
DNA of Escherichia coli is
(a) dsDNA and circular
(b) dsDNA and linear
(c) dsDNA and linear
(d) ssDNA and circular
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Escherichia coli is called in short as E.coli, are bacteria commonly found in the intestines of animals and get released to the environment, food, and water bodies. It consists of a circular plasmid in DNA
Complete step by step answer:
The DNA of E.coli is double- stranded(dsDNA) and circular. The normal structure of DNA is in double- stranded form. In favourable conditions, E.coli only needs 20 minutes to double its number by replication, which makes is it the most broadly studied prokaryotic organism and applied in different fields of biotechnology and recombinant technology, where it is used as the host organism for most of the work with recombinant DNA.
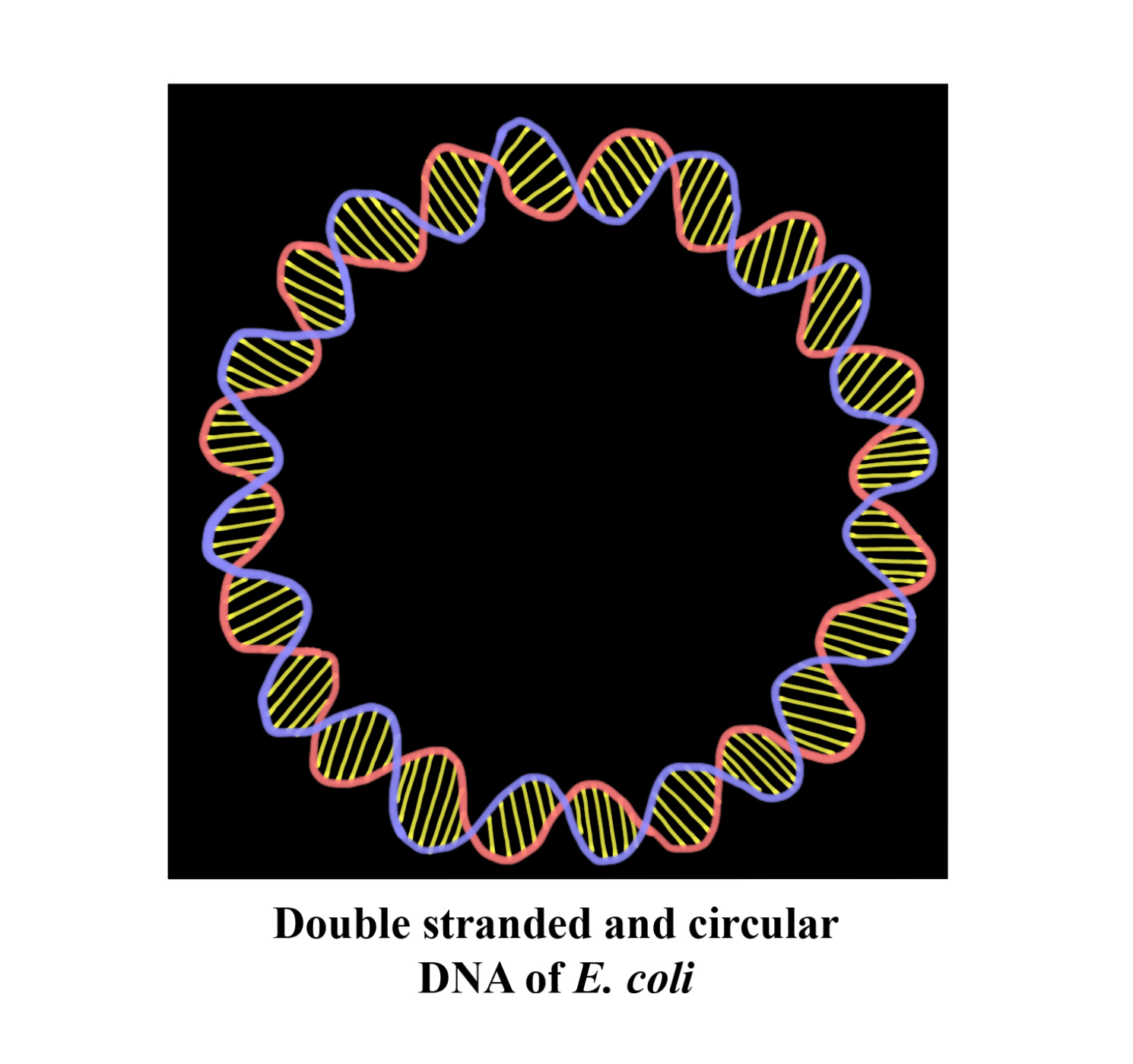
So, the correct answer is ‘dsDNA and circular’.
Additional information:
- E Coli is a facultative anaerobic bacteria of the genus Escherichia and has a rod- shaped structure. They are also coliform, gram- negative bacteria which is abundantly found in the gut of warm- blooded organisms.
- A majority of the strains of E.coli are non- virulent and do not harm humans, but some distinct variants of strains such as EPEC are known to cause gastrointestinal diseases and food spoilage.
- Most of the harmless strains form a symbiotic relationship with humans and constitute the normal microbiota of the intestine and helps humans to form vitamin k2 which helps in the clotting of blood and inhibit the growth of other harmful bacteria in the intestine.
Note:
- Diseases like cholecystitis, traveller’s diarrhoea, neonatal meningitis, pneumonia, and bacteremia are caused by harmful E.coli strains. These strains get released into the environment through faecal matter and spread to a healthy person through contaminated water.
- E Coli bacteria are known for their ability to transfer DNA by conjugation and transduction, which made them one of the most used organisms in the field of recombinant technology and genetic manipulation.
- E.coli is a gram- negative bacteria and can be identified using gram staining which involves a primary stain which is crystal violet, iodide, ethanol as a decolourizer, and a counterstain - Safranin.
Complete step by step answer:
The DNA of E.coli is double- stranded(dsDNA) and circular. The normal structure of DNA is in double- stranded form. In favourable conditions, E.coli only needs 20 minutes to double its number by replication, which makes is it the most broadly studied prokaryotic organism and applied in different fields of biotechnology and recombinant technology, where it is used as the host organism for most of the work with recombinant DNA.

So, the correct answer is ‘dsDNA and circular’.
Additional information:
- E Coli is a facultative anaerobic bacteria of the genus Escherichia and has a rod- shaped structure. They are also coliform, gram- negative bacteria which is abundantly found in the gut of warm- blooded organisms.
- A majority of the strains of E.coli are non- virulent and do not harm humans, but some distinct variants of strains such as EPEC are known to cause gastrointestinal diseases and food spoilage.
- Most of the harmless strains form a symbiotic relationship with humans and constitute the normal microbiota of the intestine and helps humans to form vitamin k2 which helps in the clotting of blood and inhibit the growth of other harmful bacteria in the intestine.
Note:
- Diseases like cholecystitis, traveller’s diarrhoea, neonatal meningitis, pneumonia, and bacteremia are caused by harmful E.coli strains. These strains get released into the environment through faecal matter and spread to a healthy person through contaminated water.
- E Coli bacteria are known for their ability to transfer DNA by conjugation and transduction, which made them one of the most used organisms in the field of recombinant technology and genetic manipulation.
- E.coli is a gram- negative bacteria and can be identified using gram staining which involves a primary stain which is crystal violet, iodide, ethanol as a decolourizer, and a counterstain - Safranin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




