
DNA contains the sugar
A. Deoxyribose
B. Ribose
C. D-Fructose
D. D-glucose
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: DNA is the nucleic acid which contains all the information and instructions for the proteins constituting in the cell. DNA is responsible for all the genetic information for every living and non living cell of humans, animals, plants and microorganisms.
Complete step by step answer:
DNA is the short form of deoxyribonucleic acid. It is made of nucleotides present in every cell of living organisms. It contains the genetic blueprint of the main building block of the cell.
The nucleotide consists of phosphate, sugar and nitrogen base. There are four types of nitrogen bases present on the two strands of DNA named as adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The phosphate group is the linkers between the two strands of the DNA. The sugar is the deoxyribose sugar.
The deoxyribose found in DNA is a different type of sugar which lacks in one oxygen atom. Thus due to the presence of one less oxygen the sugar is named as deoxy. This makes the enzymes easier to distinguish between DNA and RNA.
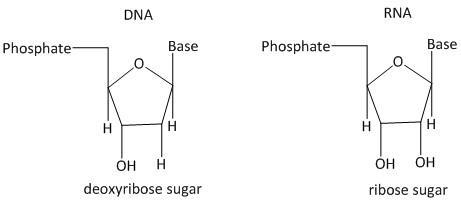
The ribose sugar is found in RNA. It is a simple sugar molecule with molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_5}\]. It is a form of sugar molecule and has a single ring pentose structure.
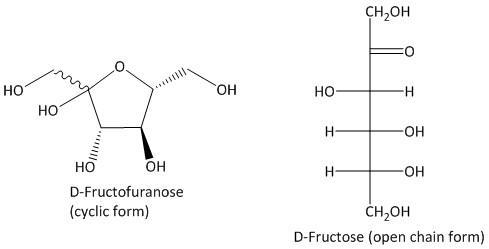
D-Fructose is a monosaccharide sugar which has a ketone functional group. The fructose is derived from cane sugars and sugar beets. The structural analysis suggests that it has a D-fructofuranose structure in cyclic form and has a ketone group in open chain form.
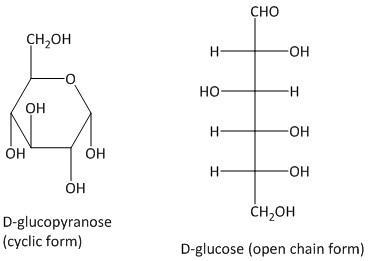
D-glucose is a single sugar with the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. It has a D-glucopyranose structure in cyclic form and contains an aldehyde functional group in open chain form.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
DNA carries all the hereditary information from one age to the next age. The DNA replication involves three steps namely initiation, elongation and termination. The nitrogen bases are coupled as A-T and G-C connected by the phosphate and sugar linkages.
Complete step by step answer:
DNA is the short form of deoxyribonucleic acid. It is made of nucleotides present in every cell of living organisms. It contains the genetic blueprint of the main building block of the cell.
The nucleotide consists of phosphate, sugar and nitrogen base. There are four types of nitrogen bases present on the two strands of DNA named as adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The phosphate group is the linkers between the two strands of the DNA. The sugar is the deoxyribose sugar.
The deoxyribose found in DNA is a different type of sugar which lacks in one oxygen atom. Thus due to the presence of one less oxygen the sugar is named as deoxy. This makes the enzymes easier to distinguish between DNA and RNA.

The ribose sugar is found in RNA. It is a simple sugar molecule with molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{10}}{O_5}\]. It is a form of sugar molecule and has a single ring pentose structure.
D-Fructose is a monosaccharide sugar which has a ketone functional group. The fructose is derived from cane sugars and sugar beets. The structural analysis suggests that it has a D-fructofuranose structure in cyclic form and has a ketone group in open chain form.

D-glucose is a single sugar with the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. It has a D-glucopyranose structure in cyclic form and contains an aldehyde functional group in open chain form.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
DNA carries all the hereditary information from one age to the next age. The DNA replication involves three steps namely initiation, elongation and termination. The nitrogen bases are coupled as A-T and G-C connected by the phosphate and sugar linkages.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




