
How does mixing water and alcohol show that atoms have a lot of empty space?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: The molecules of water are bonded with each other by hydrogen bonds, similar to the molecules of alcohol. Similarly, when the molecules of both the compounds are mixed they would experience hydrogen bond with each other as well.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecules of water have hydrogen bonding with the other molecules of water and, so it is also termed as the intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
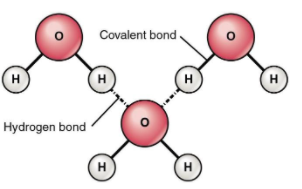
The above image shows the hydrogen bonding between three molecules of water. Notice that the hydrogen of one molecule shows hydrogen bonding with the oxygen of the other molecule.
In case of alcohol, in a similar way as water, the molecules of alcohol form hydrogen bonds with each other. This phenomena can be shown in a diagram, which is given below.
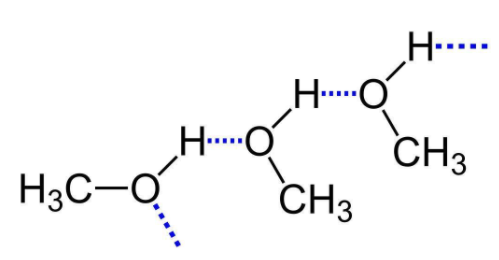
We can see that the diagram shows the hydrogen bonding in methyl alcohol which is the simplest form of alcohol. Now, notice how the oxygen of one molecule forms a hydrogen bond with the hydrogen of the molecule.
Consider, you fill up a beaker with $500mL$ of alcohol, and another beaker with $500mL$ with water. It will be visually noticeable that the beaker having $500mL$ of alcohol would be less than that of water. Now, if we add $250mL$ of each of these compounds in a beaker, it would seem less than $500mL$ of water itself. This is because the hydrogen bonds in alcohol are much stronger than the hydrogen bonds in water, and so they are held more tightly with each other. Thus the volume of the compound gets reduced. This justifies that there was empty space between the atoms of the compound as it was visually observable for us.
Note: The solution which is formed because of mixing of the alcohol and water is a type of non ideal solution meaning it deviates from the ideal behaviour or it shows positive deviation from the ideal gas law, resulting in increase of vapour pressure. This increase in the vapour pressure results in lowering of the boiling point of the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecules of water have hydrogen bonding with the other molecules of water and, so it is also termed as the intermolecular hydrogen bonding.

The above image shows the hydrogen bonding between three molecules of water. Notice that the hydrogen of one molecule shows hydrogen bonding with the oxygen of the other molecule.
In case of alcohol, in a similar way as water, the molecules of alcohol form hydrogen bonds with each other. This phenomena can be shown in a diagram, which is given below.

We can see that the diagram shows the hydrogen bonding in methyl alcohol which is the simplest form of alcohol. Now, notice how the oxygen of one molecule forms a hydrogen bond with the hydrogen of the molecule.
Consider, you fill up a beaker with $500mL$ of alcohol, and another beaker with $500mL$ with water. It will be visually noticeable that the beaker having $500mL$ of alcohol would be less than that of water. Now, if we add $250mL$ of each of these compounds in a beaker, it would seem less than $500mL$ of water itself. This is because the hydrogen bonds in alcohol are much stronger than the hydrogen bonds in water, and so they are held more tightly with each other. Thus the volume of the compound gets reduced. This justifies that there was empty space between the atoms of the compound as it was visually observable for us.
Note: The solution which is formed because of mixing of the alcohol and water is a type of non ideal solution meaning it deviates from the ideal behaviour or it shows positive deviation from the ideal gas law, resulting in increase of vapour pressure. This increase in the vapour pressure results in lowering of the boiling point of the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




