
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer
526.3k+ views
Hint: Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm, after nuclear division in plants and animal cells. It is the final process in cell division and results in two daughter cells.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Difference between cytokinesis in plant cell and animal cell is as follows:
Additional Information:
-Cytokinesis starts at metaphase in the animal cell.
-In animal cells, during cytokinesis, the cell-organelles arrange themselves equally on either side of the equator.
-The other name of the cell furrowing method is the cell cleavage method.
-In the plant cells, during cytokinesis, the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi body align at the equator.
-In the plant cells, the cell plate grows on both sides and forms a middle lamella.
-The phycoplast is a microtubular structure observed during cytokinesis in members of green algae.
- Spindle fibers are microtubules, which separates the chromosomes at the equator.
-Colchicine is an alkaloid and acts as a mitotic poison by breaking the microtubules of the spindle.
Note: In meiosis, the cytokinesis occurs twice, since the cell has to divide two times, called cytokinesis-1 and cytokinesis-2. Cytokinesis and karyokinesis (a division of the nucleus) occur at the same time in a parallel manner.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Difference between cytokinesis in plant cell and animal cell is as follows:
| Character | In Plant Cell | In Animal Cell |
| Mechanism | By cell plate method, in which the plant cell develops a cell wall at the equator, separating two daughter cells. | By cell furrow method, in which the cell membrane develops constriction at the equator, separating two daughter cells. |
| Fate of spindle | Usually persists | Start to degenerate |
| Mode of formation | Golgi body and Endoplasmic Reticulum fuse to form the cell plate | A constriction is developed by the contraction of microtubules in the cell membrane |
| Growth | The cell plate grows centrifugally, which is from the center to the periphery. | Cell furrow grows centripetally, which is from the periphery to the center. |
Figure: Cytokinesis in plants and animals cell
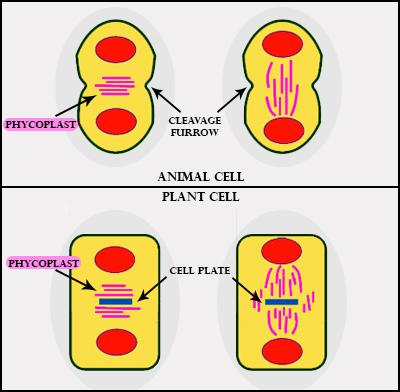

Additional Information:
-Cytokinesis starts at metaphase in the animal cell.
-In animal cells, during cytokinesis, the cell-organelles arrange themselves equally on either side of the equator.
-The other name of the cell furrowing method is the cell cleavage method.
-In the plant cells, during cytokinesis, the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi body align at the equator.
-In the plant cells, the cell plate grows on both sides and forms a middle lamella.
-The phycoplast is a microtubular structure observed during cytokinesis in members of green algae.
- Spindle fibers are microtubules, which separates the chromosomes at the equator.
-Colchicine is an alkaloid and acts as a mitotic poison by breaking the microtubules of the spindle.
Note: In meiosis, the cytokinesis occurs twice, since the cell has to divide two times, called cytokinesis-1 and cytokinesis-2. Cytokinesis and karyokinesis (a division of the nucleus) occur at the same time in a parallel manner.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




