
Why does the outer part of the cerebrum appear grey & whereas the inner part appears white?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The cerebrum is the uppermost part of the brain which contains two hemispheres split by a falx cerebri of dura mater.
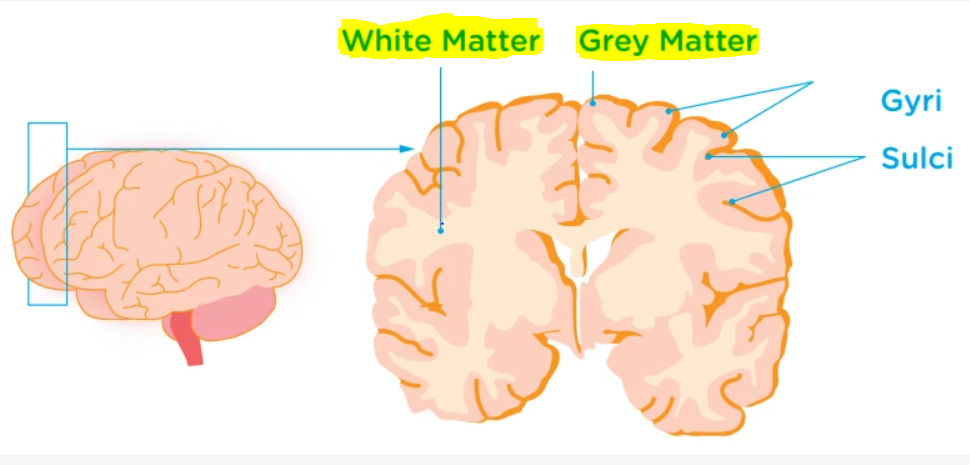
Grey matter contains the cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons so have synapses. White matter is made of axons connecting different parts of grey matter to each other.
Complete answer: Grey matter is mostly found on the brain's outer surface, or cortex. White matter is buried deep in the brain.
1. Grey matter is mostly neuron cell bodies and non-neuron brain cells called glial cells.
These glial cells provide nutrients and energy to neurons.
2. Grey matter helps transport glucose into the brain, clean the brain of excess chemicals, and may even affect the intensity of the neurons' communications.
3. These cells are not surrounded by white myelin, so they take on the natural grayish color of the neurons and glial cells. In a living person, it actually looks pinkish-brown, because it has so many tiny blood vessels called capillaries
4. The white matter of the brain is made up primarily of axon tracts, the long, spindly appendages of some brain cells. These tracts transmit the electrical signals that the brain cells, called neurons, use to communicate.
5. They're wrapped in a fatty layer called myelin, which insulates the axons and allows them to conduct signals quickly.
Note: The spinal cord, which transmits nerve impulses to and from the rest of the body, has the opposite arrangement. It has grey matter at its core with the insulating white matter on the outside.
Grey matter contains the cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons so have synapses. White matter is made of axons connecting different parts of grey matter to each other.
Complete answer: Grey matter is mostly found on the brain's outer surface, or cortex. White matter is buried deep in the brain.
1. Grey matter is mostly neuron cell bodies and non-neuron brain cells called glial cells.
These glial cells provide nutrients and energy to neurons.
2. Grey matter helps transport glucose into the brain, clean the brain of excess chemicals, and may even affect the intensity of the neurons' communications.
3. These cells are not surrounded by white myelin, so they take on the natural grayish color of the neurons and glial cells. In a living person, it actually looks pinkish-brown, because it has so many tiny blood vessels called capillaries
4. The white matter of the brain is made up primarily of axon tracts, the long, spindly appendages of some brain cells. These tracts transmit the electrical signals that the brain cells, called neurons, use to communicate.
5. They're wrapped in a fatty layer called myelin, which insulates the axons and allows them to conduct signals quickly.

Note: The spinal cord, which transmits nerve impulses to and from the rest of the body, has the opposite arrangement. It has grey matter at its core with the insulating white matter on the outside.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




