
How does onion grow and describe this process?
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: A modified stem that is the resting stage of certain seed plants, particularly perennial monocotyledons. It consists of a relatively large, usually globe-shaped, underground bud with membranous or fleshy overlapping leaves arising from a short stem with fleshy leaves which in some species are actually expanded leaf bases function as food reserves.
Complete answer:
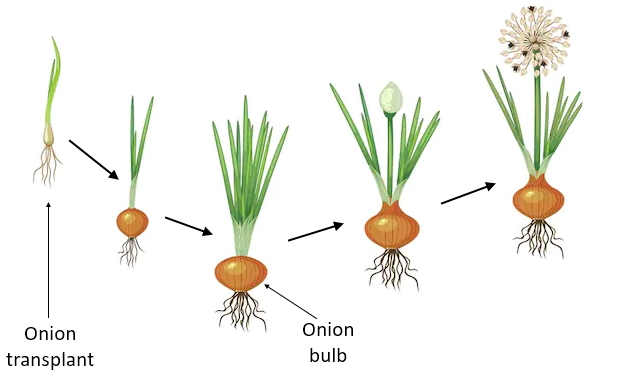
Onion plants can be grown from seeds or from bulbs. The process of growing onions from the bulb is known as vegetative propagation (a form of asexual reproduction in which the new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant). The bulb grows by the growth of the radicle and flag leaves after which the true leaves emerge.
Additional information:
Stem modifications:
-Stolon: a shoot that grows down ground and it produces roots at its nodes; a runner.
-Tuber: a fleshy, thickened, underground stem of a plant, usually containing stored starch, as for instance a potato or arrowroot.
-Cladode: these are the green branches of limited growth which have taken up the functions of photosynthesis.
-Rhizome: a horizontal underground stem of some plants that send out roots and shoots from its nodes.
-Corm: a brief, vertical, swollen underground stem of a plant that is a storage organ to enable the plant to survive winter or other adverse conditions like drought.
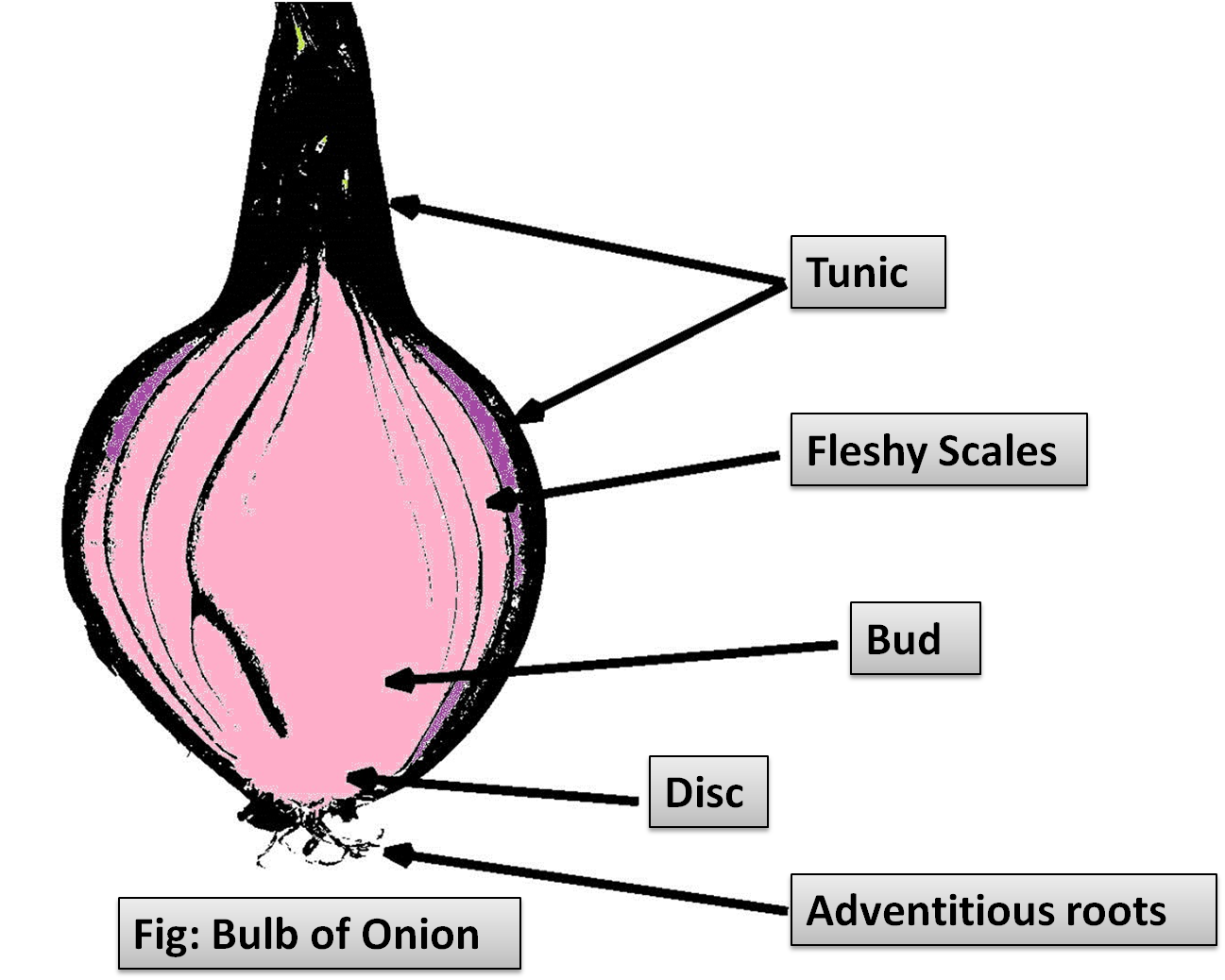
-Bulb: the bulb-shaped root portion of a plant like a tulip, from which the rest of the plant could also be regrown.
-Tendril: a skinny, spirally-coiling stem that attaches a plant to its support.
-Thorn: a sharp, protective spine of a plant.
-Bulbil: a bulb-shaped bud within the place of a flower or in a leaf axil.
Note:
