
How does phototropism occur in plants?
(a) If a plant part moves towards the light, it is called positive phototropism.
(b) If a plant part moves opposite to the direction of light, it is called positive phototropism.
(c) If a plant part does not move towards the light, it is called positive phototropism.
(d) None of the above
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The growth of organisms in response to a stimulus, especially the movement of a plant part like stems and roots in response to light is known as phototropism.
Complete answer:
The response of a plant to light causes the plant to have elongated cells on the farthest side from the light. Plants can’t move and phototropism is one of the ways so that many plants respond to external stimuli by moving a part of the plant. Phytochromes also can make the plant grow towards the light. If the plant parts grow towards a light source for their nutrients needs it is called positive phototropism. Like the flower of a sunflower plant moving towards the sun. Another example is that plant shoots show positive phototropism, and to maximize growth and photosynthetic energy the chloroplasts are rearranged in the leaves. If plant parts grow away from light as they don’t need nutrients from the sun is called negative phototropism. Like roots that grow in the soil and require nutrients from there, these are away from the soil.
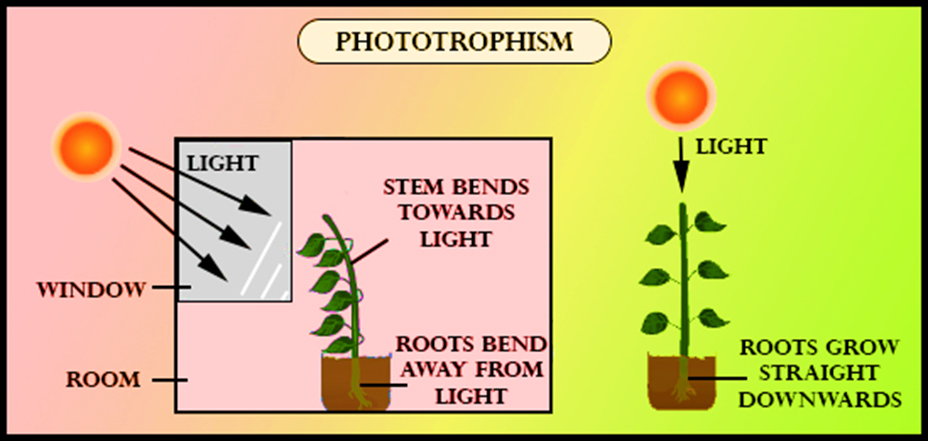
So, the correct answer is ‘If a plant part moves towards the light, it is called positive phototropism.’
Note: Phytochromes are photoreceptors, i.e. sense light attached to the small protein of about 1,24,000 Daltons in plants, bacteria, and fungi. Phytochrome is a blue or bluish-green pigment and is located in most of the organs of seed plants and free-sporing plants, also found in green algae. They regulate the germination of seeds (photoblasty), stem growth, the synthesis of chlorophyll, root growth, pigment synthesis, the size, shape and number, and movement of leaves and flowering.
Complete answer:
The response of a plant to light causes the plant to have elongated cells on the farthest side from the light. Plants can’t move and phototropism is one of the ways so that many plants respond to external stimuli by moving a part of the plant. Phytochromes also can make the plant grow towards the light. If the plant parts grow towards a light source for their nutrients needs it is called positive phototropism. Like the flower of a sunflower plant moving towards the sun. Another example is that plant shoots show positive phototropism, and to maximize growth and photosynthetic energy the chloroplasts are rearranged in the leaves. If plant parts grow away from light as they don’t need nutrients from the sun is called negative phototropism. Like roots that grow in the soil and require nutrients from there, these are away from the soil.

So, the correct answer is ‘If a plant part moves towards the light, it is called positive phototropism.’
Note: Phytochromes are photoreceptors, i.e. sense light attached to the small protein of about 1,24,000 Daltons in plants, bacteria, and fungi. Phytochrome is a blue or bluish-green pigment and is located in most of the organs of seed plants and free-sporing plants, also found in green algae. They regulate the germination of seeds (photoblasty), stem growth, the synthesis of chlorophyll, root growth, pigment synthesis, the size, shape and number, and movement of leaves and flowering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




