
Distinguish between apocarpous and syncarpous ovary.
Answer
522.7k+ views
Hint: Ovaries are the structure present in flowers that produce ovum. These are of various types that depend on the structure of carpels, their position within the flower, etc.
Complete Answer:
Additional Information:
- A carpel is the female reproductive part of the flower, interpreted as modified leaves that bear structures called ovules, inside which the egg cells ultimately form and are composed of the ovary, style, and stigma.
- In a pistil, there exists one carpel, with its ovary, style and stigma or several carpels may be joined together with a single ovary, the whole forming a single unit.
- Many flowers possess carpels according to their above definition, but some flowers do not possess carpels according to the definition because in these flowers the ovule or ovules are enclosed and borne directly on the shoot apex.
- If a single carpel is present in the gynoecium it is called a monocarpous ovary.
Note:
- The word gynoecium is derived from the words gyne, which means woman, and Oikos which means house in ancient Greek. For the female parts of a flower that produces ovules a collective term gymnosperm is most commonly used. These ovules finally get developed into the fruit and the seeds.
- The innermost whorl of a flower is the gynoecium. The gynoecium consists of one or more pistils and is typically surrounded by the stamens which are pollen-producing male reproductive organs. They are collectively called the androecium.
- A syncarpous gynoecium sometimes appears very much similar to a syncarpous gynoecium.
Complete Answer:
| Sl.No | Apocarpous ovary | Syncarpous ovary |
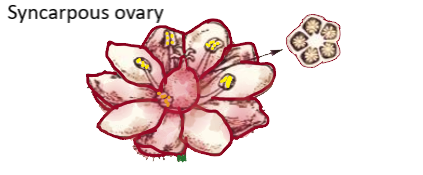
| 1. | More than one carpel is present in the flowers with an apocarpous ovary, but these carpels are distinct i.e separate or unfused. | More than one carpel is also present in the flowers with a syncarpous ovary, but these carpels are fused. |
| 2. | It forms an aggregate of fruits | It forms only one fruit with one or many seeds |
| 3. | For example, flowers of lotus, rose, buttercup, strawberry, etc. | For example, flowers of tomato, mustard, coconut, mango, etc. |
| 4. | 
| 
|
Additional Information:
- A carpel is the female reproductive part of the flower, interpreted as modified leaves that bear structures called ovules, inside which the egg cells ultimately form and are composed of the ovary, style, and stigma.
- In a pistil, there exists one carpel, with its ovary, style and stigma or several carpels may be joined together with a single ovary, the whole forming a single unit.
- Many flowers possess carpels according to their above definition, but some flowers do not possess carpels according to the definition because in these flowers the ovule or ovules are enclosed and borne directly on the shoot apex.
- If a single carpel is present in the gynoecium it is called a monocarpous ovary.
Note:
- The word gynoecium is derived from the words gyne, which means woman, and Oikos which means house in ancient Greek. For the female parts of a flower that produces ovules a collective term gymnosperm is most commonly used. These ovules finally get developed into the fruit and the seeds.
- The innermost whorl of a flower is the gynoecium. The gynoecium consists of one or more pistils and is typically surrounded by the stamens which are pollen-producing male reproductive organs. They are collectively called the androecium.
- A syncarpous gynoecium sometimes appears very much similar to a syncarpous gynoecium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




