
How does the pH change in a neutralization reaction?
Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: The pH is the main factor used to differentiate between the neutralization reaction and the buffer solution. In neutralization reaction, salt is formed by reaction acid with the base whereas the buffer solution is prepared by mixing weak acid and its conjugate base and vice versa.
Complete step by step solution:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction which takes place between the acid and the base which results in the formation of a salt by eliminating water as the by-product.
The buffer solution is a water solvent which is prepared by the mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. The property of the buffer solution is that it resists any change in pH when any small amount of acid and base is added. The difference between the neutralization reaction and the buffer solution is that the pH of the product of neutralization reaction (salt) changes frequently on adding any small amount of acid or base whereas the pH of the buffer solution does not change or show minimal change when a small quantity of acid or base is added. The further strong and weak, acid & base is given by
Strong acid-strong base neutralization
\[HC{{l}_{(aq)}}(acid)+NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}(base)\underset{reaction}{\overset{neutralization}{\longleftrightarrow}}NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}(salt)+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}(water)\]
Weak acid-weak base neutralization:
\[H_{(aq)}^{+}+N{{H}_{3(aq)}}\underset{reaction}{\overset{neutralization}{\longleftrightarrow}}NH{{_{4}^{+}}_{(aq)}}\]
Weak Base-Strong Acid: If you are starting with a weak base, as in the first curve below, the pH is lower than for a strong base until you reach neutralization. After that point, the two curves are identical.
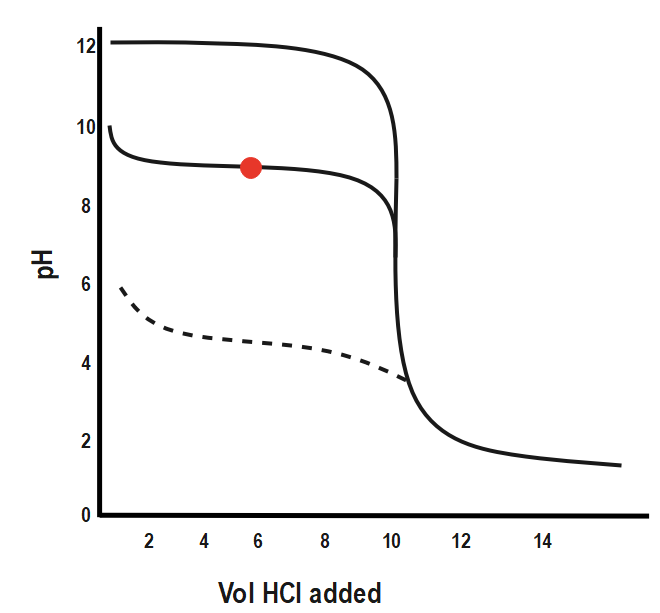
Weak Acid-Weak Base: With a weak acid and a weak base, the pH changes gradually during the whole addition.
Additional Information:
Acids are synthetic mixes that show, in water solution, a sharp taste, a destructive activity on metals, and the capacity to turn certain blue vegetables into red-colored. Bases are substance exacerbates that, in solutions, are sudsy to the touch and turn red vegetable colors blue. At the point when blended, acids and bases neutralize each other and produce salts, substances with a pungent taste, and none of the trademark properties of either acids or bases
Note:
At the point when a solution is neutralized, it implies that salts are framed from equivalent weights of acid and base. The measure of acid required is the sum that would give one mole of protons (\[{{H}^{+}}\]) and the measure of base required is the sum that would give one mole of (\[O{{H}^{-}}\]). Since salts are framed from neutralization reactions with equivalent concentrations of weights of acids and bases.
Complete step by step solution:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction which takes place between the acid and the base which results in the formation of a salt by eliminating water as the by-product.
The buffer solution is a water solvent which is prepared by the mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. The property of the buffer solution is that it resists any change in pH when any small amount of acid and base is added. The difference between the neutralization reaction and the buffer solution is that the pH of the product of neutralization reaction (salt) changes frequently on adding any small amount of acid or base whereas the pH of the buffer solution does not change or show minimal change when a small quantity of acid or base is added. The further strong and weak, acid & base is given by
Strong acid-strong base neutralization
\[HC{{l}_{(aq)}}(acid)+NaO{{H}_{(aq)}}(base)\underset{reaction}{\overset{neutralization}{\longleftrightarrow}}NaC{{l}_{(aq)}}(salt)+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{(l)}}(water)\]
Weak acid-weak base neutralization:
\[H_{(aq)}^{+}+N{{H}_{3(aq)}}\underset{reaction}{\overset{neutralization}{\longleftrightarrow}}NH{{_{4}^{+}}_{(aq)}}\]
Weak Base-Strong Acid: If you are starting with a weak base, as in the first curve below, the pH is lower than for a strong base until you reach neutralization. After that point, the two curves are identical.

Weak Acid-Weak Base: With a weak acid and a weak base, the pH changes gradually during the whole addition.

Additional Information:
Acids are synthetic mixes that show, in water solution, a sharp taste, a destructive activity on metals, and the capacity to turn certain blue vegetables into red-colored. Bases are substance exacerbates that, in solutions, are sudsy to the touch and turn red vegetable colors blue. At the point when blended, acids and bases neutralize each other and produce salts, substances with a pungent taste, and none of the trademark properties of either acids or bases
Note:
At the point when a solution is neutralized, it implies that salts are framed from equivalent weights of acid and base. The measure of acid required is the sum that would give one mole of protons (\[{{H}^{+}}\]) and the measure of base required is the sum that would give one mole of (\[O{{H}^{-}}\]). Since salts are framed from neutralization reactions with equivalent concentrations of weights of acids and bases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




