
How does energy change with a swinging pendulum?
Answer
557.4k+ views
Hint:In swinging the pendulum, the total energy is always conserved according to the law of conservation of energy which states that the energy can neither be created nor be destroyed only can be converted from one form to another.
Complete step by step answer:
The motion of a pendulum is a classic example of mechanical energy conservation. A pendulum consists of a bob (mass) attached by a string to a pivot point. As the pendulum moves a circular arc, moving back and forth in a periodic manner. Neglecting air resistance because it will be small for an aerodynamically shaped bob, only two forces are acting upon the pendulum bob. One force is gravity. The force of gravity acts in a downward direction and does work upon the pendulum bob. However, gravity is an internal force and thus does not change the total amount of mechanical energy of the bob. The other force acting upon the bob is the force of tension. However, the force of tension does not do work since it always acts in a direction perpendicular to the motion of the bob. At all points in the trajectory of the pendulum bob, the angle between the force of tension and its direction of motion is 90 degrees. Thus, the force of tension does not do work upon the bob.
Since there are no external forces doing work, the total mechanical energy of the pendulum bob is conserved. Refer to the following image
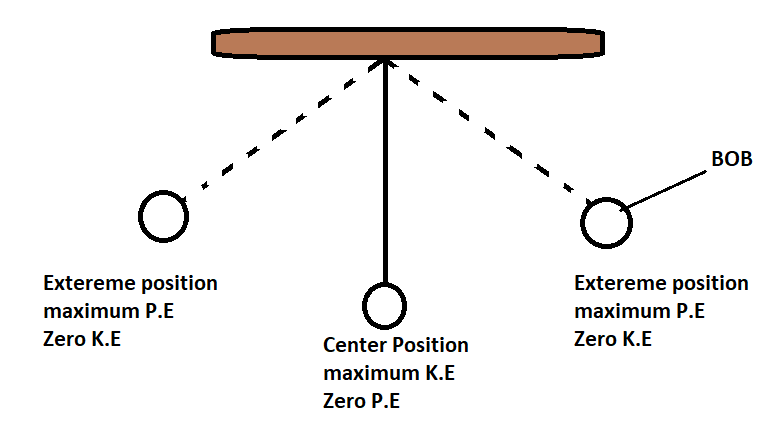
In this image when the bob it at an extreme position s its potential energy is maximum and when the bob is at the entry position its kinetic energy is maximum and potential energy will be zero during the entire motion of the bob the potential energy and kinetic energy keeps on increasing and decreasing but the sum of these always remains constant .
Note:
The potential energy is getting converted into kinetic energy when bob comes down till mid position and after mid position, the kinetic energy is getting converted to potential energy which is maximum at endpoints and kinetic energy is maximum at the center.
Complete step by step answer:
The motion of a pendulum is a classic example of mechanical energy conservation. A pendulum consists of a bob (mass) attached by a string to a pivot point. As the pendulum moves a circular arc, moving back and forth in a periodic manner. Neglecting air resistance because it will be small for an aerodynamically shaped bob, only two forces are acting upon the pendulum bob. One force is gravity. The force of gravity acts in a downward direction and does work upon the pendulum bob. However, gravity is an internal force and thus does not change the total amount of mechanical energy of the bob. The other force acting upon the bob is the force of tension. However, the force of tension does not do work since it always acts in a direction perpendicular to the motion of the bob. At all points in the trajectory of the pendulum bob, the angle between the force of tension and its direction of motion is 90 degrees. Thus, the force of tension does not do work upon the bob.
Since there are no external forces doing work, the total mechanical energy of the pendulum bob is conserved. Refer to the following image

In this image when the bob it at an extreme position s its potential energy is maximum and when the bob is at the entry position its kinetic energy is maximum and potential energy will be zero during the entire motion of the bob the potential energy and kinetic energy keeps on increasing and decreasing but the sum of these always remains constant .
Note:
The potential energy is getting converted into kinetic energy when bob comes down till mid position and after mid position, the kinetic energy is getting converted to potential energy which is maximum at endpoints and kinetic energy is maximum at the center.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




