
Why does a food chain consist of only three to four steps?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web whose first link is producer organisms and the last link is apex predator species, detritivores or decomposer species. A food chain differs from a food web. In a food web, the network of different animals' feeding relations are aggregated whereas the food chain follows a direct, linear pathway of one animal at a time. Natural interconnections between different food chains constitute a food web.
Complete answer:
The food chain is basically an energy source diagram showing the linear flow of energy through the trophic levels. The food chain begins with a producer, like a green plant, which is eaten by a primary consumer, a snail, for example. The primary consumer may be eaten by a secondary consumer, such as a frog, which in turn may be consumed by a tertiary consumer, like a snake. The primary producers, otherwise known as autotrophs, utilize either solar energy or inorganic chemical compounds to create complex organic compounds. Species at higher trophic levels cannot channel solar energy for their use and so must consume either producers or other life that itself consumes the producers. Decomposers are organisms that feed on dead animals and break down the organic compounds into simple nutrients which are eventually returned to the soil. These simple nutrients are utilised by plants to create organic compounds.
The length of a food chain is a continuous variable which provides a measure of the passage of energy and is important because the amount of energy transferred is inversely proportional to the trophic level. In general, only ten percent of the total energy at one trophic level is passed to the next, as the remainder is used in metabolic processes. No more than five trophic levels usually exist in a food chain. Humans will be able to receive more energy by going back a level in the food chain and consuming the food before. For instance, more energy per pound is obtained by consuming a salad than an animal which ate lettuce. However, this is not practical in all cases. For example, humans do not have the ability to directly digest grass or the nutrients from wild plants but can naturally obtain them by consuming the meat from deer, antelopes, or other grass-eating animals. A food chain’s length is limited to just 3 or 4 steps due to the decrease of energy along the levels downward, i.e., the energy added to the biomass of each trophic level is significantly lower than the one preceding it. This loss of energy occurs as a result of material wastage from subsequent trophic levels along with the maintenance of various life processes. Therefore, shorter the food chain, more is the energy available for the final consumer. At each level of the food chain, the amount of energy transferred is less whereby the biomass gets smaller.
Note:
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species since the removal of even one element can result in the extinction of species in some cases. A shorter food chain is considerably more efficient as less amount of energy is lost. Humans, as dominant consumers, affect food webs through agriculture, pollution, habitat destruction, overfishing, hunting, the increasing demand for food and shelter along with population growth and its consequent effect on the soil and aquatic ecosystems.
