le \left| {{x}^{2}} \right|\le {{\left| x \right|}^{2}}$.
Hence $\forall \varepsilon >0\exists \delta =\sqrt{\varepsilon }>0$ such that whenever $\left| x-0 \right|<\delta \Rightarrow \left| {{x}^{2}} \right|<\varepsilon \Rightarrow \left| {{x}^{2}}\sin \left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)-0 \right|<\varepsilon $.
Hence f(x) is continuous at x= 0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




