
How does allosteric control of metabolic pathways by end-product inhibition include negative feedback and non –competitive inhibition?
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: In a metabolic pathway, enzymes can bind to a substrate at an active site leading to the formation of a product. The end product of that pathway when bound to an allosteric site of an enzyme of the pathway leads to negative feedback (decrease in product formation) also known as feedback inhibition or end-product inhibition.
Complete answer:
Every cell of a human body performs metabolic pathways where a substrate is converted into products with the help of enzymes. Enzymes are proteins in a chemical reaction that can help to either increase, decrease, or completely stop the production of a product. These enzymes bind to the active site of a substrate and slow down or increase the rate of product formation or can stop product production based on the need of a cell. This monitoring the rate of chemical reaction based on cell requirement is known as feedback inhibition.
Allosteric control or allosteric regulation is a process that helps in achieving feedback inhibition. Enzymes have a regulatory site called an allosteric site; where products can combine to this site changing the shape of active enzymes leading to non-competitive inhibition. This halts the production of a product temporarily according to the cell’s needs.
Feedback inhibition of end-product inhibition is a type of negative feedback by which a metabolic pathway is regulated. Here, the end product of the pathway acts as an inhibitor and binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme from previous steps of the pathways inactivating the enzyme by non-competitive inhibition. An example of end-product inhibition is the threonine – isoleucine pathway.
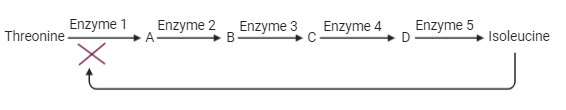
Here isoleucine, the end product of this metabolic pathway binds with the allosteric site of enzyme 1 and inhibits it.
Note:
Feedback inhibition or end product inhibition is initiated when an excess amount of end product is produced e.g. isoleucine. If the amount of product required is less or it drops down, the reaction continues without interruption by the end product.
Complete answer:
Every cell of a human body performs metabolic pathways where a substrate is converted into products with the help of enzymes. Enzymes are proteins in a chemical reaction that can help to either increase, decrease, or completely stop the production of a product. These enzymes bind to the active site of a substrate and slow down or increase the rate of product formation or can stop product production based on the need of a cell. This monitoring the rate of chemical reaction based on cell requirement is known as feedback inhibition.
Allosteric control or allosteric regulation is a process that helps in achieving feedback inhibition. Enzymes have a regulatory site called an allosteric site; where products can combine to this site changing the shape of active enzymes leading to non-competitive inhibition. This halts the production of a product temporarily according to the cell’s needs.
Feedback inhibition of end-product inhibition is a type of negative feedback by which a metabolic pathway is regulated. Here, the end product of the pathway acts as an inhibitor and binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme from previous steps of the pathways inactivating the enzyme by non-competitive inhibition. An example of end-product inhibition is the threonine – isoleucine pathway.

Here isoleucine, the end product of this metabolic pathway binds with the allosteric site of enzyme 1 and inhibits it.
Note:
Feedback inhibition or end product inhibition is initiated when an excess amount of end product is produced e.g. isoleucine. If the amount of product required is less or it drops down, the reaction continues without interruption by the end product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




