
How does intensity affect the photoelectric effect?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint:In the photoelectric effect, when an incident light strikes on the surface of a metal that causes the electrons to be ejected. Their kinetic energy and the number of emitted electrons can be measured as a function of the intensity and light frequency. The energy in the light wave (its intensity is in \[J/{m^2}s\] ) must be transferred to the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons. As there is the change in the frequency of the light wave it should emit the number of electrons that break away from the metal. This frequency dependence was expected because the oscillating electric field of the light wave oscillates the electrons in the metal back and forth and the electrons and the electrons in the metal respond at different frequencies. In simpler words, it was expected that the number of emitted electrons should be depending upon the frequency, and their kinetic energy should be depending upon the intensity of the light wave (at fixed wavelength).
Complete step-by-step answer:
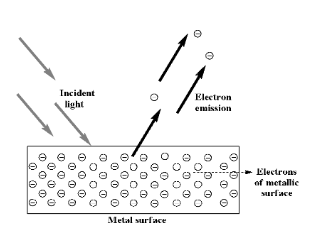
If the frequency of the electromagnetic waves is greater than the metal extraction threshold and electrons are emitted from the metal surface, then an increase in light intensity will result in a proportional increase in the electric current of the electrical circuit where the emitted electrons are conveyed.
This is explained simply by the photon model of light. In this model, an electromagnetic wave does not carry its energy like a continuum, but as a multitude of energy grains that have the same individually divisible amount of energy. The indivisible grain of light energy, also called "light dart" by Einstein, then the electromagnetic energy quanta or photons are given by Planck-Einstein's law:
\[{E_{photon}} = h\,\nu \]
Where \[\nu \] is the frequency of light. For every single photon at the same frequency.
From the point of view of photons, the denser light is not made of "higher waves", but rather of a greater number of photons.
It is therefore obvious that if each photon can expel an electron, the more intense the light, the greater the number of electrons that will be expelled. If the frequency is below the threshold, even the brightest light will be equally unable to expel even a single electron. It is impossible to explain these experimental results with the wavy model of light.
Note:Photo- simply tells us that electrons have been ejected from a metal surface by incident light. When light strikes on metal, the electrons can be ejected from the metal's surface in a phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. This process is also known as the photoemission, and the photoelectrons are referred to when electrons are ejected from the metal. In terms of behaviour and properties, photoelectrons are no different from other electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:

If the frequency of the electromagnetic waves is greater than the metal extraction threshold and electrons are emitted from the metal surface, then an increase in light intensity will result in a proportional increase in the electric current of the electrical circuit where the emitted electrons are conveyed.
This is explained simply by the photon model of light. In this model, an electromagnetic wave does not carry its energy like a continuum, but as a multitude of energy grains that have the same individually divisible amount of energy. The indivisible grain of light energy, also called "light dart" by Einstein, then the electromagnetic energy quanta or photons are given by Planck-Einstein's law:
\[{E_{photon}} = h\,\nu \]
Where \[\nu \] is the frequency of light. For every single photon at the same frequency.
From the point of view of photons, the denser light is not made of "higher waves", but rather of a greater number of photons.
It is therefore obvious that if each photon can expel an electron, the more intense the light, the greater the number of electrons that will be expelled. If the frequency is below the threshold, even the brightest light will be equally unable to expel even a single electron. It is impossible to explain these experimental results with the wavy model of light.
Note:Photo- simply tells us that electrons have been ejected from a metal surface by incident light. When light strikes on metal, the electrons can be ejected from the metal's surface in a phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. This process is also known as the photoemission, and the photoelectrons are referred to when electrons are ejected from the metal. In terms of behaviour and properties, photoelectrons are no different from other electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




