
How does molecular geometry affect the melting point of an organic compound?
Answer
537.6k+ views
Hint:Atoms of a molecule, when arranged in a three-dimensional structure, give the molecular geometry of that molecule. There are various geometrical parameters that determine the shape of a molecule and the position of the atoms in it. Some of the parameters are molecular bond length, torsional angles, molecular bond angles, etc
Complete step-by-step answer:The temperature at which the substance changes its state from solid-state to liquid state is known as the melting point of that substance. There are various factors affecting the melting point of a substance. Three of the main factors are the size and composition of the molecule, the number of impurities in a sample compound, and the forces of attraction.
Now, let us try to understand how the geometrical shape of a molecule affects the melting point of the organic compound. There are two factors corresponding to the molecular geometry of a molecule that has an effect on its melting point
1. Size of the molecule: If two compounds exist in similar conditions, the melting point of the compound having a smaller size will be lower.
This is because, in small compounds, molecules are bonded by intermolecular forces whereas macromolecules are bonded by covalent bonds. Since covalent bonds are much stronger than intermolecular bonds, the energy required to break them is high and hence large compounds have a higher melting point than small compounds.
For example, while the melting point of ethanol is $-114.1{}^\circ C$, bigger compounds like ethyl cellulose molecules have a melting point of $151{}^\circ C$.
2. Packing of the molecule: A compound in which the molecules are packed together tightly will have a higher melting point than the compounds whose molecules are loosely packed or do not pack well.
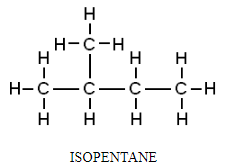
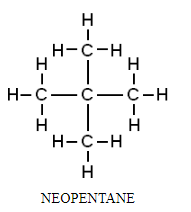
For example, among isomers of pentane, isopentane has a lower melting point than symmetrical neopentane because its atoms are more loosely packed.
Note:The melting point of a substance can be used to find the presence or absence of impurity in an organic compound. A substance will usually have a melting point range within one to two degrees. But when there is an existence of impurity in an organic compound, the range of the melting point will broaden.
Complete step-by-step answer:The temperature at which the substance changes its state from solid-state to liquid state is known as the melting point of that substance. There are various factors affecting the melting point of a substance. Three of the main factors are the size and composition of the molecule, the number of impurities in a sample compound, and the forces of attraction.
Now, let us try to understand how the geometrical shape of a molecule affects the melting point of the organic compound. There are two factors corresponding to the molecular geometry of a molecule that has an effect on its melting point
1. Size of the molecule: If two compounds exist in similar conditions, the melting point of the compound having a smaller size will be lower.
This is because, in small compounds, molecules are bonded by intermolecular forces whereas macromolecules are bonded by covalent bonds. Since covalent bonds are much stronger than intermolecular bonds, the energy required to break them is high and hence large compounds have a higher melting point than small compounds.
For example, while the melting point of ethanol is $-114.1{}^\circ C$, bigger compounds like ethyl cellulose molecules have a melting point of $151{}^\circ C$.
2. Packing of the molecule: A compound in which the molecules are packed together tightly will have a higher melting point than the compounds whose molecules are loosely packed or do not pack well.
For example, among isomers of pentane, isopentane has a lower melting point than symmetrical neopentane because its atoms are more loosely packed.


Note:The melting point of a substance can be used to find the presence or absence of impurity in an organic compound. A substance will usually have a melting point range within one to two degrees. But when there is an existence of impurity in an organic compound, the range of the melting point will broaden.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




