
Discuss the optical isomerism in tartaric acid.
Answer
526.9k+ views
Hint: Tartaric acid is an organic compound with formula${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{6}}$. Dissymmetric molecules show optical activity. The compounds which change the direction of light when a plane of polarised light is passed through them are optically active.
Complete step by step solution: As we know, optical isomers are compounds having the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial arrangements and will have non-superimposable mirror images. These non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
Optical activity of a molecule does not depend on its chirality. If the molecule is dissymmetric and has at least one non-superimposable mirror image, it exhibits optical activity.
The chiral centre is an atom to which 4 different groups of atoms are bonded so that they can form a non-superimposable mirror image.
To draw the optical isomers of tartaric acid, we need to draw its structure first. It has two chiral centres.
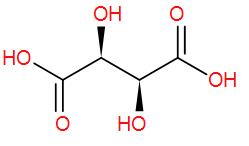
To understand the optical activity better, we can draw its structure as-
Or we can draw it in the sawhorse structure-
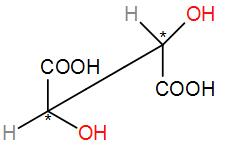 The two carbons with the ‘*’ marks are the chiral carbons.
The two carbons with the ‘*’ marks are the chiral carbons.
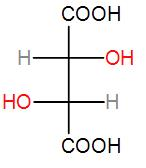
The above compound is optically active as it has no elements of symmetry like\[\sigma ,i,{{S}_{n}}or{{C}_{n}}\]. The compound is asymmetric with two chiral centres. It has an enantiomer which is-
 and can be drawn in sawhorse form as-
and can be drawn in sawhorse form as-
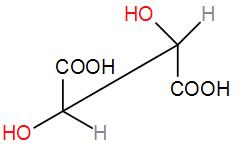
As we can see the above two isomers are mirror images of each other and are known as enantiomers. These are the 2 optically active isomers of tartaric acid. The first one is L-tartaric acid i.e. rotates the plane of polarised light towards the right side and the next one is R-tartaric acid i.e. rotates the plane of polarised light towards the left side.
Besides these enantiomers, tartaric acid also has an optical isomer which has a centre of symmetry although it has two chiral centres. It is optically inactive and is called meso-tartaric acid.
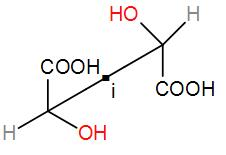
Hence, tartaric acid has 3 optical isomers out of which two are optically active, enantiomers and the other is optically inactive, meso compound.
Note: It is important to remember here that optical activity does not depend on the chirality of a molecule. As we can see here, tartaric acid has 2 chiral centres yet it has an optically inactive isomer.
It is also important to remember that meso compounds are also optical isomers, but they contain a plane of symmetry. Therefore, all molecules irrespective of their chirality exhibit optical activity when they are not superimposable on their mirror images.
Complete step by step solution: As we know, optical isomers are compounds having the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial arrangements and will have non-superimposable mirror images. These non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
Optical activity of a molecule does not depend on its chirality. If the molecule is dissymmetric and has at least one non-superimposable mirror image, it exhibits optical activity.
The chiral centre is an atom to which 4 different groups of atoms are bonded so that they can form a non-superimposable mirror image.
To draw the optical isomers of tartaric acid, we need to draw its structure first. It has two chiral centres.

To understand the optical activity better, we can draw its structure as-
Or we can draw it in the sawhorse structure-


The above compound is optically active as it has no elements of symmetry like\[\sigma ,i,{{S}_{n}}or{{C}_{n}}\]. The compound is asymmetric with two chiral centres. It has an enantiomer which is-


As we can see the above two isomers are mirror images of each other and are known as enantiomers. These are the 2 optically active isomers of tartaric acid. The first one is L-tartaric acid i.e. rotates the plane of polarised light towards the right side and the next one is R-tartaric acid i.e. rotates the plane of polarised light towards the left side.
Besides these enantiomers, tartaric acid also has an optical isomer which has a centre of symmetry although it has two chiral centres. It is optically inactive and is called meso-tartaric acid.

Hence, tartaric acid has 3 optical isomers out of which two are optically active, enantiomers and the other is optically inactive, meso compound.
Note: It is important to remember here that optical activity does not depend on the chirality of a molecule. As we can see here, tartaric acid has 2 chiral centres yet it has an optically inactive isomer.
It is also important to remember that meso compounds are also optical isomers, but they contain a plane of symmetry. Therefore, all molecules irrespective of their chirality exhibit optical activity when they are not superimposable on their mirror images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