Vegetative propagation is the natural asexual reproduction of the plant which undergo reproduction with the help of various vegetative propagules. Asexual plant propagation methods produce new plants from vegetative parts of the original plant, like the leaves, stems and roots. These methods are generally mentioned as vegetative propagation. Many plants can reproduce this manner naturally, but vegetative propagation also can be artificially induced.
Complete answer:
Onion plants can be grown from seeds or from bulbs. The process of growing onions from the bulb is known as vegetative propagation (a form of asexual reproduction in which the new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant). The bulb grows by the growth of the radicle and flag leaves after which the true leaves emerge.

Additional information:
Stem modifications:
-Stolon: a shoot that grows down ground and it produces roots at its nodes; a runner.
-Tuber: a fleshy, thickened, underground stem of a plant, usually containing stored starch, as for instance a potato or arrowroot.
-Cladode: these are the green branches of limited growth which have taken up the functions of photosynthesis.
-Rhizome: a horizontal underground stem of some plants that send out roots and shoots from its nodes.
-Corm: a brief, vertical, swollen underground stem of a plant that is a storage organ to enable the plant to survive winter or other adverse conditions like drought.
-Bulb: the bulb-shaped root portion of a plant like a tulip, from which the rest of the plant could also be regrown.
-Tendril: a skinny, spirally-coiling stem that attaches a plant to its support.
-Thorn: a sharp, protective spine of a plant.
-Bulbil: a bulb-shaped bud within the place of a flower or in a leaf axil.

Note:
Vegetative propagation is the natural asexual reproduction of the plant which undergo reproduction with the help of various vegetative propagules. Asexual plant propagation methods produce new plants from vegetative parts of the original plant, like the leaves, stems and roots. These methods are generally mentioned as vegetative propagation. Many plants can reproduce this manner naturally, but vegetative propagation also can be artificially induced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




