
Distinguish between static friction, limiting friction and kinetic friction. How do they vary with the applied force? Explain by diagram.
Answer
530.2k+ views
Hint – In this question, using the idea that when a body is not in motion and is at rest, static-friction allows the body to hold its position when an external force is applied to it. Limiting friction can be viewed as a threshold friction used to avoid motion when an external force is applied, kinetic friction comes into play when the external force has reached the limiting friction value, the friction now applied is kinetic friction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
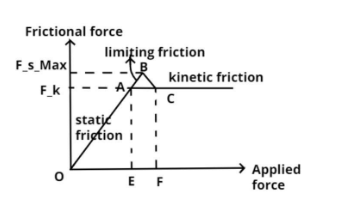
Static friction
Static friction is a self-adjusting force because it comes into play when the body is lying over the surface of another body without any motion.
So from point O to A it is called static friction.
Limiting friction
If we have not applied any force on a body to move the body, the frictional force also becomes zero. If we start applying force, with the applied force, the frictional force also starts increasing. This happens until the applied force is less than the limiting frictional force.
When that body overcomes the force of static friction, the maximum value of static friction is reached, which is known as limiting friction.
So, we increase the force from point E till point F.
As shown in the figure the maximum value of static friction is ${\left( {{F_s}} \right)_{\max }}$ at point B which is called as limiting friction of the body to overcome the force of static friction.
So from point A to B it is called as limiting friction.
Kinetic friction
After the limiting friction, the frictional force is not going to increase further. At this stage, the object moves overcoming the frictional force which is at a constant value. This is called kinetic friction.
As shown in the figure after the limiting friction the frictional force is constant when we increase the applied force known as Kinetic friction denoted by ${F_k}$.
So to overcome this limiting friction kinetic friction comes into play from point B to point C thereafter it is constant.
So this is the required answer.
Note – In the graphical representation region OE is the region where the object is stationary holding its current position and the static friction is acting upon it, the region EF is where external force has been applied and the friction is opposing the change of state, after F the object is in motion and now kinetic friction is acting upon the object.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Static friction
Static friction is a self-adjusting force because it comes into play when the body is lying over the surface of another body without any motion.
So from point O to A it is called static friction.
Limiting friction
If we have not applied any force on a body to move the body, the frictional force also becomes zero. If we start applying force, with the applied force, the frictional force also starts increasing. This happens until the applied force is less than the limiting frictional force.
When that body overcomes the force of static friction, the maximum value of static friction is reached, which is known as limiting friction.
So, we increase the force from point E till point F.
As shown in the figure the maximum value of static friction is ${\left( {{F_s}} \right)_{\max }}$ at point B which is called as limiting friction of the body to overcome the force of static friction.
So from point A to B it is called as limiting friction.
Kinetic friction
After the limiting friction, the frictional force is not going to increase further. At this stage, the object moves overcoming the frictional force which is at a constant value. This is called kinetic friction.
As shown in the figure after the limiting friction the frictional force is constant when we increase the applied force known as Kinetic friction denoted by ${F_k}$.
So to overcome this limiting friction kinetic friction comes into play from point B to point C thereafter it is constant.
So this is the required answer.
Note – In the graphical representation region OE is the region where the object is stationary holding its current position and the static friction is acting upon it, the region EF is where external force has been applied and the friction is opposing the change of state, after F the object is in motion and now kinetic friction is acting upon the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