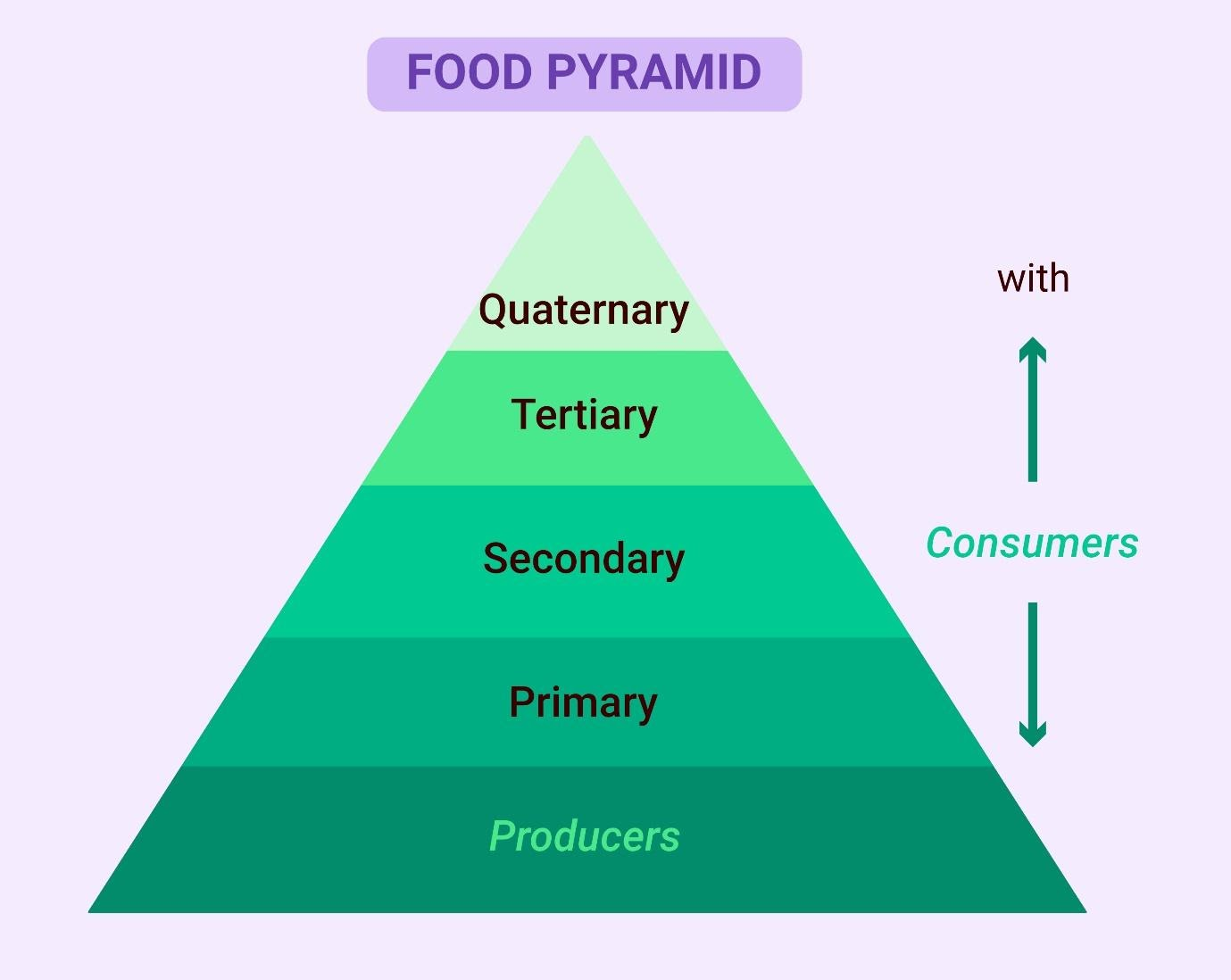
Figure: Food Pyramid
Complete answer:
The food chain is basically an energy source diagram showing the linear flow of energy through the trophic levels. The food chain begins with a producer, like a green plant, which is eaten by a primary consumer, a snail, for example. The primary consumer may be eaten by a secondary consumer, such as a frog, which in turn may be consumed by a tertiary consumer, like a snake. The primary producers, otherwise known as autotrophs, utilize either solar energy or inorganic chemical compounds to create complex organic compounds. Species at higher trophic levels cannot channel solar energy for their use and so must consume either producers or other life that itself consumes the producers. Decomposers are organisms that feed on dead animals and break down the organic compounds into simple nutrients which are eventually returned to the soil. These simple nutrients are utilised by plants to create organic compounds.
The length of a food chain is a continuous variable which provides a measure of the passage of energy and is important because the amount of energy transferred is inversely proportional to the trophic level. In general, only ten percent of the total energy at one trophic level is passed to the next, as the remainder is used in metabolic processes. No more than five trophic levels usually exist in a food chain. Humans will be able to receive more energy by going back a level in the food chain and consuming the food before. For instance, more energy per pound is obtained by consuming a salad than an animal which ate lettuce. However, this is not practical in all cases. For example, humans do not have the ability to directly digest grass or the nutrients from wild plants but can naturally obtain them by consuming the meat from deer, antelopes, or other grass-eating animals. A food chain’s length is limited to just 3 or 4 steps due to the decrease of energy along the levels downward, i.e., the energy added to the biomass of each trophic level is significantly lower than the one preceding it. This loss of energy occurs as a result of material wastage from subsequent trophic levels along with the maintenance of various life processes. Therefore, shorter the food chain, more is the energy available for the final consumer. At each level of the food chain, the amount of energy transferred is less whereby the biomass gets smaller.
Note:
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species since the removal of even one element can result in the extinction of species in some cases. A shorter food chain is considerably more efficient as less amount of energy is lost. Humans, as dominant consumers, affect food webs through agriculture, pollution, habitat destruction, overfishing, hunting, the increasing demand for food and shelter along with population growth and its consequent effect on the soil and aquatic ecosystems.

Figure: Food Pyramid
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




