
Discuss the necessity of radius of gyration. Define it. On what factors does it depend and it does not depend? Can you locate a similarity between the centre of mass and radius of gyration? What can you infer if a uniform ring and a uniform disc have the same radius of gyration?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: The radius of gyration is occasionally used to express a body's moment of inertia about an axis. The radius of gyration can be defined as the imaginary distance from the centroid at which the cross-sectional area is believed to be centred at a point in order to achieve the same moment of inertia. The letter \[k\] stands for it.
Complete step by step answer:
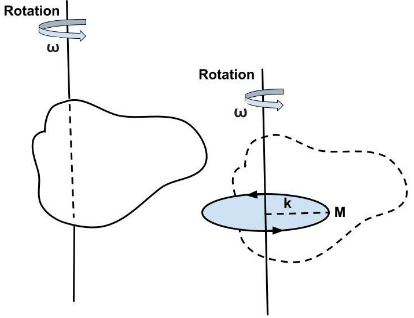
Definition: The radius of gyration of a rotating body about an axis is defined as the distance between the axis of rotation and the point at which the full mass of the body can be assumed to be concentrated in order to produce the same moment of inertia as the body about the given axis. The moment of inertia \[\left( {MI} \right)\] of a body along a given rotation axis is determined by:
(I) It’s mass and
(ii) It’s mass distribution about the rotation axis.
By defining the \[\left( {MI} \right)\] as the product of the mass \[\left( M \right)\] and the square of a specific distance \[\left( k \right)\]from the axis of rotation, these two components can be separated. This distance is known as the gyration radius, and it is defined as follows. Thus,
$I = \sum {{m_i}} r_i^2 = M{k^2} \\
\Rightarrow k = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{M}} \\ $
Physical significance: If \[I\] is less, i.e., if the mass is distributed close to the axis, the radius of gyration is less; if \[I\] is larger, i.e., if the mass is dispersed further from the axis, the radius of gyration is more. As a result, it gives a notion of the mass distribution around the axis of rotation. The centre of mass \[\left( {CM} \right)\] coordinates identify a location where the total mass $M$ of a system of particles or a rigid body can be thought to be concentrated to the point that the acceleration of this point mass obeys Newton's second law of motion, viz,
${\overrightarrow F _{net}} = M{\overrightarrow a _{CM}}$
where ${\overrightarrow F _{net}}$ is the sum of all external forces acting on the body or individual particles of a particle system.
Similarly, the radius of gyration locates a point away from the axis of rotation where the total mass M can be thought to be concentrated, and the angular acceleration of that point mass about the axis of rotation obeys the relation,
${\overrightarrow \tau _{net}} = M\overrightarrow \alpha $
where \[{\overrightarrow \tau _{net}}\] is the sum of all external torques operating on the body or individual particles in a system.
A thin ring of radius \[{R_r}\] gyrates about its transverse symmetry axis with a radius of gyration of
\[{k_r} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_{CM}}}}{{{M_d}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_r}= \sqrt {R_r^2} = {R_r}\]
A thin disc of radius \[{R_d}\] gyrates about its transverse symmetry axis with a radius of gyration of
${k_d} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_{CM}}}}{{{M_d}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_d} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {{M_d}R_d^2} }}{2}}}{{{M_d}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_d} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}{R_d}$
Given, ${k_r} = {k_d}$.
${R_r} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_d}}}$ or, equivalently, ${R_d} = \sqrt 2 {R_r}$
Note: The radius of gyration is a measurement that is used to examine how different structural geometries would behave when compressed along an axis. It's used to anticipate buckling in compression members and beams.
Complete step by step answer:
Definition: The radius of gyration of a rotating body about an axis is defined as the distance between the axis of rotation and the point at which the full mass of the body can be assumed to be concentrated in order to produce the same moment of inertia as the body about the given axis. The moment of inertia \[\left( {MI} \right)\] of a body along a given rotation axis is determined by:
(I) It’s mass and
(ii) It’s mass distribution about the rotation axis.
By defining the \[\left( {MI} \right)\] as the product of the mass \[\left( M \right)\] and the square of a specific distance \[\left( k \right)\]from the axis of rotation, these two components can be separated. This distance is known as the gyration radius, and it is defined as follows. Thus,
$I = \sum {{m_i}} r_i^2 = M{k^2} \\
\Rightarrow k = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{M}} \\ $
Physical significance: If \[I\] is less, i.e., if the mass is distributed close to the axis, the radius of gyration is less; if \[I\] is larger, i.e., if the mass is dispersed further from the axis, the radius of gyration is more. As a result, it gives a notion of the mass distribution around the axis of rotation. The centre of mass \[\left( {CM} \right)\] coordinates identify a location where the total mass $M$ of a system of particles or a rigid body can be thought to be concentrated to the point that the acceleration of this point mass obeys Newton's second law of motion, viz,
${\overrightarrow F _{net}} = M{\overrightarrow a _{CM}}$
where ${\overrightarrow F _{net}}$ is the sum of all external forces acting on the body or individual particles of a particle system.
Similarly, the radius of gyration locates a point away from the axis of rotation where the total mass M can be thought to be concentrated, and the angular acceleration of that point mass about the axis of rotation obeys the relation,
${\overrightarrow \tau _{net}} = M\overrightarrow \alpha $
where \[{\overrightarrow \tau _{net}}\] is the sum of all external torques operating on the body or individual particles in a system.
A thin ring of radius \[{R_r}\] gyrates about its transverse symmetry axis with a radius of gyration of
\[{k_r} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_{CM}}}}{{{M_d}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_r}= \sqrt {R_r^2} = {R_r}\]
A thin disc of radius \[{R_d}\] gyrates about its transverse symmetry axis with a radius of gyration of
${k_d} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_{CM}}}}{{{M_d}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_d} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt {{M_d}R_d^2} }}{2}}}{{{M_d}}} \\
\Rightarrow {k_d} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}{R_d}$
Given, ${k_r} = {k_d}$.
${R_r} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_d}}}$ or, equivalently, ${R_d} = \sqrt 2 {R_r}$

Note: The radius of gyration is a measurement that is used to examine how different structural geometries would behave when compressed along an axis. It's used to anticipate buckling in compression members and beams.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




