
How does a Schiff reagent react with an aldehyde?
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: Schiff’s reagent is used for the detection of an aldehyde group in a compound. Schiff’s test can be used to differentiate between an aldehyde and ketone. Schiff’s reagent is an acidic solution of fuchsin. The final product formed is a magenta colour adduct.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
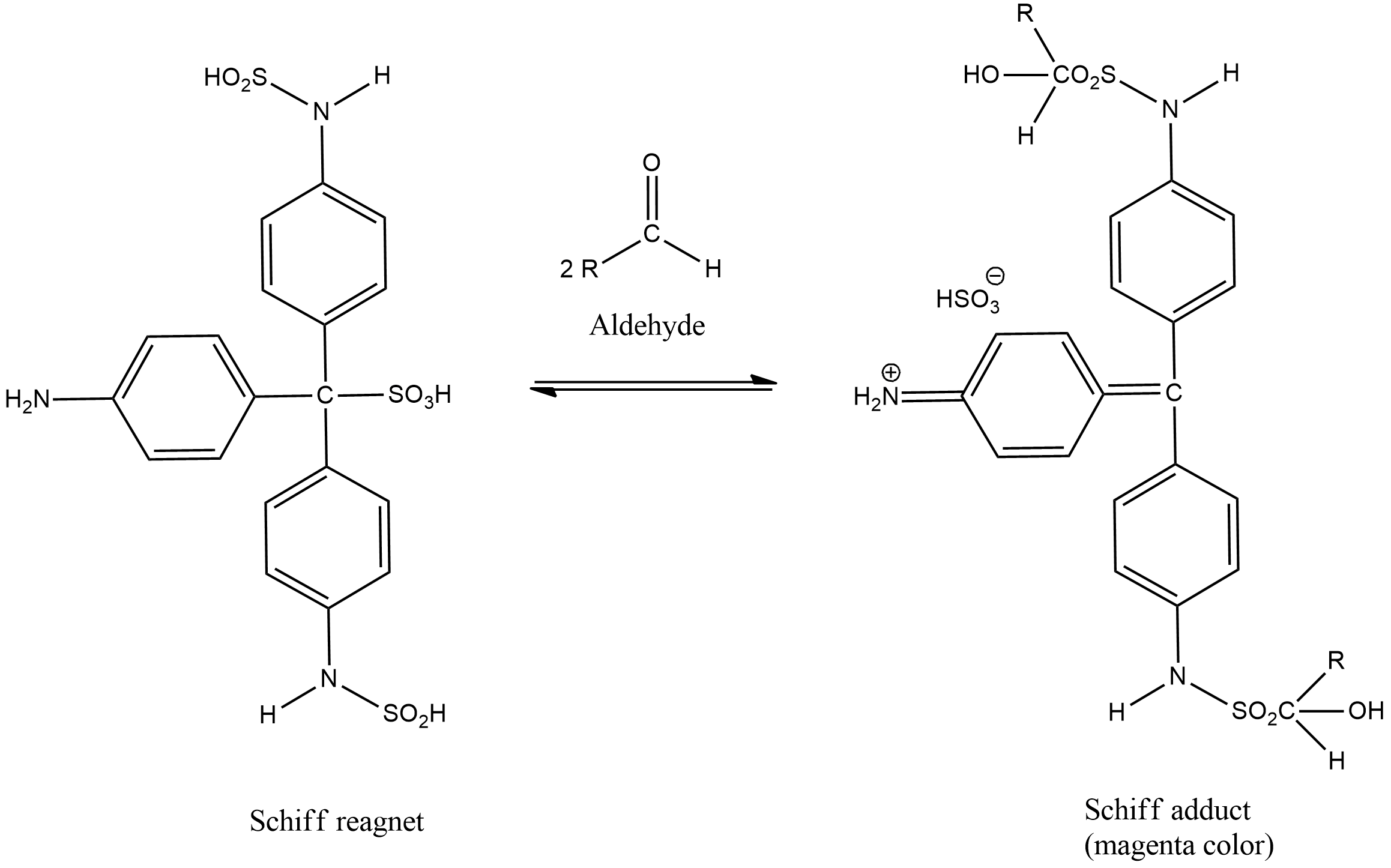
Schiff’s reagent is an acidic solution of fuchsin decolorized by Sulphur dioxide or potassium metabisulphite. It is used for checking the presence of aldehyde in an analyte. It can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. Schiff’s reagent is prepared by passing Sulphur dioxide into a solution of the dye fuchsin.
In the qualitative test for aldehydes, the unknown sample is added to the decolorized Schiff reagent. The solution becomes colorless due to the formation of an additional product. If the sample contains aldehyde then it will react with Schiff reagent which results in the development of a magenta colour. The coloration is due to the formation of complex compounds. Aldehydes abstract sulfurous acid from the Schiff’s reagent and restore the magenta colour.
Mechanism of Schiff’s test:
The bisulfite and the pararosaniline react together to form a decolorized adduct. This adduct has a central carbon which is sulfonated. Now the free and uncharged amine groups belong to the aromatic ring that reacts with the aldehyde group to form an aldimine. This aldimine group is a very good electrophile and thus it undergoes further reaction with the bisulfite ion. Finally a bisulfite adduct is formed which is magenta in colour.
Note:
Other tests for the detection of aldehyde are sodium bisulfite test, Fehling’s test, Tollen’s etc. The solution becomes colorless due to the formula of an additional product. Sometimes ketones also give a pink coloration when Schiff’s reagent is added to it but this coloration is not a positive test.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Schiff’s reagent is an acidic solution of fuchsin decolorized by Sulphur dioxide or potassium metabisulphite. It is used for checking the presence of aldehyde in an analyte. It can be used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. Schiff’s reagent is prepared by passing Sulphur dioxide into a solution of the dye fuchsin.
In the qualitative test for aldehydes, the unknown sample is added to the decolorized Schiff reagent. The solution becomes colorless due to the formation of an additional product. If the sample contains aldehyde then it will react with Schiff reagent which results in the development of a magenta colour. The coloration is due to the formation of complex compounds. Aldehydes abstract sulfurous acid from the Schiff’s reagent and restore the magenta colour.
Mechanism of Schiff’s test:
The bisulfite and the pararosaniline react together to form a decolorized adduct. This adduct has a central carbon which is sulfonated. Now the free and uncharged amine groups belong to the aromatic ring that reacts with the aldehyde group to form an aldimine. This aldimine group is a very good electrophile and thus it undergoes further reaction with the bisulfite ion. Finally a bisulfite adduct is formed which is magenta in colour.

Note:
Other tests for the detection of aldehyde are sodium bisulfite test, Fehling’s test, Tollen’s etc. The solution becomes colorless due to the formula of an additional product. Sometimes ketones also give a pink coloration when Schiff’s reagent is added to it but this coloration is not a positive test.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




